Related Research Articles
In computing, a file server is a computer attached to a network that provides a location for shared disk access, i.e. storage of computer files that can be accessed by the workstations that are able to reach the computer that shares the access through a computer network. The term server highlights the role of the machine in the traditional client–server scheme, where the clients are the workstations using the storage. A file server does not normally perform computational tasks or run programs on behalf of its client workstations.
Internet Small Computer Systems Interface or iSCSI is an Internet Protocol-based storage networking standard for linking data storage facilities. iSCSI provides block-level access to storage devices by carrying SCSI commands over a TCP/IP network. iSCSI facilitates data transfers over intranets and to manage storage over long distances. It can be used to transmit data over local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), or the Internet and can enable location-independent data storage and retrieval.

Network-attached storage (NAS) is a file-level computer data storage server connected to a computer network providing data access to a heterogeneous group of clients. The term "NAS" can refer to both the technology and systems involved, or a specialized device built for such functionality.
IBM Spectrum Protect is a data protection platform that gives enterprises a single point of control and administration for backup and recovery. It is the flagship product in the IBM Spectrum Protect family.
In computer science, storage virtualization is "the process of presenting a logical view of the physical storage resources to" a host computer system, "treating all storage media in the enterprise as a single pool of storage."
TrueNAS is the branding for a range of free and open-source network-attached storage (NAS) operating systems produced by iXsystems, and based on FreeBSD and Linux, using the OpenZFS file system. It is licensed under the terms of the BSD License and runs on commodity x86-64 hardware.

A computer appliance is a home appliance with software or firmware that is specifically designed to provide a specific computing resource. Such devices became known as appliances because of the similarity in role or management to a home appliance, which are generally closed and sealed, and are not serviceable by the user or owner. The hardware and software are delivered as an integrated product and may even be pre-configured before delivery to a customer, to provide a turn-key solution for a particular application. Unlike general purpose computers, appliances are generally not designed to allow the customers to change the software and the underlying operating system, or to flexibly reconfigure the hardware.
A clustered file system is a file system which is shared by being simultaneously mounted on multiple servers. There are several approaches to clustering, most of which do not employ a clustered file system. Clustered file systems can provide features like location-independent addressing and redundancy which improve reliability or reduce the complexity of the other parts of the cluster. Parallel file systems are a type of clustered file system that spread data across multiple storage nodes, usually for redundancy or performance.
A Global Namespace (GNS) is a heterogeneous, enterprise-wide abstraction of all file information, open to dynamic customization based on user-defined parameters. This becomes of particular importance as multiple network based file systems proliferate within an organization—the challenge becomes one of effective file management.
In computing, a virtual file server is a system consisting of one of more virtualized devices that store computer files such as documents, sound files, photographs, movies, images or databases. The server can be accessed by workstations or application servers through the Virtual Fileserver Network (VFN).
In computing, virtualization or virtualisation is the act of creating a virtual version of something at the same abstraction level, including virtual computer hardware platforms, storage devices, and computer network resources.

Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage and computing power, without direct active management by the user. Large clouds often have functions distributed over multiple locations, each location being a data center. Cloud computing relies on sharing of resources to achieve coherence and typically using a "pay-as-you-go" model which can help in reducing capital expenses but may also lead to unexpected operating expenses for unaware users.

A storage area network (SAN) or storage network is a computer network which provides access to consolidated, block-level data storage. SANs are primarily used to access data storage devices, such as disk arrays and tape libraries from servers so that the devices appear to the operating system as direct-attached storage. A SAN typically is a dedicated network of storage devices not accessible through the local area network (LAN).
In computer science, memory virtualization decouples volatile random access memory (RAM) resources from individual systems in the data centre, and then aggregates those resources into a virtualized memory pool available to any computer in the cluster. The memory pool is accessed by the operating system or applications running on top of the operating system. The distributed memory pool can then be utilized as a high-speed cache, a messaging layer, or a large, shared memory resource for a CPU or a GPU application.
Input/output (I/O) virtualization is a methodology to simplify management, lower costs and improve performance of servers in enterprise environments. I/O virtualization environments are created by abstracting the upper layer protocols from the physical connections.
Wanova, Inc, headquartered in San Jose, California, provides software to help IT organizations manage, support and protect data on desktop and laptop computers. Wanova's primary product, Wanova Mirage, was designed as an alternative to server-hosted desktop virtualization technologies.
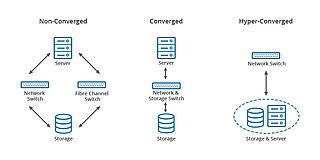
Converged infrastructure is a way of structuring an information technology (IT) system which groups multiple components into a single optimized computing package. Components of a converged infrastructure may include servers, data storage devices, networking equipment and software for IT infrastructure management, automation and orchestration.

Converged storage is a storage architecture that combines storage and computing resources into a single entity. This can result in the development of platforms for server centric, storage centric or hybrid workloads where applications and data come together to improve application performance and delivery. The combination of storage and compute differs to the traditional IT model in which computation and storage take place in separate or siloed computer equipment. The traditional model requires discrete provisioning changes, such as upgrades and planned migrations, in the face of server load changes, which are increasingly dynamic with virtualization, where converged storage increases the supply of resources along with new VM demands in parallel.

Cloud computing architecture refers to the components and subcomponents required for cloud computing. These components typically consist of a front end platform ,back end platforms, a cloud based delivery, and a network. Combined, these components make up cloud computing architecture.
Software-defined storage (SDS) is a marketing term for computer data storage software for policy-based provisioning and management of data storage independent of the underlying hardware. Software-defined storage typically includes a form of storage virtualization to separate the storage hardware from the software that manages it. The software enabling a software-defined storage environment may also provide policy management for features such as data deduplication, replication, thin provisioning, snapshots and backup.