Related Research Articles

The Assembly of First Nations is an assembly of Canadian First Nations represented by their chiefs. Established in 1982 and modelled on the United Nations General Assembly, it emerged from the National Indian Brotherhood, which dissolved in the late 1970s.

The Wetʼsuwetʼen are a First Nation who live on the Bulkley River and around Burns Lake, Broman Lake, and François Lake in the northwestern Central Interior of British Columbia. The endonym Wetʼsuwetʼen means "People of the Wa Dzun Kwuh River ".
Edward John is a prominent First Nations political leader in Canada.
The Carrier Sekani Tribal Council is a tribal council representing six First Nations in the Central Interior of British Columbia. It was originally known as the Lakes District Tribal Council. The CSTC was incorporated in 1981 and is a registered non-profit society.
In Canada, an Indian band or band, sometimes referred to as a First Nation band or simply a First Nation, is the basic unit of government for those peoples subject to the Indian Act. Bands are typically small groups of people: the largest in the country, the Six Nations of the Grand River First Nation had 22,294 members in September 2005, and many have a membership below 100 people. Each First Nation is typically represented by a band council chaired by an elected chief, and sometimes also a hereditary chief. As of 2013, there were 614 bands in Canada. Membership in a band is controlled in one of two ways: for most bands, membership is obtained by becoming listed on the Indian Register maintained by the government. As of 2013, there were 253 First Nations which had their own membership criteria, so that not all status Indians are members of a band.

The Squamish Nation is a First Nations government of the Squamish people. The Squamish Nation government includes an elected council and an administrative body based primarily in West Vancouver, North Vancouver, and Squamish, BC.
The Union of British Columbia Indian Chiefs (UBCIC) is a First Nations political organization founded in 1969 in response to Jean Chrétien's White Paper proposal to assimilate Status Indians and disband the Department of Indian Affairs.

The Kwakiutl First Nation is a First Nations government based on northern Vancouver Island in British Columbia, Canada, focused on the community of Port Hardy, British Columbia in the Queen Charlotte Strait region, and also known as the Fort Rupert Band, known in traditional Kwakwaka'wakw terms as the Kwagu'ł or Kwagyewlth. It is a member of the Kwakiutl District Council. It is currently in stage 4 of the British Columbia Treaty Process, having submitted a statement of intent in 1997.

George Abbott is a former politician and cabinet minister for the Canadian province of British Columbia. He was a member of the Legislative Assembly of British Columbia, representing the riding of Shuswap from 1996 to 2013. As part of the British Columbia Liberal Party caucus, he served in several cabinet posts under premiers Gordon Campbell and Christy Clark, and ran for party leadership in 2011.
The British Columbia Treaty Process (BCTP) is a land claims negotiation process started in 1993 to resolve outstanding issues, including claims to un-extinguished indigenous rights, with British Columbia's First Nations.
Anishinaabe tribal political organizations are political consortiums of Anishinaabe nations that advocate for the political interests of their constituencies. Anishinaabe people of Canada are considered as First Nations, and of the United States as Native Americans.

Pimicikamak is an indigenous people in Canada. Pimicikamak is related to, but constitutionally, legally, historically and administratively distinct from, the Cross Lake First Nation which is a statutory creation that provides services on behalf of the Canadian Government. Pimicikamak government is based on self-determination and has a unique form.
The Gitxsan Treaty Society handles Treaty negotiations in the BC Treaty Process for a number of First Nations in northwestern British Columbia
The lack of treaties between the First Nations of British Columbia (BC) and the Canadian Crown is a long-standing problem that became a major issue in the 1990s. In 1763, the British Crown declared that only it could acquire land from First Nations through treaties. Historically, only two treaties were signed with the First Nations of British Columbia. The first of these was the Douglas Treaties, negotiated by Sir James Douglas with the native people of southern Vancouver Island from 1850 to 1854. The second treaty, Treaty 8, signed in 1899, was part of the Numbered Treaties that were signed with First Nations across the Prairie regions. British Columbian Treaty 8 signatories are located in the Peace River Country or the far north-east of BC. For over nine decades no more treaties were signed with First Nations of BC; many Native people wished to negotiate treaties, but successive BC provincial governments refused until the 1990s. A major development was the 1997 decision of the Supreme Court of Canada in the Delgamuukw v. British Columbia case that Aboriginal title still exists in British Columbia and that when dealing with Crown land, the government must consult with and may have to compensate First Nations whose rights are affected.

The Ɂakisq̓nuk First Nation, also spelled Akisqnuk First Nation, and formerly known as the Columbia Lake First Nation are a Ktunaxa First Nation in the Kootenays district of the Canadian province of British Columbia. In the British Columbia Treaty Process they are part of the Ktunaxa Nation Council.
The Lower Kootenay First Nation is a First Nation based in the East Kootenay region of British Columbia. In the British Columbia Treaty Process They are part of the Ktunaxa Kinbasket Tribal Council.

The Tobacco Plains Indian Band are a First Nation based in the East Kootenay region of British Columbia. In the British Columbia Treaty Process They are part of the Ktunaxa Kinbasket Tribal Council.
The Tsimshian Tribal Council was the governing coalition of the band governments of the Tsimshian people in Prince Rupert. In British Columbia, the governments of Canada started engaging in the British Columbia Treaty Process with First Nation bands in the province. Originally the Tsimshian Tribal Council pursued negotiations until late 2005 when the Tsimshian Tribal Council, the organization for treaty negotiations, dissolved amid legal and political turmoil.
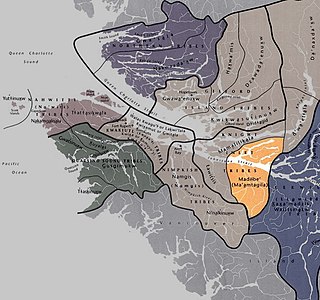
The Ma’amtagila First Nation (also styled Maamtagila), formerly known as Mahteelthpe or Matilpi, are an Indigenous nation and part of the Kwakwaka'wakw peoples. Their territory is located in the Queen Charlotte Strait-Johnstone Strait area in the Discovery Islands between Vancouver Island and the British Columbia mainland in Canada.
The self-formation of political organizations of Indigenous peoples in Canada has been a constant process over many centuries.
References
- ↑ "What's New in BC Treaty Negotiations". Ministry of Indian and Northern Affairs (Canada). April 4, 2007. Archived from the original on August 28, 2007.
- 1 2 "About - First Nations Summit". fns.bc.ca. Retrieved 2023-11-20.
- ↑ "First Nations Leadership Council | British Columbia Assembly of First Nations". www.bcafn.ca. Retrieved 2023-11-20.