Related Research Articles

The Romani, also spelled Romany or Rromani, colloquially known as the Roma, are an Indo-Aryan ethnic group who traditionally lived a nomadic, itinerant lifestyle. Linguistic and genetic evidence suggests that the Romani originated in the Indian subcontinent; in particular, the region of present-day Rajasthan. Their subsequent westward migration, possibly in waves, is now believed by historians to have occurred around 1000 CE. Their original name is from the Sanskrit word डोम (doma) and means a member of a Dalit caste of travelling musicians and dancers. The Roma population moved west into the Persian Ghaznavid Empire and later into the Byzantine Empire. The Roma arrived in Europe around the 13th to 14th century. Although they are dispersed, their most concentrated populations are located in Europe, especially central, eastern, and southern Europe, as well as western Asia.

The Indo-Aryan languages are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family. As of the early 21st century, they have more than 800 million speakers, primarily concentrated in India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Nepal and Maldives. Moreover, apart from the Indian subcontinent, large immigrant and expatriate Indo-Aryan–speaking communities live in Northwestern Europe, Western Asia, North America, the Caribbean, Southeast Africa, Polynesia and Australia, along with several million speakers of Romani languages primarily concentrated in Southeastern Europe. There are over 200 known Indo-Aryan languages.
Romani is an Indo-Aryan macrolanguage of the Romani communities. According to Ethnologue, seven varieties of Romani are divergent enough to be considered languages of their own. The largest of these are Vlax Romani, Balkan Romani (600,000), and Sinte Romani (300,000). Some Romani communities speak mixed languages based on the surrounding language with retained Romani-derived vocabulary – these are known by linguists as Para-Romani varieties, rather than dialects of the Romani language itself.

The Romani Holocaust or the Romani genocide—also known as the Porajmos, the Pharrajimos, and the Samudaripen —was the planned effort by Nazi Germany and its World War II allies and collaborators to commit ethnic cleansing and eventually genocide against European Roma and Sinti peoples during the Holocaust era.

Romani music is the music of the Romani people who have their origins in northern India but today live mostly in Europe.
Angloromani or Anglo-Romani is a mixed language of Indo-European origin involving the presence of Romani vocabulary and syntax in the English used by descendants of Romanichal Travellers in the United Kingdom, Australia, Canada, New Zealand, United States, and South Africa.

Vlax Romani is a dialect group of the Romani language. Vlax Romani varieties are spoken mainly in Southeastern Europe by the Romani people. Vlax Romani can also be referred to as an independent language or as one dialect of the Romani language. Vlax Romani is the second most widely spoken dialect subgroup of the Romani language worldwide, after Balkan Romani.
The Romani language has for most of its history been an entirely oral language, with no written form in common use. Although the first example of written Romani dates from 1542, it is not until the twentieth century that vernacular writing by native Romani people arose.

Romanichals are a Romani subgroup within the United Kingdom and other parts of the English-speaking world. There are an estimated 500,000 Romani in the United Kingdom; almost all live in England. Most Romanichal speak Angloromani, a mixed language that blends Romani vocabulary with English syntax.

Roma, traditionally Țigani, constitute one of Romania's largest minorities. According to the 2011 census, their number was 621,573 people or 3.3% of the total population, being the second-largest ethnic minority in Romania after Hungarians. There are different estimates about the size of the total population of people with Romani ancestry in Romania, varying from 4.6 per cent to over 10 percent of the population, because many people of Romani descent do not declare themselves Roma. For example, in 2007 the Council of Europe estimated that approximately 1.85 million Roma lived in Romania, based on an average between the lowest estimate and the highest estimate available at the time. This figure is equivalent to 8.32% of the population.
The Romani people, also referred to as Roma, Sinti or Kale, depending on the sub-group, are an Indo-Aryan ethnic group which primarily lives in Europe. The Romani may have migrated from what is the modern Indian state of Rajasthan, migrating to the northwest around 250 BCE. Their subsequent westward migration, possibly in waves, is now believed to have occurred beginning in about 500 CE. It has also been suggested that emigration from India may have taken place in the context of the raids by Mahmud of Ghazni. As these soldiers were defeated, they were moved west with their families into the Byzantine Empire.

Romani people in Bulgaria constitute Europe's densest gypsy minority. The Romani people in Bulgaria may speak Bulgarian, Turkish or Romani, depending on the region.

Esma Redžepova-Teodosievska was a Macedonian Romani vocalist, songwriter and humanitarian. She was nicknamed "the Queen of the Gypsies" per her contribution to Romani culture and music.

Anti-Romani sentiment is a form of bigotry which consists of hostility, prejudice, discrimination, racism and xenophobia which is specifically directed at Romani people. Non-Romani itinerant groups in Europe such as the Yenish, Irish and Highland Travellers are frequently given the name "gypsy" and as a result, they are frequently confused with the Romani people. As a result, sentiments which were originally directed at the Romani people are also directed at other traveler groups and they are frequently referred to as "antigypsy" sentiments.

Many languages are spoken, written and signed in Norway.
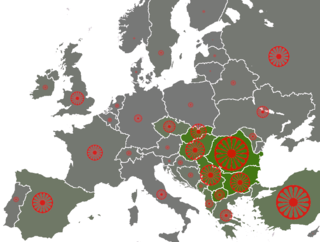
The Romani people have several distinct populations, the largest being the Roma and the Calé, who reached Anatolia and the Balkans in the early 12th century, from a migration out of the Indian subcontinent beginning about 1st century – 2nd century AD. They settled in the areas of present-day Turkey, Greece, Serbia, Romania, Croatia, Moldova, Bulgaria, North Macedonia, Hungary, Albania, Kosovo, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Czech Republic, Slovenia and Slovakia, by order of volume, and Spain. From the Balkans, they migrated throughout Europe and, in the nineteenth and later centuries, to the Americas. The Roma population in the United States is estimated at more than one million.

Romani people in Hungary are Hungarian citizens of Romani descent. According to the 2011 census, they comprise 3.18% of the total population, which alone makes them the largest minority in the country, although various estimations have put the number of Romani people as high as 8% of the total population. They are sometimes referred as Hungarian Gypsies, but that is considered to be a racial slur.

Balkan Romani, Balkaniko Romanes, or Balkan Gypsy is a specific non-Vlax dialect of the Romani language, spoken by groups within the Balkans, which include countries such as Albania, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Greece, Kosovo, North Macedonia, Serbia, Slovenia, Turkey etc. The Balkan Romani language is typically an oral language.

The Romani people are also known by a variety of other names; in English as gypsies or gipsies, and Roma; in Greek as γύφτοι (gíftoi) or τσιγγάνοι (tsiggánoi), in Central and Eastern Europe as Tsingani ; in France as gitans besides the dated terms bohémiens and manouches; in Italy as rom and sinti besides the dated terms zingari, sigani, and gitani; in Spain as gitanos; and in Portugal as ciganos.
Romani cuisine is the cuisine of the ethnic Romani people. There is no specific "Roma cuisine"; it varies and is culinarily influenced by the respective countries where they have often lived for centuries. Hence, it is influenced by European cuisine even though the Romani people originated from the Indian subcontinent. Their cookery incorporates Indian and South Asian influences, but is also very similar to Hungarian cuisine. The many cultures that the Roma contacted are reflected in their cooking, resulting in many different cuisines. Some of these cultures are Middle European, Germany, Great Britain, and Spain. The cuisine of Muslim Romani people is also influenced by Balkan cuisine and Turkish cuisine. Many Roma don’t eat food prepared by a non-Roma.