Wheat mildew is a wheat disease that affects the ear, and is brought on by causes somewhat similar to those that cause blight, though at a more advanced period of the season. If this disorder comes on immediately after the first appearance of the ear, the straw is also affected—but if the grain is nearly or fully formed, injury to the straw is less discernible. Wheat may mildew where the straw is perfectly fresh, but only rarely. A severe mildew, however, retards further grain and straw maturation and leads to death. Something akin to mildew is the gum, which, in all warm moist seasons, attaches itself to the ear, and often causes considerable damage. All these different disorders are generally accompanied by insects, and by minute parasitic vegetable growths, considered by many to be the cause of the damage. Their appearance, however, may justly be attributed to the diseased state of the plant; for wherever putrefaction takes place, either in animal or vegetable substances, the presence of these parasites will never be wanting.
De Chaunac is a French-American hybrid wine grape variety used to make red wines. It was developed by Albert Seibel c. 1860. It is also known as Seibel 9549 and is a cross of Seibel 5163 and possibly Seibel 793. The grape was named after Adhemar de Chaunac, a pioneer in the Ontario wine industry.
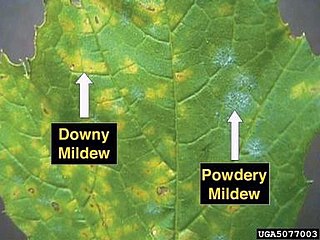
Mildew is a form of fungus. It is distinguished from its closely related counterpart, mold, largely by its color: moulds appear in shades of black, blue, red, and green, whereas mildew is white. It appears as a thin, superficial growth consisting of minute hyphae produced especially on living plants or organic matter such as wood, paper or leather. Both mould and mildew produce distinct offensive odors, and both have been identified as the cause of certain human ailments.

Powdered milk or dried milk is a manufactured dairy product made by evaporating milk to dryness. One purpose of drying milk is to preserve it; milk powder has a far longer shelf life than liquid milk and does not need to be refrigerated, due to its low moisture content. Another purpose is to reduce its bulk for economy of transportation. Powdered milk and dairy products include such items as dry whole milk, nonfat (skimmed) dry milk, dry buttermilk, dry whey products and dry dairy blends. Many dairy products exported conform to standards laid out in Codex Alimentarius. Many forms of milk powder are traded on exchanges.

Downy mildew refers to any of several types of oomycete microbes that are obligate parasites of plants. Downy mildews exclusively belong to Peronosporaceae. In commercial agriculture, they are a particular problem for growers of crucifers, grapes and vegetables that grow on vines. The prime example is Peronospora farinosa featured in NCBI-Taxonomy and HYP3. This pathogen does not produce survival structures in the northern states of the United States, and overwinters as live mildew colonies in Gulf Coast states. It progresses northward with cucurbit production each spring. Yield loss associated with downy mildew is most likely related to soft rots that occur after plant canopies collapse and sunburn occurs on fruit. Cucurbit downy mildew only affects leaves of cucurbit plants.

Jonagold is a cultivar of apple which was developed in 1953 in New York State Agricultural Experiment Station of Cornell University's College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, a cross between the crisp Golden Delicious and the blush-crimson Jonathan. They form a large sweet fruit with a thin skin. Because of their large size they are now favoured by commercial growers in many parts of the world. Jonagold is triploid, with sterile pollen, and as such, requires a second type of apple for pollen and is incapable of pollenizing other cultivars. The Jonagored Apple, a sport mutation of Jonagold, was once covered under United States Patent PP05937, now expired.

Uncinula necator is a fungus that causes powdery mildew of grape. It is a common pathogen of Vitis species, including the wine grape, Vitis vinifera. The fungus is believed to have originated in North America. European varieties of Vitis vinifera are more or less susceptible to this fungus. Uncinula necator infects all green tissue on the grapevine, including leaves and young berries. It can cause crop loss and poor wine quality if untreated. The sexual stage of this pathogen requires free moisture to release ascospores from its cleistothecia in the spring. However, free moisture is not needed for secondary spread via conidia; high atmospheric humidity is sufficient. Its anamorph is called Oidium tuckeri.
Daniel Peter was a Swiss chocolatier. A neighbour of Henri Nestlé in Vevey, he was one of the first chocolatiers to make milk chocolate, in 1875 or 1876, by adding powdered milk to the chocolate.

Chelois is a variety of hybrid grape used in the production of red wines. The fruit are small blue-black berries, which appear in compact, medium-sized clusters. Chelois is among the less hardy hybrids of red-wine grapes.
Vinyl coated polyester is a material frequently used for flexible fabric structures. It is made up of a polyester scrim, a bonding or adhesive agent, and an exterior PVC coating. The scrim supports the coating and provides the tensile strength, elongation, tear strength, and dimensional stability of the resulting fabric. Depending on its formula, the PVC coating makes the material waterproof and resistant to dirt, mildew, oil, salt, chemicals and UV rays and gives the material added strength and durability. It can be sewn or heat sealed by way of RF(Radio Frequency) welding or hot-air welding.

Blumeria graminis is a fungus that causes powdery mildew on grasses, including cereals. It is the only species in the genus Blumeria. It has also been called Erysiphe graminis and Oidium monilioides or Oidium tritici.

Lactuca serriola, also called prickly lettuce, milk thistlecompass plant, and scarole, is an annual or biennial plant in the dandelion tribe within the daisy family. It has a slightly fetid odor and is commonly considered a weed of orchards, roadsides and field crops. It is the closest wild relative of cultivated lettuce.

Peronosporaceae are a family of water moulds that contains 21 genera, comprising more than 600 species. Most of them are called downy mildews.
Leveillula taurica is an obligate fungal pathogen, from the phylum Ascomycota, which causes powdery mildew on onion. This disease prefers warm, dry environments. It is rare in the United States, and is currently restricted to western states. Globally, it is also a minor problem with limited occurrences in the Middle East, Europe, and South America. L. taurica causes powdery mildew of onions, but is also known to infect other allium, solanaceous, and cucurbit species. The disease has appeared in parts of the Middle East, the Mediterranean, and South and North America. Currently, it is not a cause for major concern in the U.S. and throughout the world, as its geographic extent is sparse. In addition, it is relatively easy to control through basic sanitation and reducing water stress.

Podosphaera pannosa is a plant pathogen. It produces a powdery mildew on members of the rose family.

Erysiphe cichoracearum is a plant pathogen that causes powdery mildew disease of cucurbits, including melon, cucumber, pumpkin, and squash. The primary symptoms are white, powder-like spots on the leaves and stems. Sphaerotheca fuliginea causes a similar looking powdery mildew of cucurbits.

Fenarimol, sold under the tradenames Bloc, Rimidin and Rubigan, is a fungicide which acts against rusts, blackspot and mildew fungi. It is used on ornamental plants, trees, lawns, tomatoes, peppers, eggplants, cucumbers and melons. It is mainly used to control powdery mildew. It works by inhibiting the fungus's biosynthesis of important steroid molecules.
Salva Cheese from Crema is a PDO table cow’s milk cheese, made with raw curd; it is a washed rind cheese that undergoes a medium or long aging period. Salva is traditionally eaten in the central plain of Lombardy and produced particularly in the area of Crema, Bergamo and Brescia.











