Related Research Articles

The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom and the model on which most modern central banks have been based. Established in 1694 to act as the English Government's banker and debt manager, and still one of the bankers for the government of the United Kingdom, it is the world's second oldest central bank.

The Financial Services Authority (FSA) was a quasi-judicial body accountable for the regulation of the financial services industry in the United Kingdom between 2001 and 2013. It was founded as the Securities and Investments Board (SIB) in 1985. Its board was appointed by the Treasury, although it operated independently of government. It was structured as a company limited by guarantee and was funded entirely by fees charged to the financial services industry.

Mervyn Allister King, Baron King of Lothbury is a British economist and public servant who served as the Governor of the Bank of England from 2003 to 2013. He is a School Professor of Economics at the London School of Economics. He is also the Chairman of the Philharmonia.
The Office for National Statistics is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department which reports directly to the UK Parliament.
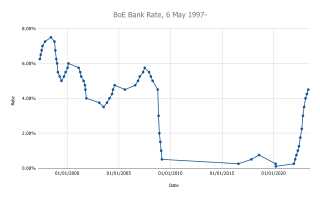
The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) is a committee of the Bank of England, which meets for three and a half days, eight times a year, to decide the official interest rate in the United Kingdom.

Monitor was an executive non-departmental public body of the Department of Health, responsible between 2004 and 2016 for ensuring healthcare provision in NHS England was financially effective. It was the sector regulator for health services in England. Its chief executive was Ian Dalton and it was chaired by Dido Harding. Monitor was merged with the NHS Trust Development Authority to form NHS Improvement on 1 April 2016.
Sir Paul Tucker is a British central banker and author. He was formerly the Deputy Governor of the Bank of England, with responsibility for financial stability, and served on the Bank's Monetary Policy Committee from June 2002 until October 2013 and its interim and then full Financial Policy Committee from June 2011. In November 2012 he was turned down for the position of governor in favour of Mark Carney. In June 2013, Tucker announced that he would leave the Bank of England, and later that he would be moving to Harvard. He was knighted in the 2014 New Year Honours for services to central banking. His first book, Unelected Power, was published in May 2018 and his second book, Global Discord was published in November 2022.
The UK Statistics Authority is a non-ministerial government department of the Government of the United Kingdom responsible for oversight of the Office for National Statistics, maintaining a national code of practice for official statistics, and accrediting statistics that comply with the Code as National Statistics. UKSA was established on 1 April 2008 by the Statistics and Registration Service Act 2007, and is directly accountable to the Parliament of the United Kingdom.

Andrew John Bailey is a British central banker and Governor of the Bank of England since 16 March 2020.

The Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, commonly referred to as Dodd–Frank, is a United States federal law that was enacted on July 21, 2010. The law overhauled financial regulation in the aftermath of the Great Recession, and it made changes affecting all federal financial regulatory agencies and almost every part of the nation's financial services industry.
Basel III is the third of three Basel Accords, a framework that sets international standards and minimums for bank capital requirements, stress tests, liquidity regulations, and leverage, with the goal of mitigating the risk of bank runs and bank failures. It was developed in response to the deficiencies in financial regulation revealed by the 2007–2008 financial crisis and builds upon the standards of Basel II, introduced in 2004, and Basel I, introduced in 1988.

The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) is a financial regulatory body in the United Kingdom. It operates independently of the UK Government and is financed by charging fees to members of the financial services industry. The FCA regulates financial firms providing services to consumers and maintains the integrity of the financial markets in the United Kingdom.
The Prudential Regulation Authority (PRA) is a United Kingdom financial services regulatory body, formed as one of the successors to the Financial Services Authority (FSA). The authority is responsible for the prudential regulation and supervision of banks, building societies, credit unions, insurers and major investment firms. It sets standards and supervises financial institutions at the level of the individual firm. Although it was initially structured as a limited company wholly owned by the Bank of England, the PRA's functions have now been taken over by the Bank and are exercised through the Prudential Regulation Committee. The company has since been liquidated.

Metro Bank PLC is a retail and commercial bank operating in the United Kingdom, founded by Anthony Thomson and Vernon Hill in 2010. At its launch it was the first new high street bank to launch in the United Kingdom in over 150 years. It is listed on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 250 Index.

Green Investment Group Limited (GIG), formerly the UK Green Investment Bank, is a specialist in green infrastructure principal investment, project delivery and the management of portfolio assets and related services. It is owned by the Macquarie Group.

The Health and Social Care Act 2012 is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It provided for the most extensive reorganisation of the structure of the National Health Service in England to date. It removed responsibility for the health of citizens from the Secretary of State for Health, which the post had carried since the inception of the NHS in 1948. It abolished primary care trusts (PCTs) and strategic health authorities (SHAs) and transferred between £60 billion and £80 billion of "commissioning", or healthcare funds, from the abolished PCTs to several hundred clinical commissioning groups, partly run by the general practitioners (GPs) in England. A new executive agency of the Department of Health, Public Health England, was established under the act on 1 April 2013.

The United Kingdom government austerity programme was a fiscal policy that was adopted for a period in the early 21st century following the era of the Great Recession. Coalition and Conservative governments in office from 2010 to 2019 used the term, and it was applied again by many observers to describe Conservative Party policies from 2021 to 2024, during the cost of living crisis. With the exception of the short-lived Truss ministry, the governments in power over the second period did not formally re-adopt the term. The two austerity periods are separated by increased spending during the COVID-19 pandemic. The first period was one of the most extensive deficit reduction programmes seen in any advanced economy since the Second World War, with emphasis placed on shrinking the state, rather than consolidating fiscally as was more common elsewhere in Europe.

The Financial Services Act 2012 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which implements a new regulatory framework for the financial system and financial services in the UK. It replaces the Financial Services Authority with two new regulators, namely the Financial Conduct Authority and the Prudential Regulation Authority, and creates the Financial Policy Committee of the Bank of England. This framework went into effect on 1 April 2013.
Challenger banks are small, recently created retail banks that compete directly with the longer-established banks in the UK, sometimes by specialising in areas underserved by the "big four" banks. As well as new entrants to the market, some challenger banks were created following divestment from larger banking groups or wind-down of a failed large bank.

George Osborne served as Chancellor of the Exchequer from May 2010 to July 2016 in the David Cameron–Nick Clegg coalition Conservative-Liberal Democrat government and the David Cameron majority Conservative government. His tenure pursued austerity policies aimed at reducing the budget deficit and launched the Northern Powerhouse initiative. He had previously served as Shadow Chancellor in the Shadow Cabinet of David Cameron from 2005 to 2010.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Elliott, Larry (17 June 2010). "Bank of England's City watchdog to meet in autumn". The Guardian. Retrieved 7 October 2010.
- 1 2 3 "Q&A: Osborne's financial regulation reforms". BBC News. 17 June 2010. Retrieved 7 October 2010.
- ↑ Treanor, Jill (12 June 2011). "Financial policy committee faces difficult birth". The Observer. Retrieved 28 March 2012.
- 1 2 Inman, Phillip (28 March 2012). "Bank of England split on tackling next house price boom". The Guardian. Retrieved 28 March 2012.