
The double bass, also known as the upright bass, the acoustic bass, the bull fiddle, or simply the bass, is the largest and lowest-pitched chordophone in the modern symphony orchestra. It has four or five strings, and its construction is in between that of the gamba and the violin family.

The guitar is a stringed musical instrument that is usually fretted and typically has six or twelve strings. It is usually held flat against the player's body and played by strumming or plucking the strings with the dominant hand, while simultaneously pressing selected strings against frets with the fingers of the opposite hand. A guitar pick may also be used to strike the strings. The sound of the guitar is projected either acoustically, by means of a resonant hollow chamber on the guitar, or amplified by an electronic pickup and an amplifier.

A power chord, also called a fifth chord, is a colloquial name for a chord on guitar, especially on electric guitar, that consists of the root note and the fifth, as well as possibly octaves of those notes. Power chords are commonly played with an amp with intentionally added distortion or overdrive effects. Power chords are a key element of many styles of rock, especially heavy metal and punk rock.

A capo is a device a musician uses on the neck of a stringed instrument to transpose and shorten the playable length of the strings—hence raising the pitch. It is a common tool for players of guitars, mandolins, mandolas, banjos, ukuleles and bouzoukis. The word derives from the Italian capotasto, which means the nut of a stringed instrument. The earliest known use of capotasto is by Giovanni Battista Doni who, in his Annotazioni of 1640, uses it to describe the nut of a viola da gamba. The first patented capo was designed by James Ashborn of Wolcottville, Connecticut year 1850.

A twelve-string guitar is a steel-string guitar with 12 strings in six courses, which produces a thicker, more ringing tone than a standard six-string guitar. Typically, the strings of the lower four courses are tuned in octaves, with those of the upper two courses tuned in unison. The gap between the strings within each dual-string course is narrow, and the strings of each course are fretted and plucked as a single unit. The neck is wider, to accommodate the extra strings, and is similar to the width of a classical guitar neck. The sound, particularly on acoustic instruments, is fuller and more harmonically resonant than six-string instruments. The 12-string guitar can be played like a 6-string guitar as players still use the same notes, chords and guitar techniques like a standard 6-string guitar, but advanced techniques can be challenging as players need to play or pluck two strings simultaneously.

Scordatura is a tuning of a string instrument that is different from the normal, standard tuning. It typically attempts to allow special effects or unusual chords or timbre, or to make certain passages easier to play. It is common to notate the finger position as if played in regular tuning, while the actual pitch resulting is altered. When all the strings are tuned by the same interval up or down, as in the case of the viola in Mozart's Sinfonia Concertante for Violin, Viola and Orchestra, the part is transposed as a whole.
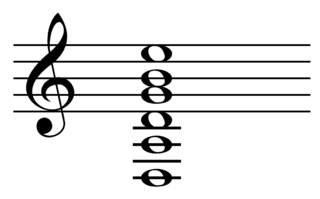
Drop D tuning is an alternative form of guitar tuning in which the lowest (sixth) string is tuned down from the usual E of standard tuning by one whole step to D. So where standard tuning is E2A2D3G3B3E4 (EADGBe), drop D is D2A2D3G3B3E4 (DADGBe). Drop D tuning, as well as other lowered altered tunings, are often used with the electric guitar in heavy metal music. It is also used in blues, country, folk (often with acoustic guitar), and classical guitar.

The seven-string guitar adds one additional string to the more common six-string guitar, commonly used to extend the bass range or also to extend the treble range.

An eight-string guitar is a guitar with eight strings, or one more than the Russian guitar's seven. Eight-string guitars are less common than six- and seven-string guitars, but they are used by a few classical, jazz, and metal guitarists. The eight-string guitar allows a wider tonal range, or non-standard tunings, or both.

Fingerstyle guitar is the technique of playing the guitar or bass guitar by plucking the strings directly with the fingertips, fingernails, or picks attached to fingers, as opposed to flatpicking. The term "fingerstyle" is something of a misnomer, since it is present in several different genres and styles of music—but mostly, because it involves a completely different technique, not just a "style" of playing, especially for the guitarist's picking/plucking hand. The term is often used synonymously with fingerpicking except in classical guitar circles, although fingerpicking can also refer to a specific tradition of folk, blues and country guitar playing in the US. The terms "fingerstyle" and "fingerpicking" are also applied to similar string instruments such as the banjo.

In music, a guitar chord is a set of notes played on a guitar. A chord's notes are often played simultaneously, but they can be played sequentially in an arpeggio. The implementation of guitar chords depends on the guitar tuning. Most guitars used in popular music have six strings with the "standard" tuning of the Spanish classical guitar, namely E–A–D–G–B–E' ; in standard tuning, the intervals present among adjacent strings are perfect fourths except for the major third (G,B). Standard tuning requires four chord-shapes for the major triads.

Guitar tunings are the assignment of pitches to the open strings of guitars, including classical guitars, acoustic guitars, and electric guitars. Tunings are described by the particular pitches that are made by notes in Western music. By convention, the notes are ordered and arranged from the lowest-pitched string to the highest-pitched string, or the thickest string to thinnest, or the lowest frequency to the highest. This sometimes confuses beginner guitarists, since the highest-pitched string is referred to as the 1st string, and the lowest-pitched is the 6th string.

The Russian guitar (sometimes referred to as a "Gypsy guitar") is an acoustic seven-string guitar that was developed in Russia toward the end of the 18th century: it shares most of its organological features with the Spanish guitar, although some historians insist on English guitar descent. It is known in Russian as the semistrunnaya gitara (семиструнная гитара), or affectionately as the semistrunka (семиструнка), which translates to "seven-stringer". These guitars are most commonly tuned to an open G chord as follows: D2 G2 B2 D3 G3 B3 D4. In classical literature, the lowest string (D) occasionally is tuned down to the C.

The term violone can refer to several distinct large, bowed musical instruments which belong to either the viol or violin family. The violone is sometimes a fretted instrument, and may have six, five, four, or even only three strings. The violone is also not always a contrabass instrument. In modern parlance, one usually tries to clarify the 'type' of violone by adding a qualifier based on the tuning or on geography, or by using other terms that have a more precise connotation. The term violone may be used correctly to describe many different instruments, yet distinguishing among these types can be difficult, especially for those not familiar with the historical instruments of the viol and violin families and their respective variations in tuning.
An extended-range bass is an electric bass guitar with a wider frequency range than a standard-tuned four-string bass guitar.
In music, standard tuning refers to the typical tuning of a string instrument. This notion is contrary to that of scordatura, i.e. an alternate tuning designated to modify either the timbre or technical capabilities of the desired instrument.

There are many varieties of ten-string guitar, including:

Each bass guitar tuning assigns pitches to the strings of an electric bass. Because pitches are associated with notes, bass-guitar tunings assign open notes to open strings. There are several techniques for accurately tuning the strings of an electric bass. Bass method or lesson books introduce one or more tuning techniques, such as:

Among alternative tunings for guitar, a major-thirds tuning is a regular tuning in which each interval between successive open strings is a major third. Other names for major-thirds tuning include major-third tuning, M3 tuning, all-thirds tuning, and augmented tuning. By definition, a major-third interval separates two notes that differ by exactly four semitones.


















