A document type definition (DTD) is a set of markup declarations that define a document type for an SGML-family markup language.

The HyperText Markup Language, or HTML is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It can be assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaScript.

Markup refers to data included in an electronic document which is distinct from the document's content in that it is typically not included in representations of the document for end users, for example on paper or a computer screen, or in an audio stream. Markup is often used to control the display of the document or to enrich its content to facilitate automated processing. A markup language is a set of rules governing what markup information may be included in a document and how it is combined with the content of the document in a way to facilitate use by humans and computer programs. The idea and terminology evolved from the "marking up" of paper manuscripts, which is traditionally written with a red pen or blue pencil on authors' manuscripts.
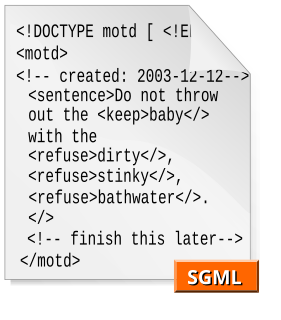
The Standard Generalized Markup Language is a standard for defining generalized markup languages for documents. ISO 8879 Annex A.1 states that generalized markup is "based on two postulates":

Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language and file format for storing, transmitting, and reconstructing arbitrary data. It defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. The World Wide Web Consortium's XML 1.0 Specification of 1998 and several other related specifications—all of them free open standards—define XML.
DocBook is a semantic markup language for technical documentation. It was originally intended for writing technical documents related to computer hardware and software, but it can be used for any other sort of documentation.
Mathematical Markup Language (MathML) is a mathematical markup language, an application of XML for describing mathematical notations and capturing both its structure and content. It aims at integrating mathematical formulae into World Wide Web pages and other documents. It is part of HTML5 and an ISO standard ISO/IEC 40314 since 2015.
XSD, a recommendation of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), specifies how to formally describe the elements in an Extensible Markup Language (XML) document. It can be used by programmers to verify each piece of item content in a document, to assure it adheres to the description of the element it is placed in.
An HTML element is a type of HTML document component, one of several types of HTML nodes. HTML document is composed of a tree of simple HTML nodes, such as text nodes, and HTML elements, which add semantics and formatting to parts of document. Each element can have HTML attributes specified. Elements can also have content, including other elements and text.
YAML is a human-readable data-serialization language. It is commonly used for configuration files and in applications where data is being stored or transmitted. YAML targets many of the same communications applications as Extensible Markup Language (XML) but has a minimal syntax which intentionally differs from SGML. It uses both Python-style indentation to indicate nesting, and a more compact format that uses [...] for lists and {...} for maps thus JSON files are valid YAML 1.2.
In web development, "tag soup" is a pejorative for syntactically or structurally incorrect HTML written for a web page. Because web browsers have historically treated HTML syntax or structural errors leniently, there has been little pressure for web developers to follow published standards, and therefore there is a need for all browser implementations to provide mechanisms to cope with the appearance of "tag soup", accepting and correcting for invalid syntax and structure where possible.
OPML is an XML format for outlines. Originally developed by UserLand as a native file format for the outliner application in its Radio UserLand product, it has since been adopted for other uses, the most common being to exchange lists of web feeds between web feed aggregators.
The term CDATA, meaning character data, is used for distinct, but related, purposes in the markup languages SGML and XML. The term indicates that a certain portion of the document is general character data, rather than non-character data or character data with a more specific, limited structure.
In computer programming, whitespace is any character or series of characters that represent horizontal or vertical space in typography. When rendered, a whitespace character does not correspond to a visible mark, but typically does occupy an area on a page. For example, the common whitespace symbol U+0020 SPACE represents a blank space punctuation character in text, used as a word divider in Western scripts.
This article describes the technical specifications of the OpenDocument office document standard, as developed by the OASIS industry consortium. A variety of organizations developed the standard publicly and make it publicly accessible, meaning it can be implemented by anyone without restriction. The OpenDocument format aims to provide an open alternative to proprietary document formats.
XML documents have a hierarchical structure and can conceptually be interpreted as a tree structure, called an XML tree.
The Internationalization Tag Set (ITS) is a set of attributes and elements designed to provide internationalization and localization support in XML documents.
Extensible HyperText Markup Language (XHTML) is part of the family of XML markup languages. It mirrors or extends versions of the widely used HyperText Markup Language (HTML), the language in which Web pages are formulated.
The Office Open XML file formats are a set of file formats that can be used to represent electronic office documents. There are formats for word processing documents, spreadsheets and presentations as well as specific formats for material such as mathematical formulae, graphics, bibliographies etc.
A well-formed document in XML is a document that "adheres to the syntax rules specified by the XML 1.0 specification in that it must satisfy both physical and logical structures".