
Sailing employs the wind—acting on sails, wingsails or kites—to propel a craft on the surface of the water, on ice (iceboat) or on land over a chosen course, which is often part of a larger plan of navigation.

Dinghy sailing is the activity of sailing small boats by using five essential controls:
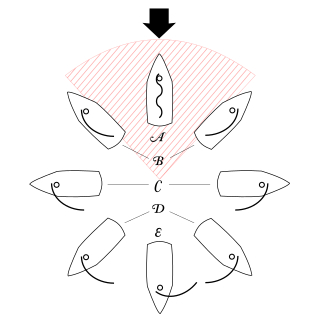
A point of sail is a sailing craft's direction of travel under sail in relation to the true wind direction over the surface.

A jibe (US) or gybe (Britain) is a sailing maneuver whereby a sailing vessel reaching downwind turns its stern through the wind, which then exerts its force from the opposite side of the vessel. Because the mainsail boom can swing across the cockpit quickly, jibes are potentially dangerous to person and rigging compared to tacking. Therefore, accidental jibes are to be avoided while the proper technique must be applied so as to control the maneuver. For square-rigged ships, this maneuver is called wearing ship.

A daggerboard is a retractable centreboard used by various sailing craft. While other types of centreboard may pivot to retract, a daggerboard slides in a casing. The shape of the daggerboard converts the forward motion into a windward lift, countering the leeward push of the sail. The theoretical centre of lateral resistance is on the trailing edge of the daggerboard.

Dinghy racing is a competitive sport using dinghies, which are small boats which may be rowboats, have an outboard motor, or be sailing dinghies. Dinghy racing has affected aspects of the modern sailing dinghy, including hull design, sail materials and sailplan, and techniques such as planing and trapezing.

The Topper is an 11 foot 43 kg (95 lb) sailing dinghy designed by Ian Proctor. The Topper was a one-design boat until 2023 when a new version was produced, and is sailed mostly around the British Isles. It was recognised as a World Sailing Class. The boat previously constructed from polypropylene, and now roto moulded, is popular as a racing boat or for sail training. The class association (ITCA) organise racing events, which range from small travellers to major championships. The RYA run squads alongside the events; in these squads young sailors who are given specialist race coaching.

A centreboard or centerboard (US) is a retractable hull appendage which pivots out of a slot in the hull of a sailboat, known as a centreboard trunk (UK) or centerboard case (US). The retractability allows the centreboard to be raised to operate in shallow waters, to move the centre of lateral resistance, to reduce drag when the full area of the centreboard is not needed, or when removing the boat from the water, as when trailering. A centreboard which consists of solely a pivoting metal plate is called a centerplate; the term "centreboard" may refer to either a wooden or a metal pivoting retractable foil. A daggerboard is similar but slides vertically rather than pivoting.
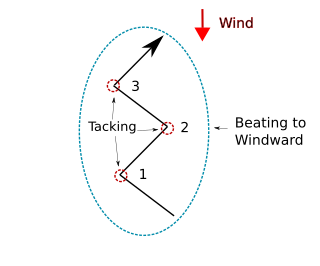
Tacking or coming about is a sailing maneuver by which a sailing craft, whose next destination is into the wind, turns its bow toward and through the wind so that the direction from which the wind blows changes from one side of the boat to the other, allowing progress in the desired direction. Sailing vessels are unable to sail higher than a certain angle towards the wind, so "beating to windward" in a zig-zag fashion with a series of tacking maneuvers, allows a vessel to sail towards a destination that is closer to the wind that the vessel can sail directly.

The International 505 is a One-Design high-performance two-person monohull planing sailing dinghy, with spinnaker, utilising a trapeze for the crew.

The Fireball is a British sailing dinghy that was designed by Peter Milne as a one-design racer and first built in 1962.

The Laser 4000 is a racing dinghy designed by Phil Morrison crewed by two persons. Its one-design weight-equalised system enables physically differing sailors to compete on a level playing field. It is most popular in Europe, particularly the UK, France and Italy.

A sailing hydrofoil, hydrofoil sailboat, or hydrosail is a sailboat with wing-like foils mounted under the hull. As the craft increases its speed the hydrofoils lift the hull up and out of the water, greatly reducing wetted area, resulting in decreased drag and increased speed. A sailing hydrofoil can achieve speeds exceeding double and in some cases triple the wind speed.

A trailer sailer is a type of sailboat that has been designed to be easily transported using a boat trailer towed by an automobile. They are generally larger than a sailing dinghy. Trailer sailers include day sailers and small cabin cruisers, suitable for living on.

The Banshee, sometimes called the Banshee 13, is an American sailing dinghy that was designed by Richard L. Reid as a one-design racer and first built in 1969.
The 29erXX is a high performance sailing skiff, it was designed to allow light crews, particularly female crews, to sail twin trapeze boats and as a training boat for the more powerful 49er. The class gained International Sailing Federation Class status in May 2011, but lost it in 2014.
Velocity made good, or VMG, is a term used in sailing, especially in yacht racing, indicating the speed of a sailboat towards the direction of the wind. The concept is useful because a sailboat cannot sail directly upwind, and thus often can not, or should not, sail directly to a mark to reach it as quickly as possible. It is also often less than optimal to sail directly downwind.

The Hobie Tiger or Hobie Tiger 18, is a French catamaran sailboat that was designed by Hobie Cat Europe as a Formula 18 racer and first built in 1995.

The Farr 3.7 is a one-person sailing dinghy designed by Bruce Farr in 1971. The design plans are sold by the 3.7 Class Owners Association and they are built by a mix of professionals and home built by amateurs. The 3.7 Class is recognised by Yachting New Zealand as a national class and yachts are sailed in New Zealand, Australia and Great Britain. Full sets of plans have been sold worldwide to a number of individuals with greatest numbers in Germany, Japan, USA, South Korea, Poland, France, Belgium, Russia, Spain, Uruguay.
The Beneteau First 14, originally the Seascape 14, is a French one design planing sailing dinghy that was designed by Samuel Manuard as a racer and first built in 2017.

















