
Film stock is an analog medium that is used for recording motion pictures or animation. It is a strip or sheet of transparent plastic film base coated on one side with a gelatin emulsion containing microscopically small light-sensitive silver halide crystals. The sizes and other characteristics of the crystals determine the sensitivity, contrast and resolution of the film. The emulsion will gradually darken if left exposed to light, but the process is too slow and incomplete to be of any practical use. Instead, a very short exposure to the image formed by a camera lens is used to produce only a very slight chemical change, proportional to the amount of light absorbed by each crystal. This creates an invisible latent image in the emulsion, which can be chemically developed into a visible photograph. In addition to visible light, all films are sensitive to X-rays and high-energy particles. Most are at least slightly sensitive to invisible ultraviolet (UV) light. Some special-purpose films are sensitive into the infrared (IR) region of the spectrum.

Keykode is an Eastman Kodak Company advancement on edge numbers, which are letters, numbers and symbols placed at regular intervals along the edge of 35 mm and 16 mm film to allow for frame-by-frame specific identification. It was introduced in 1990.

35 mm film (millimeter) is the film gauge most commonly used for motion pictures and chemical still photography. The name of the gauge refers to the width of the photographic film, which consists of strips 34.98 ±0.03 mm (1.377 ±0.001 inches) wide. The standard negative pulldown for movies is four perforations per frame along both edges, which results in 16 frames per foot of film. For still photography, the standard frame has eight perforations on each side.
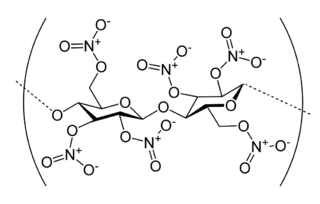
Nitrocellulose is a highly flammable compound formed by nitrating cellulose through exposure to nitric acid or another powerful nitrating agent. When used as a propellant or low-order explosive, it was originally known as guncotton.

135 is photographic film in a film format used for still photography. It is a cartridge film with a film gauge of 35 mm (1.4 in), typically used for hand-held photography in 35 mm film cameras. Its engineering standard for the film is controlled by ISO 1007.

Photographic paper is a paper coated with a light-sensitive chemical formula, used for making photographic prints. When photographic paper is exposed to light, it captures a latent image that is then developed to form a visible image; with most papers the image density from exposure can be sufficient to not require further development, aside from fixing and clearing, though latent exposure is also usually present. The light-sensitive layer of the paper is called the emulsion. The most common chemistry was based on silver salts but other alternatives have also been used.

A perforation is a small hole in a thin material or web. There is usually more than one perforation in an organized fashion, where all of the holes collectively are called a perforation. The process of creating perforations is called perforating, which involves puncturing the workpiece with a tool.
Bottles made of polyethylene terephthalate can be used to make lower grade products, such as carpets. To make a food grade plastic, the bottles need to be hydrolysed down to monomers, which are purified and then re-polymerised to make new PET. In many countries, PET plastics are coded with the resin identification code number "1" inside the universal recycling symbol, usually located on the bottom of the container.
Negative cutting is the process of cutting motion picture negative to match precisely the final edit as specified by the film editor. Original camera negative (OCN) is cut with scissors and joined using a film splicer and film cement. Negative cutting is part of the post-production process and occurs after editing and prior to striking internegatives and release prints. The process of negative cutting has changed little since the beginning of cinema in the early 20th century. In the early 1980s computer software was first used to aid the cutting process. Kodak introduced barcode on motion picture negative in the mid-1990s. This enabled negative cutters to more easily track shots and identify film sections based on keykode.

Polyester is a category of polymers that contain the ester functional group in their main chain. As a specific material, it most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyesters include naturally occurring chemicals, such as in the cutin of plant cuticles, as well as synthetics such as polybutyrate. Natural polyesters and a few synthetic ones are biodegradable, but most synthetic polyesters are not. The material is used extensively in clothing.

A film base is a transparent substrate which acts as a support medium for the photosensitive emulsion that lies atop it. Despite the numerous layers and coatings associated with the emulsion layer, the base generally accounts for the vast majority of the thickness of any given film stock. Historically there have been three major types of film base in use: nitrocellulose, cellulose acetate, and polyester.

Tape-automated bonding (TAB) is a process that places bare integrated circuits onto a printed circuit board (PCB) by attaching them to fine conductors in a polyamide or polyimide film, thus providing a means to directly connect to external circuits.

Fusion splicing is the act of joining two optical fibers end-to-end.The goal is to fuse the two fibers together in such a way that light passing through the fibers is not scattered or reflected back by the splice, and so that the splice and the region surrounding it are almost as strong as the intact fiber. The source of heat is usually an electric arc, but can also be a laser, or a gas flame, or a tungsten filament through which current is passed.
Eastman Color Positive (ECP) is a photographic processing system created by Kodak in the 1950s for the development of monopack color positive print for direct projection motion picture film stock. ECP is not used for positive intermediate films as these are "pre-print" elements and are never used for direct projection. One essential difference is the presence of an orange "mask" on all films processed by ECN, and no "mask" on all films processed by ECP.
The conservation and restoration of film is the physical care and treatment of film-based materials. These include photographic materials and motion picture.


















