
Flanders is the Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, language, politics, and history, and sometimes involving neighbouring countries. The demonym associated with Flanders is Fleming, while the corresponding adjective is Flemish, which can also refer to the collective of Dutch dialects spoken in that area, or more generally the Belgian variant of Standard Dutch. The official capital of Flanders is the City of Brussels, although the Brussels-Capital Region that includes it has an independent regional government. The powers of the government of Flanders consist, among others, of economic affairs in the Flemish Region and the community aspects of Flanders life in Brussels, such as Flemish culture and education.

Walloons are a Gallo-Romance ethnic group native to Wallonia and the immediate adjacent regions of Flanders, France, Germany, Luxembourg and the Netherlands. Walloons primarily speak langues d'oïl such as Belgian French, Picard and Walloon. Walloons are primarily Roman Catholic, with a historical minority of Protestantism which dates back to the Reformation era.

The politics of Belgium take place in the framework of a federal, representative democratic, constitutional monarchy. The King of the Belgians is the head of state, and the prime minister of Belgium is the head of government, in a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Federal legislative power is vested in both the government and the two chambers of parliament, the Senate and the Chamber of Representatives. The federation is made up of (language-based) communities and (territorial) regions. Philippe is the seventh and current King of the Belgians, having ascended the throne on 21 July 2013.

Walloon Brabant is a province located in Belgium's French-speaking region of Wallonia. It borders on the province of Flemish Brabant and the provinces of Liège, Namur and Hainaut. Walloon Brabant's capital and largest city is Wavre.

Wallonia, officially the Walloon Region, is one of the three regions of Belgium—along with Flanders and Brussels. Covering the southern portion of the country, Wallonia is primarily French-speaking. It accounts for 55% of Belgium's territory, but only a third of its population. The Walloon Region and the French Community of Belgium, which is the political entity responsible for matters related mainly to culture and education, are independent concepts, because the French Community of Belgium encompasses both Wallonia and the bilingual Brussels-Capital Region but not the German-speaking Community of Belgium.

Belgium is a federal state comprising three communities and three regions that are based on four language areas. For each of these subdivision types, the subdivisions together make up the entire country; in other words, the types overlap.
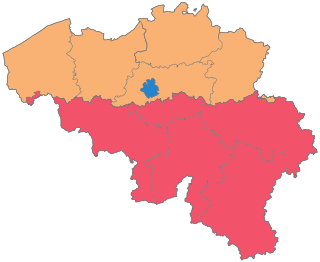
The Kingdom of Belgium is divided into three regions. Two of these regions, Flanders and Wallonia, are each subdivided into five provinces. The third region, Brussels, does not belong to any province and nor is it subdivided into provinces. Instead, it has amalgamated both regional and provincial functions into a single "Capital Region" administration.

The Flemish Movement is an umbrella term which encompasses various political groups in the Belgian region of Flanders and, less commonly, in French Flanders. Ideologically, it encompasses groups which have sought to promote Flemish culture and the Dutch language as well as those seeking greater political autonomy for Flanders within Belgium. It also encompassed nationalists who seek the secession of Flanders from Belgium, either through outright independence or unification with the Netherlands.

Greater Netherlands is an irredentist concept which unites the Netherlands, Flanders, and sometimes Brussels. Additionally, a Greater Netherlands state may include the annexation of the French Westhoek, Suriname, formerly Dutch-speaking areas of Germany and France, or even the ethnically Dutch and/or Afrikaans-speaking parts of South Africa, though such variants are mostly limited to far-right groups. A related proposal is the Pan-Netherlands concept, which includes Wallonia and potentially also Luxembourg.

The Flemish Region, usually simply referred to as Flanders, is one of the three regions of Belgium—alongside the Walloon Region and the Brussels-Capital Region. Covering the northern portion of the country, the Flemish Region is primarily Dutch-speaking. With an area of 13,522 km2 (5,221 sq mi), it accounts for only 45% of Belgium's territory, but 57% of its population. It is one of the most densely populated regions of Europe with around 490/km2 (1,300/sq mi).

Belgian nationalism, sometimes pejoratively referred to as Belgicism, is a nationalist ideology. In its modern form it favours the reversal of federalism and the creation of a unitary state in Belgium. The ideology advocates reduced or no autonomy for the Flemish Community who constitute Flanders, the French Community of Belgium and the German-speaking Community of Belgium who constitute Wallonia and the Brussels-Capital Region which is inhabited by both Walloons and Flemings, and the dissolution of the regional counterparts of each ethnic group within Belgium.

Moritz Ferdinand Freiherr von Bissing was a German officer from Prussia.
The Walloon Movement traces its ancestry to 1856 when literary and folkloric movements based around the Society of Walloon language and literature began forming. Despite the formation of the Society of Walloon Literature, it was not until around 1880 that a "Walloon and French-speaking defense movement" appeared, following the linguistic laws of the 1870s. The movement asserted the existence of Wallonia and a Walloon identity while maintaining the defense of the French language.
The partition of Belgium is a hypothetical situation, which has been discussed by both Belgian and international media, envisioning a split of Belgium along linguistic divisions, with the Flemish Community (Flanders) and the French-speaking Community (Wallonia) becoming independent states. Alternatively, it is hypothesized that Flanders could join the Netherlands and Wallonia could join France.

The Imperial German General Government of Belgium was a German Army occupation administration which administered one of the three separate occupation zones established in German-occupied Belgium during the First World War.

The Belgian provincial, municipal and district elections of 2012 took place on 14 October. As with the previous 2006 elections, these are no longer organised by the Belgian federal state but instead by the respective regions:
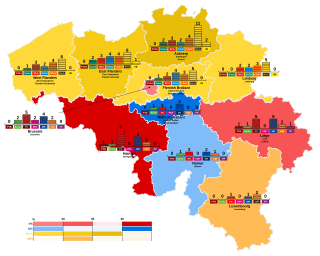
Federal elections were held in Belgium on 25 May 2014. All 150 members of the Chamber of Representatives were elected, whereas the Senate was no longer directly elected following the 2011–2012 state reform. These were the first elections held under King Philippe's reign.

The Vlaamsche Hoogeschool, commonly referred to by its detractors as von Bissing university, is a Dutch-speaking university established at Ghent in German-occupied Belgium in October 1916. Distinct from the existing State University of Ghent, the University formed part of the German Flamenpolitik and was a response to the long-established grievance of the Flemish Movement which campaigned against Ghent University's curriculum being taught only in French, despite the university being located in Dutch-speaking Flanders. The institution took its informal name from Moritz von Bissing, the German Governor-General of Belgium from 1914 to 1917, who was himself one of the Flamenpolitik 's chief advocates.

The Council of Flanders was formed by members of the "activist" or "maximalist" faction of the Flemish Movement in German-occupied Belgium on 4 February 1917 with tacit German support. Its founders, who included Pieter Tack and August Borms, wanted to realize the independence of Flanders from Belgium using German support provided as part of the Flamenpolitik. The Council originally included 46 members, but eventually expanded to include 93. Despite hopes that the council would be allowed full legislative powers, it never became more than a consultative body. It also suffered from internal factionalism and infighting.

The German occupation of Belgium of World War I was a military occupation of Belgium by the forces of the German Empire between 1914 and 1918. Beginning in August 1914 with the invasion of neutral Belgium, the country was almost completely overrun by German troops before the winter of the same year as the Allied forces withdrew westwards. The Belgian government went into exile, while King Albert I and the Belgian Army continued to fight on a section of the Western Front. Under the German military, Belgium was divided into three separate administrative zones. The majority of the country fell within the General Government, a formal occupation administration ruled by a German general, while the others, closer to the front line, came under more repressive direct military rule.
















