Related Research Articles
Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors are a class of medication used primarily for the treatment of high blood pressure and heart failure.
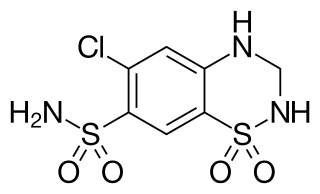
Hydrochlorothiazide is a diuretic medication often used to treat high blood pressure and swelling due to fluid build up. Other uses include diabetes insipidus, renal tubular acidosis, and to decrease the risk of kidney stones in those with a high calcium level in the urine. For high blood pressure it is sometimes considered as a first-line treatment, although chlortalidone is more effective with a similar rate of adverse effects. HCTZ is taken by mouth and may be combined with other blood pressure medications as a single pill to increase effectiveness.
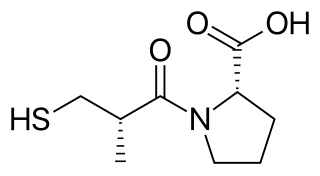
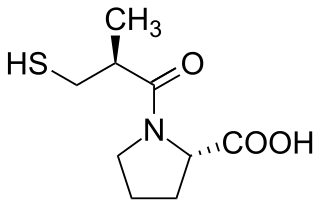
Captopril, sold under the brand name Capoten among others, is an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor used for the treatment of hypertension and some types of congestive heart failure.
Antihypertensives are a class of drugs that are used to treat hypertension. Antihypertensive therapy seeks to prevent the complications of high blood pressure, such as stroke and myocardial infarction. Evidence suggests that reduction of the blood pressure by 5 mmHg can decrease the risk of stroke by 34%, of ischaemic heart disease by 21%, and reduce the likelihood of dementia, heart failure, and mortality from cardiovascular disease. There are many classes of antihypertensives, which lower blood pressure by different means. Among the most important and most widely used medications are thiazide diuretics, calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists (ARBs), and beta blockers.

Enalapril, sold under the brand name Vasotec among others, is a medication used to treat high blood pressure, diabetic kidney disease, and heart failure. For heart failure, it is generally used with a diuretic, such as furosemide. It is given by mouth or by injection into a vein. Onset of effects are typically within an hour when taken by mouth and last for up to a day.
Atenolol is a beta blocker medication primarily used to treat high blood pressure and heart-associated chest pain. Other uses include the prevention of migraines and treatment of certain irregular heart beats. It is taken by mouth or by injection into a vein. It can also be used with other blood pressure medications.

Amiloride, sold under the trade name Midamor among others, is a medication typically used with other medications to treat high blood pressure or swelling due to heart failure or cirrhosis of the liver. Amiloride is often used with a thiazide or other loop diuretic. It is taken by mouth. Onset of action is about two hours and it lasts for about a day.

Lisinopril is a medication of the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor class used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, and after heart attacks. For high blood pressure it is usually a first line treatment, although in black people calcium-channel blockers or thiazide diuretics work better. It is also used to prevent kidney problems in people with diabetes. Lisinopril is taken by mouth. Full effect may take up to four weeks to occur.

Quinapril, sold under the brand name Accupril among others, is a medication used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, and diabetic kidney disease. It is a reasonable initial treatment for high blood pressure. It is taken by mouth.

Potassium-sparing diuretics are diuretic drugs that do not promote the secretion of potassium into the urine.

Prazosin is a medication primarily used to treat high blood pressure, symptoms of an enlarged prostate, and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). It is a less preferred treatment of high blood pressure. Other uses may include heart failure and Raynaud syndrome. It is taken by mouth.

Losartan, sold under the trade name Cozaar among others, is a medication mainly used to treat high blood pressure. It is also used for diabetic kidney disease, heart failure, and left ventricular enlargement. It is taken by mouth. It may be used alone or in addition to other blood pressure medication. Up to six weeks may be required for the full effects to occur.
Alpha-1 blockers constitute a variety of drugs that reduce the effect alpha-1-adrenergic receptors. They are mainly used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), hypertension and post-traumatic stress disorder. Alpha-1 adrenergic receptors occur in vascular smooth muscle, the central nervous system, and other tissues. When alpha blockers bind to these receptors in vascular smooth muscle, they cause vasodilation.

Olmesartan, sold under the trade name Benicar among others, is a medication used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, and diabetic kidney disease. It is a reasonable initial treatment for high blood pressure. It is taken by mouth. Versions are available as the combination olmesartan/hydrochlorothiazide and olmesartan/amlodipine.

Carvedilol, sold under the brand name Coreg among others, is a medication used to treat high blood pressure, congestive heart failure (CHF), and left ventricular dysfunction in people who are otherwise stable. For high blood pressure, it is generally a second-line treatment. It is taken by mouth.

Aliskiren is the first in a class of drugs called direct renin inhibitors. It is used for essential (primary) hypertension. While used for high blood pressure, other better studied medications are typically recommended due to concerns of higher side effects and less evidence of benefit.
A sympatholytic drug is a medication that opposes the downstream effects of postganglionic nerve firing in effector organs innervated by the sympathetic nervous system (SNS). They are indicated for various functions; for example, they may be used as antihypertensives. They are also used to treat anxiety, such as generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder and PTSD.

Alpha-blockers, also known as α-blockers or α-adrenoreceptor antagonists, are a class of pharmacological agents that act as antagonists on α-adrenergic receptors (α-adrenoceptors).
Management of heart failure requires a multimodal approach. It involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medications, and possibly the use of devices or surgery.

Fimasartan is a non-peptide angiotensin II receptor antagonist (ARB) used for the treatment of hypertension and heart failure. Through oral administration, fimasartan blocks angiotensin II receptor type 1 (AT1 receptors), reducing pro-hypertensive actions of angiotensin II, such as systemic vasoconstriction and water retention by the kidneys. Concurrent administration of fimasartan with diuretic hydrochlorothiazide has shown to be safe in clinical trials. Fimasartan was approved for use in South Korea in September 9, 2010 and is available under the brand name Kanarb through Boryung Pharmaceuticals, who are presently seeking worldwide partnership. Fimasartan is being marketed in India under the brand name of Fimanta and Fimagen through Ajanta Pharma Ltd.
References
- ↑ Graham RM, Thornell IR, Gain JM, Bagnoli C, Oates HF, Stokes GS (1976). "Prazosin: the first-dose phenomenon". British Medical Journal. 2 (6047): 1293–4. doi:10.1136/bmj.2.6047.1293. PMC 1689975 . PMID 793676.
- ↑ "Hytrin (Terazosin Hcl) drug warnings and precautions – prescription drugs and medications at RxList". Archived from the original on 2008-06-16. Retrieved 2007-10-20.
- ↑ "Minipress (Prazosin HCl) drug warnings and precautions – prescription drugs and medications at RxList". Archived from the original on 2007-11-02. Retrieved 2007-10-20.
- ↑ Elliott HL, McLean K, Sumner DJ, Meredith PA, Reid JL (1981). "Immediate cardiovascular responses to oral prazosin—effects of concurrent beta-blockers". Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 29 (3): 303–9. doi:10.1038/clpt.1981.40. PMID 6110503.
- ↑ http://www.medicinescomplete.com/mc/bnf/current/PHP1124-angiotensin-converting-enzyme-inhibitors.htm