Related Research Articles

Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life; or more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place. Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farms, both in freshwater bodies and the oceans. About 500 million people worldwide are economically dependent on fisheries. 171 million tonnes of fish were produced in 2016, but overfishing is an increasing problem — causing declines in some populations.

Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally, resulting in the species becoming increasingly underpopulated in that area. Overfishing can occur in water bodies of any sizes, such as ponds, wetlands, rivers, lakes or oceans, and can result in resource depletion, reduced biological growth rates and low biomass levels. Sustained overfishing can lead to critical depensation, where the fish population is no longer able to sustain itself. Some forms of overfishing, such as the overfishing of sharks, has led to the upset of entire marine ecosystems. Types of overfishing include: growth overfishing, recruitment overfishing, ecosystem overfishing.

A conventional idea of a sustainable fishery is that it is one that is harvested at a sustainable rate, where the fish population does not decline over time because of fishing practices. Sustainability in fisheries combines theoretical disciplines, such as the population dynamics of fisheries, with practical strategies, such as avoiding overfishing through techniques such as individual fishing quotas, curtailing destructive and illegal fishing practices by lobbying for appropriate law and policy, setting up protected areas, restoring collapsed fisheries, incorporating all externalities involved in harvesting marine ecosystems into fishery economics, educating stakeholders and the wider public, and developing independent certification programs.
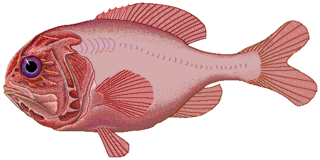
The orange roughy, also known as the red roughy, slimehead and deep sea perch, is a relatively large deep-sea fish belonging to the slimehead family (Trachichthyidae). The UK Marine Conservation Society has categorized orange roughy as "vulnerable to exploitation". It is found in 3 to 9 °C, deep waters of the Western Pacific Ocean, eastern Atlantic Ocean, Indo-Pacific, and in the eastern Pacific off Chile. The orange roughy is notable for its extraordinary lifespan, attaining over 200 years. It is important to commercial deep-trawl fisheries. The fish is a bright, brick-red color, fading to a yellowish-orange after death.

The Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) is a non-profit organization which aims to set standards for sustainable fishing. Fisheries that wish to demonstrate they are well-managed and sustainable compared to the MSC's standards are assessed by a team of Conformity Assessment Bodies (CABs).
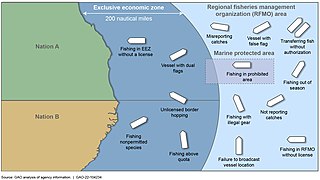
Illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing (IUU) is an issue around the world. Fishing industry observers believe IUU occurs in most fisheries, and accounts for up to 30% of total catches in some important fisheries.
Sustainable seafood is seafood that is caught or farmed in ways that consider the long-term vitality of harvested species and the well-being of the oceans, as well as the livelihoods of fisheries-dependent communities. It was first promoted through the sustainable seafood movement which began in the 1990s. This operation highlights overfishing and environmentally destructive fishing methods. Through a number of initiatives, the movement has increased awareness and raised concerns over the way our seafood is obtained.

Friend of the Sea is a project of the World Sustainability Organization for the certification and promotion of seafood from sustainable fisheries and sustainable aquaculture. It is the only certification scheme which, with the same logo, certifies both wild and farmed seafood.
Sustainable seafood advisory lists and certification are programs aimed at increasing consumer awareness of the environmental impact and sustainability of their seafood purchasing choices.
The Seafood Choices Alliance was a program of the nonprofit ocean conservation organization, SeaWeb. It was established in 2001 to bring together the disparate elements and diverse approaches in a growing "seafood choices" movement in the United States and expanded into Europe in 2005. The stated goals of Seafood Choices Alliance are to promote sustainable seafood and to make the seafood industry socially, environmentally and economically sustainable.

International Seafood Sustainability Foundation (ISSF) was formed in 2009 as a global, non-profit partnership among the tuna industry, scientists and World Wide Fund for Nature. The multistakeholder group states its mission is "to undertake science-based initiatives for the long-term conservation and sustainable use of tuna stocks, reducing bycatch and promoting ecosystem health". Regional Fisheries Management Organizations (RFMOs) are primarily responsible for managing the world's tuna stocks—skipjack, yellowfin and albacore tuna, the species most commonly processed for canned and shelf-stable tuna products, but their parliamentary procedures too often allow the short-term economic and political interests of nations to prevent sustainable measures from being adopted. ISSF works to ensure that effective international management practices are in place to maintain the health of all the tuna stocks.
Sustainable sushi is sushi made from fished or farmed sources that can be maintained or whose future production does not significantly jeopardize the ecosystems from which it is acquired. Concerns over the sustainability of sushi ingredients arise from greater concerns over environmental, economic and social stability, and human health.
SeaChoice is an environmental advocacy group based in Canada. Launched in 2006, SeaChoice was created to increase consumer awareness around seafood sustainability in Canada. For 10 years, its primary goal was shifting seafood procurement to more sustainable options, with a focus on seafood suppliers and Canadian retailers. Having made significant progress in the retail landscape between 2006 and 2016, with many of their retail partners meeting their sustainable seafood commitments, SeaChoice set a new goal to increase sustainability throughout the entire seafood supply chain, from water to table.
Velondriake, meaning “to live with the sea” in the Vezo dialect of the Malagasy language, is a locally managed marine area (LMMA). Established in 2006 in southwest Madagascar, Velondriake is home to over 7,000 resident Vezo people and covers a marine and coastal area of about 64,000 ha making it one of the largest LMMAs in the western Indian Ocean. The LMMA includes extensive coral reefs, mangroves, seagrass beds, baobab forests, spiny forest and other threatened habitats. The LMMA includes five permanent coral reef reserves, two permanent mangrove reserves, and numerous periodic fisheries closures (PFCs), primarily for octopus on reefs and for mud crab in mangroves.

Thai Union Group is a Thailand-based producer of seafood-based food products. It was founded in 1977, and was listed on the Stock Exchange of Thailand (SET) on 22 November 1994.
Gulf Wild is a nonprofit organization operating in the Gulf of Mexico. Gulf Wild works with commercial fishermen to encourage and facilitate fishery conservation and innovation. Gulf Wild has implemented traceability practices including placing a numbered gill tag on every Gulf Wild fish. This numbered tag tracks who harvested the fish, from where, and at what port the fish landed. Consumers can use the gill tag number to access this information via the Gulf Wild website.
The Aquaculture Stewardship Council (ASC) is an independent non-profit organisation and labelling organization that establishes protocol on farmed seafood while ensuring sustainable aquaculture. The ASC provides producers with a certification of environmental sustainability and social responsibility.

Ocean Outcomes (O2) is an international nonprofit organization which works with commercial fisheries, seafood industry, local communities, government, NGOs, and other fishery stakeholders to develop and implement solutions towards more sustainable fisheries. O2's work includes fishery assessments, fishery improvement projects (FIPs), buyer engagement programs, supply chain analysis, and other contractual fishery-related work. Founded in 2015, O2 has team members and fishery projects across Northeast Asia, including on the ground operations in China, Japan, and South Korea.

Julie E. Packard is an American ocean conservationist and philanthropist. She helped create the Monterey Bay Aquarium in the early 1980s and is its executive director, a position she has held since its opening in 1984. She speaks at conferences and symposia related to ocean conservation, and writes online about current issues. She is a fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences and is a recipient of the Audubon Medal.

Sustainable Development Goal 14 is about "Life below water" and is one of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations in 2015. The official wording is to "Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development". The Goal has ten targets to be achieved by 2030. Progress towards each target is being measured with one indicator each.
References
- ↑ Conservation Alliance for Seafood Solutions. Guidelines for Supporting Fishery Improvement Projects March 7, 2015
- ↑ Packard Foundation. Progress toward Sustainable Seafood - By the Numbers 2015 Edition P. 25, June 2015
- ↑ "FIP Directory | Fishery Progress". fisheryprogress.org. Retrieved 2021-09-01.