
In medicine, a prosthesis, or a prosthetic implant, is an artificial device that replaces a missing body part, which may be lost through physical trauma, disease, or a condition present at birth. Prostheses are intended to restore the normal functions of the missing body part. Amputee rehabilitation is primarily coordinated by a physiatrist as part of an inter-disciplinary team consisting of physiatrists, prosthetists, nurses, physical therapists, and occupational therapists. Prostheses can be created by hand or with computer-aided design (CAD), a software interface that helps creators design and analyze the creation with computer-generated 2-D and 3-D graphics as well as analysis and optimization tools.

A composite material is a material which is produced from two or more constituent materials. These constituent materials have notably dissimilar chemical or physical properties and are merged to create a material with properties unlike the individual elements. Within the finished structure, the individual elements remain separate and distinct, distinguishing composites from mixtures and solid solutions. Composite materials with more than one distinct layer are called composite laminates.
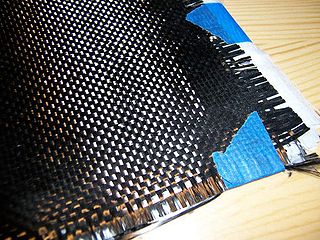
Carbon fibers or carbon fibres are fibers about 5 to 10 micrometers (0.00020–0.00039 in) in diameter and composed mostly of carbon atoms. Carbon fibers have several advantages: high stiffness, high tensile strength, high strength to weight ratio, high chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance, and low thermal expansion. These properties have made carbon fiber very popular in aerospace, civil engineering, military, motorsports, and other competition sports. However, they are relatively expensive compared to similar fibers, such as glass fiber, basalt fibers, or plastic fibers.
Van Phillips is an American inventor of prosthetics.
Össur hf. is a company based in Iceland that develops, manufactures and sells non-invasive equipment for orthopaedics, including bracing and support products, compression therapy, and prosthetics. The company is headquartered in Reykjavík, with offices in the Americas, Europe, and Asia, and distributors in other markets.
Brian Frasure is a Paralympian athlete from the United States competing mainly in category T44 sprint events.
Carbon fiber-reinforced polymers, carbon-fibre-reinforced polymers, carbon-fiber-reinforced plastics, carbon-fiber reinforced-thermoplastic, also known as carbon fiber, carbon composite, or just carbon, are extremely strong and light fiber-reinforced plastics that contain carbon fibers. CFRPs can be expensive to produce, but are commonly used wherever high strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness (rigidity) are required, such as aerospace, superstructures of ships, automotive, civil engineering, sports equipment, and an increasing number of consumer and technical applications.

Alan Fonteles Cardoso Oliveira is a Paralympian athlete from Brazil competing mainly in category T44 sprint events. Oliveira is a double-below-the-knee amputee, classifying him in the Paralympic T43 class; athletes in this class run in T44 event.
T42 is a disability sport classification for disability athletics, applying to athletes with single above the knee amputations or a disability that is comparable. This class includes ISOD classified A2 and A9 competitors.
T43 is a disability sport classification for disability athletics, applying to athletes with "Double below knee amputation or similar disability." It includes ISOD classified athletes from the A4 and A9 classes.

T44 is a disability sport classification for disability athletics, applying to "Single below knee amputation or an athlete who can walk with moderately reduced function in one or both legs." It includes ISOD A4 and A9 classes.

Markus Rehm is a German Paralympic athlete, and in the long jump has won three Paralympic, six world and five European titles. He began in sports at age 20 and became a long jump F44 world champion in 2011. His club is TSV Bayer 04 Leverkusen and he is a medical specialist. Rehm is nicknamed "The Blade Jumper", as he is a long jumper with a blade-type leg prosthesis. Rehm's right leg was amputated below the knee after a wakeboarding accident. He uses a carbon-fibre bladed prosthesis, from which he jumps off.

Blake Leeper is a United States Paralympic athlete, eight-time Paralympic Track and Field international medalist, world record holder and three-time American record holder.

The mechanics of the running blades used by South African former Paralympic runner Oscar Pistorius depend on special carbon-fiber-reinforced polymer prosthetics. Pistorius has double below-the-knee amputations and competed in both non-disabled and T44 amputee athletics events. Pistorius's eligibility to run in international non-disabled events is sanctioned by the International Association of Athletics Federations (IAAF).
Amputee sports classification is a disability specific sport classification used for disability sports to facilitate fair competition among people with different types of amputations. This classification was set up by International Sports Organization for the Disabled (ISOD), and is currently managed by IWAS who ISOD merged with in 2005. Several sports have sport specific governing bodies managing classification for amputee sportspeople.
A2 is an amputee sport classification used by the International Sports Organization for the Disabled (ISOD).for people with acquired or congenital amputations. A2 sportspeople have one leg amputated above the knee. Their amputations impact their sport performance, including having balance issues, increased energy costs, higher rates of oxygen consumption, and issues with their gait.
A3 is an amputee sport classification used by the International Sports Organization for the Disabled (ISOD) for people with acquired or congenital amputations. A3 classified sportspeople have both legs amputated below knee. Their amputations impact their sport performance, including having balance issues, increased energy costs, higher rates of oxygen consumption, and issues with their gait. Sports people in this class are eligible to participate in include athletics, swimming, sitting volleyball, archery, weightlifting, badminton, lawn bowls, sitzball and wheelchair basketball.
A4 is an amputee sport classification used by the International Sports Organization for the Disabled (ISOD).for people with acquired or congenital amputations. People in this class have one leg amputated below the knee. Their amputations impact their sport performance, including having balance issues, increased energy costs, higher rates of oxygen consumption, and issues with their gait. Sports people in this class are eligible to participate in include athletics, swimming, sitting volleyball, archery, weightlifting, wheelchair basketball, amputee basketball, amputee football, lawn bowls, and sitzball.
A1 is an amputee sport classification used by the International Sports Organization for the Disabled (ISOD) for people with acquired or congenital amputations. This class is for sportspeople who have both legs amputated above the knee. Their amputations impact their sport performance, including having balance issues, increased energy costs, higher rates of oxygen consumption, and issues with their gait. Sports people in this class are eligible to participate in include athletics, swimming, sitting volleyball, archery, weightlifting, badminton, lawn bowls, sitzball and wheelchair basketball.
P44 is a Modern pentathlon classification. Sportspeople in this class include people with amputations.








