
A bulletin board system (BBS), also called a computer bulletin board service (CBBS), is a computer server running software that allows users to connect to the system using a terminal program. Once logged in, the user performs functions such as uploading and downloading software and data, reading news and bulletins, and exchanging messages with other users through public message boards and sometimes via direct chatting. In the early 1980s, message networks such as FidoNet were developed to provide services such as NetMail, which is similar to internet-based email.

Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) is a set of communication standards for simultaneous digital transmission of voice, video, data, and other network services over the digitalised circuits of the public switched telephone network. Work on the standard began in 1980 at Bell Labs and was formally standardized in 1988 in the CCITT "Red Book". By the time the standard was released, newer networking systems with much greater speeds were available, and ISDN saw relatively little uptake in the wider market. One estimate suggests ISDN use peaked at a worldwide total of 25 million subscribers at a time when 1.3 billion analog lines were in use. ISDN has largely been replaced with digital subscriber line (DSL) systems of much higher performance.
Telnet is a client/server application protocol that provides access to virtual terminals of remote systems on local area networks or the Internet. It is a protocol for bidirectional 8-bit communications. Its main goal was to connect terminal devices and terminal-oriented processes.

In telecommunications, a network interface device is a device that serves as the demarcation point between the carrier's local loop and the customer's premises wiring. Outdoor telephone NIDs also provide the subscriber with access to the station wiring and serve as a convenient test point for verification of loop integrity and of the subscriber's inside wiring.
In open systems, a virtual terminal (VT) is an application service that:
- Allows host terminals on a multi-user network to interact with other hosts regardless of terminal type and characteristics,
- Allows remote log-on by local area network managers for the purpose of management,
- Allows users to access information from another host processor for transaction processing,
- Serves as a backup facility.

A terminal emulator, or terminal application, is a computer program that emulates a video terminal within some other display architecture. Though typically synonymous with a shell or text terminal, the term terminal covers all remote terminals, including graphical interfaces. A terminal emulator inside a graphical user interface is often called a terminal window.
An application layer is an abstraction layer that specifies the shared communication protocols and interface methods used by hosts in a communications network. An application layer abstraction is specified in both the Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP) and the OSI model. Although both models use the same term for their respective highest-level layer, the detailed definitions and purposes are different.
An online service provider (OSP) can, for example, be an Internet service provider, an email provider, a news provider (press), an entertainment provider, a search engine, an e-commerce site, an online banking site, a health site, an official government site, social media, a wiki, or a Usenet newsgroup.

Freedom of Mobile Multimedia Access (FOMA) is the brand name of the W-CDMA-based 3G telecommunications services being offered by the Japanese telecommunications service provider NTT DoCoMo. It is an implementation of the Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) and was the world's first 3G mobile data service to commence commercial operations.

In computing, text-based user interfaces (TUI), is a retronym describing a type of user interface (UI) common as an early form of human–computer interaction, before the advent of bitmapped displays and modern conventional graphical user interfaces (GUIs). Like modern GUIs, they can use the entire screen area and may accept mouse and other inputs. They may also use color and often structure the display using box-drawing characters such as ┌ and ╣. The modern context of use is usually a terminal emulator.

The Bloomberg Terminal is a computer software system provided by the financial data vendor Bloomberg L.P. that enables professionals in the financial service sector and other industries to access Bloomberg Professional Services through which users can monitor and analyze real-time financial market data and place trades on the electronic trading platform. It was developed by employees working for businessman Michael Bloomberg. The system also provides news, price quotes, and messaging across its proprietary secure network. It is well known among the financial community for its black interface, which has become a recognizable trait of the service. The first version of the terminal was released in December 1982.

Secure Terminal Equipment (STE) is the U.S. government's current, encrypted telephone communications system for wired or "landline" communications. STE is designed to use ISDN telephone lines which offer higher speeds of up to 128 kbit/s and are all digital. The greater bandwidth allows higher quality voice and can also be utilized for data and fax transmission through a built-in RS-232 port. STE is intended to replace the older STU-III office system and the KY-68 tactical system. STE sets are backwards compatible with STU-III phones, but not with KY-68 sets.
In telecommunications networks, a node is either a redistribution point or a communication endpoint.
The IP Multimedia Subsystem or IP Multimedia Core Network Subsystem (IMS) is a standardised architectural framework for delivering IP multimedia services. Historically, mobile phones have provided voice call services over a circuit-switched-style network, rather than strictly over an IP packet-switched network. Various voice over IP technologies are available on smartphones; IMS provides a standard protocol across vendors.
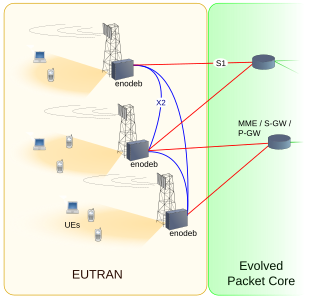
E-UTRA is the air interface of 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) Long Term Evolution (LTE) upgrade path for mobile networks. It is an acronym for Evolved UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access, also known as the Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access in early drafts of the 3GPP LTE specification. E-UTRAN is the combination of E-UTRA, user equipment (UE), and a Node B.
Telenet was an American commercial packet-switched network which went into service in 1975. It was the first FCC-licensed public data network in the United States. Various commercial and government interests paid monthly fees for dedicated lines connecting their computers and local networks to this backbone network. Free public dialup access to Telenet, for those who wished to access these systems, was provided in hundreds of cities throughout the United States.
A virtual console (VC) – also known as a virtual terminal (VT) – is a conceptual combination of the keyboard and display for a computer user interface. It is a feature of some Unix-like operating systems such as Linux, BSD, illumos, UnixWare, and macOS in which the system console of the computer can be used to switch between multiple virtual consoles to access unrelated user interfaces. Virtual consoles date back at least to Xenix and Concurrent CP/M in the 1980s.
Remote Desktop Services (RDS), known as Terminal Services in Windows Server 2008 and earlier, is one of the components of Microsoft Windows that allow a user to initiate and control an interactive session on a remote computer or virtual machine over a network connection. RDS was first released in 1998 as Terminal Server in Windows NT 4.0 Terminal Server Edition, a stand-alone edition of Windows NT 4.0 Server that allowed users to log in remotely. Starting with Windows 2000, it was integrated under the name of Terminal Services as an optional component in the server editions of the Windows NT family of operating systems, receiving updates and improvements with each version of Windows. Terminal Services were then renamed to Remote Desktop Services with Windows Server 2008 R2 in 2009.
A headless computer is a computer system or device that has been configured to operate without a monitor, keyboard, and mouse. A headless system is typically controlled over a network connection, although some headless system devices require a serial connection to be made over RS-232 for administration of the device. Headless operation of a server is typically employed to reduce operating costs.

devpts is a virtual filesystem directory available in the Linux kernel since version 2.1.93. It is normally mounted at /dev/pts and contains solely devices files which represent slaves to the multiplexing master located at /dev/ptmx which in turn is used to implement terminal emulators.










