A request that this article title be changed to Flemish is under discussion. Please do not move this article until the discussion is closed. |
Flemish is a Dutch dialect cluster spoken in the Flemish Region.
Contents
Flemish may also refer to:
A request that this article title be changed to Flemish is under discussion. Please do not move this article until the discussion is closed. |
Flemish is a Dutch dialect cluster spoken in the Flemish Region.
Flemish may also refer to:

Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to the southwest, and the North Sea to the northwest. It covers an area of 30,528 km2 (11,787 sq mi) and has a population of more than 11.5 million, making it the 22nd most densely populated country in the world and the 6th most densely populated country in Europe, with a density of 376/km2 (970/sq mi). Belgium is part of an area known as the Low Countries, historically a somewhat larger region than the Benelux group of states, as it also included parts of northern France. The capital and largest city is Brussels; other major cities are Antwerp, Ghent, Charleroi, Liège, Bruges, Namur, and Leuven.

Flanders is the Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, language, politics, and history, and sometimes involving neighbouring countries. The demonym associated with Flanders is Fleming, while the corresponding adjective is Flemish. The official capital of Flanders is the City of Brussels, although the Brussels-Capital Region that includes it has an independent regional government. The powers of the government of Flanders consist, among others, of economic affairs in the Flemish Region and the community aspects of Flanders life in Brussels, such as Flemish culture and education.

The politics of Belgium take place in the framework of a federal, representative democratic, constitutional monarchy. The King of the Belgians is the head of state, and the prime minister of Belgium is the head of government, in a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Federal legislative power is vested in both the government and the two chambers of parliament, the Senate and the Chamber of Representatives. The federation is made up of (language-based) communities and (territorial) regions. Philippe is the seventh and current King of the Belgians, having ascended the throne on 21 July 2013.

Belgium is a federal state comprising three communities and three regions that are based on four language areas. For each of these subdivision types, the subdivisions together make up the entire country; in other words, the types overlap.

Zeelandic Flanders is the southernmost region of the province of Zeeland in the south-western Netherlands. It lies south of the Western Scheldt that separates the region from the remainder of Zeeland and the Netherlands to the north. Zeelandic Flanders is bordered to the south and to the east by Belgium.

Voeren is a Flemish Dutch-speaking municipality with facilities for the French-speaking minority, located in the Belgian province of Limburg. Bordering the Netherlands to the north and the Wallonia region's Liège Province to the south, it is geographically detached from the rest of Flanders, making Voeren an exclave of Flanders. Voeren's name is derived from that of a small right-bank tributary of the Meuse, the Voer, which flows through the municipality.

The Dutch Language Union is an international regulatory institution that governs issues regarding the Dutch language. It is best known for its spelling reforms which are promulgated by member states, grammar books, the Green Booklet and its support of Dutch language courses and studies worldwide. It was founded on a treaty concluded between the Netherlands and Belgium on 9 September 1980. Suriname has been an associate member of the Taalunie since 2004.

The Flemish Movement is an umbrella term which encompasses various political groups in the Belgian region of Flanders and, less commonly, in French Flanders. Ideologically, it encompasses groups which have sought to promote Flemish culture and the Dutch language as well as those seeking greater political autonomy for Flanders within Belgium. It also encompassed nationalists who seek the secession of Flanders from Belgium, either through outright independence or unification with the Netherlands.

The Flemish Region, usually simply referred to as Flanders is one of the three regions of Belgium—alongside the Walloon Region and the Brussels-Capital Region. Covering the northern portion of the country, the Flemish Region is primarily Dutch-speaking. With an area of 13,522 km2 (5,221 sq mi), it accounts for only 45% of Belgium's territory, but 57% of its population. It is one of the most densely populated regions of Europe with around 490/km2 (1,300/sq mi).

The Flemish Community is one of the three institutional communities of Belgium, established by the Belgian constitution and having legal responsibilities only within the precise geographical boundaries of the Dutch-language area and of the bilingual area of Brussels-Capital. Unlike in the French Community of Belgium, the competences of the Flemish Community have been unified with those of the Flemish Region and are exercised by one directly elected Flemish Parliament based in Brussels.
Because modern Belgium is a multilingual country, Belgian literature is often treated as a branch of French literature or Dutch literature. Some writing also exists in the regional languages of Belgium, with published works in both the Walloon language, closely related to French, and also in various regional Flemish or Dutch-related dialects.
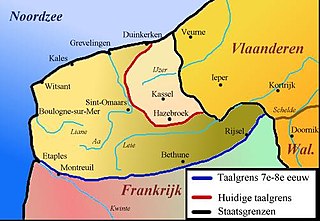
French Flemish is a West Flemish dialect spoken in the north of contemporary France. Place names attest to Flemish having been spoken since the 8th century in the part of Flanders that was ceded to France at the 1659 Treaty of the Pyrenees, and which hence became known as French Flanders. Its dialect subgroup, called French Flemish, meanwhile, became a minority dialect that survives mainly in Dunkirk, Bourbourg, Calais, Saint-Omer with an ethnic enclave Haut-Pont (Haute-Ponte) known for its predominantly Flemish community and Bailleul. French-Flemish has about 20,000 daily users, and twice that number of occasional speakers. The language's status appears to be moribund, but there has been an active movement to retain French Flemish in the region.
Dutch is a West Germanic language, that originated from the Old Frankish dialects.

The Kingdom of Belgium has three official languages: Dutch (Flemish), French, and German.
The partition of Belgium is a hypothetical situation, which has been discussed by both Belgian and international media, envisioning a split of Belgium along linguistic divisions, with the Flemish Community (Flanders) and the French-speaking Community (Wallonia) becoming independent states. Alternatively, it is hypothesized that Flanders could join the Netherlands and Wallonia could join France or Luxembourg.
Dutch dialects are primarily the dialects that are both cognate with the Dutch language and are spoken in the same language area as the Dutch standard language. Dutch dialects are remarkably diverse and are found within Europe mainly in the Netherlands and northern Belgium.

The Flemish or Flemings are an ethnic group native to Flanders, Belgium, who speak Flemish Dutch. Flemish people make up the majority of Belgians, at about 60%.

The Lion of Flanders, or the Battle of the Golden Spurs is a major novel first published in 1838 by the Belgian writer Hendrik Conscience (1812–1883) and is an early example of historical fiction. The book focuses on the medieval Franco-Flemish War and the Battle of the Golden Spurs of 1302 in particular. It is written in Conscience's typical stylistic romanticism and has been described as the "Flemish national epic".

Flemish (Vlaams) is a Low Franconian dialect cluster of the Dutch language. It is sometimes referred to as Flemish Dutch, Belgian Dutch, or Southern Dutch. Flemish is native to the region known as Flanders in northern Belgium; it is spoken by Flemings, the dominant ethnic group of the region. Outside of Belgium Flanders, it is also spoken to some extent in French Flanders and the Dutch Zeelandic Flanders.
The Dutch language used in Belgium can also be referred to as Flemish Dutch or Belgian Dutch. Dutch is the mother tongue of about 60% of the population in Belgium, spoken by approximately 6.5 million out of a population of 11 million people. It is the only official language in Flanders, that is to say the provinces of Antwerp, Flemish Brabant, Limburg, and East Flanders and West Flanders. Alongside French, it is also an official language of Brussels. However, in the Brussels Capital Region and in the adjacent Flemish-Brabant municipalities, Dutch has been largely displaced by French as an everyday language.