
Flanders is the Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, language, politics, and history, and sometimes involving neighbouring countries. The demonym associated with Flanders is Fleming, while the corresponding adjective is Flemish. The official capital of Flanders is the City of Brussels, although the Brussels-Capital Region that includes it has an independent regional government. The powers of the government of Flanders consist, among others, of economic affairs in the Flemish Region and the community aspects of Flanders life in Brussels, such as Flemish culture and education.

Walloons are a Gallo-Romance ethnic group native to Wallonia and the immediate adjacent regions of France, Germany, Luxembourg and the Netherlands. Walloons primarily speak langues d'oïl such as Belgian French, Picard and Walloon. Walloons are historically and primarily Roman Catholic.

The politics of Belgium take place in the framework of a federal, representative democratic, constitutional monarchy. The King of the Belgians is the head of state, and the prime minister of Belgium is the head of government, in a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Federal legislative power is vested in both the government and the two chambers of parliament, the Senate and the Chamber of Representatives. The federation is made up of (language-based) communities and (territorial) regions. Philippe is the seventh and current King of the Belgians, having ascended the throne on 21 July 2013.

Flemish Brabant is a province of Flanders, one of the three regions of Belgium. It borders on the Belgian provinces of Antwerp, Limburg, Liège, Walloon Brabant, Hainaut and East Flanders. Flemish Brabant also surrounds the Brussels-Capital Region. Its capital is Leuven. It has an area of 2,118 km2 (818 sq mi) which is divided into two administrative districts containing 65 municipalities. As of January 2019, Flemish Brabant has a population of 1,146,175.
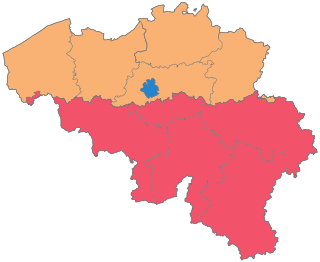
The Kingdom of Belgium is divided into three regions. Two of these regions, Flanders and Wallonia, are each subdivided into five provinces. The third region, Brussels, does not belong to any province and nor is it subdivided into provinces. Instead, it has amalgamated both regional and provincial functions into a single "Capital Region" administration.

The Flemish Movement is an umbrella term which encompasses various political groups in the Belgian region of Flanders and, less commonly, in French Flanders. Ideologically, it encompasses groups which have sought to promote Flemish culture and the Dutch language as well as those seeking greater political autonomy for Flanders within Belgium. It also encompassed nationalists who seek the secession of Flanders from Belgium, either through outright independence or unification with the Netherlands.

Greater Netherlands is an irredentist concept which unites the Netherlands, Flanders, and sometimes Brussels. Additionally, a Greater Netherlands state may include the annexation of the French Westhoek, Suriname, formerly Dutch-speaking areas of Germany and France, or even the ethnically Dutch and/or Afrikaans-speaking parts of South Africa, though such variants are mostly limited to far-right groups. A related proposal is the Pan-Netherlands concept, which includes Wallonia and potentially also Luxembourg.

Belgian nationalism, sometimes pejoratively referred to as Belgicism, is a nationalist ideology. In its modern form it favours the reversal of federalism and the creation of a unitary state in Belgium. The ideology advocates reduced or no autonomy for the Flemish Community who constitute Flanders, the French Community of Belgium and the German-speaking Community of Belgium who constitute Wallonia and the Brussels-Capital Region which is inhabited by both Walloons and Flemings, and the dissolution of the regional counterparts of each ethnic group within Belgium.

Belgians are people identified with the Kingdom of Belgium, a federal state in Western Europe. As Belgium is a multinational state, this connection may be residential, legal, historical, or cultural rather than ethnic. The majority of Belgians, however, belong to two distinct linguistic groups or communities native to the country, i.e. its historical regions: Flemings in Flanders, who speak Dutch; and Walloons in Wallonia, who speak French or Walloon. There is also a substantial Belgian diaspora, which has settled primarily in the United States, Canada, France, and the Netherlands.

Spanish Netherlands was the Habsburg Netherlands ruled by the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs from 1556 to 1714. They were a collection of States of the Holy Roman Empire in the Low Countries held in personal union by the Spanish Crown. This region comprised most of the modern states of Belgium and Luxembourg, as well as parts of northern France, the southern Netherlands, and western Germany with the capital being Brussels. The Army of Flanders was given the task of defending the territory.

The Kingdom of Belgium has three official languages: Dutch (Flemish), French, and German.
The Walloon Movement traces its ancestry to 1856 when literary and folkloric movements based around the Society of Walloon language and literature began forming. Despite the formation of the Society of Walloon Literature, it was not until around 1880 that a "Walloon and French-speaking defense movement" appeared, following the linguistic laws of the 1870s. The movement asserted the existence of Wallonia and a Walloon identity while maintaining the defense of the French language.
The partition of Belgium is a hypothetical situation, which has been discussed by both Belgian and international media, envisioning a split of Belgium along linguistic divisions, with the Flemish Community (Flanders) and the French-speaking Community (Wallonia) becoming independent states. Alternatively, it is hypothesized that Flanders could join the Netherlands and Wallonia could join France or Luxembourg.

State reform, in the context of Belgium, is the ongoing process of seeking and finding constitutional and legal solutions to the problems and tensions in the different segments of the Belgian population, mostly between the Dutch-speakers of Flanders and the French-speakers of Wallonia. In general, Belgium has evolved from a unitary state to a federal state with communities, regions, and language areas.

The Francization of Brussels refers to the evolution, over the past two centuries, of this historically Dutch-speaking city into one where French has become the majority language and lingua franca. The main cause of this transition was the rapid, yet non-compulsory assimilation of the Flemish population, amplified by immigration from France and Wallonia.

The Flemish or Flemings are an ethnic group native to Flanders, Belgium, who speak Flemish Dutch. Flemish people make up the majority of Belgians, at about 60%.

This article describes the history of Flanders. The definition of the territory called "Flanders", however, has varied throughout history.

Flemish (Vlaams) is a Low Franconian dialect cluster of the Dutch language. It is sometimes referred to as Flemish Dutch, Belgian Dutch, or Southern Dutch. Flemish is native to the region known as Flanders in northern Belgium; it is spoken by Flemings, the dominant ethnic group of the region. Outside of Belgium Flanders, it is also spoken to some extent in French Flanders and the Dutch Zeelandic Flanders.

The Catholic University of Leuven was one of Belgium's major universities. It split along linguistic lines after a period of civil unrest in 1967–68 commonly known as the Leuven Affair in French and Flemish Leuven, based on a contemporary slogan, in Dutch. The crisis shook Belgian politics and led to the fall of the government of Paul Vanden Boeynants. It marked an escalation of the linguistic tension in Belgium after World War II and had lasting consequences for other bilingual institutions in Belgium within higher education and politics alike. In 1970 the first of several state reforms occurred, marking the start of Belgium's transition to a federal state.
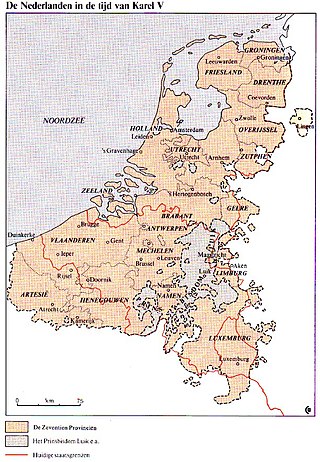
Gewest is a Dutch term often translated as "region". It was used to describe the various different polities making up the Low Countries, which covered what is now the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg and parts of northern France, until the annexation by France in the late 18th century. The term is now mostly associated with the official titles of the constituent states of Belgium.
















