
A commodity market is a market that trades in the primary economic sector rather than manufactured products, such as cocoa, fruit and sugar. Hard commodities are mined, such as gold and oil. Futures contracts are the oldest way of investing in commodities. Commodity markets can include physical trading and derivatives trading using spot prices, forwards, futures, and options on futures. Farmers have used a simple form of derivative trading in the commodity market for centuries for price risk management.

In economics, a commodity is an economic good, usually a resource, that has full or substantial fungibility: that is, the market treats instances of the good as equivalent or nearly so with no regard to who produced them.
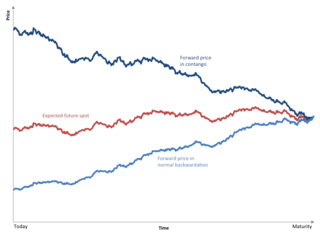
Contango is a situation where the futures price of a commodity is higher than the expected spot price of the contract at maturity. In a contango situation, arbitrageurs or speculators are "willing to pay more [now] for a commodity [to be received] at some point in the future than the actual expected price of the commodity [at that future point]. This may be due to people's desire to pay a premium to have the commodity in the future rather than paying the costs of storage and carry costs of buying the commodity today." On the other side of the trade, hedgers are happy to sell futures contracts and accept the higher-than-expected returns. A contango market is also known as a normal market, or carrying-cost market.

In finance, speculation is the purchase of an asset with the hope that it will become more valuable in the near future.
In economics, the cross elasticity of demand or cross-price elasticity of demand measures the percentage change of the quantity demanded for a good to the percentage change in the price of another good, ceteris paribus. In real life, the quantity demanded of good is dependent on not only its own price but also the price of other "related" products.

In finance, a futures contract is a standardized legal agreement to buy or sell something at a predetermined price at a specified time in the future, between parties not known to each other. The asset transacted is usually a commodity or financial instrument. The predetermined price the parties agree to buy and sell the asset for is known as the forward price. The specified time in the future—which is when delivery and payment occur—is known as the delivery date. Because it is a function of an underlying asset, a futures contract is a derivative product.

In finance, a forward contract or simply a forward is a non-standardized contract between two parties to buy or sell an asset at a specified future time at a price agreed on at the time of conclusion of the contract, making it a type of derivative instrument. The party agreeing to buy the underlying asset in the future assumes a long position, and the party agreeing to sell the asset in the future assumes a short position. The price agreed upon is called the delivery price, which is equal to the forward price at the time the contract is entered into.

A hedge is an investment position intended to offset potential losses or gains that may be incurred by a companion investment. A hedge can be constructed from many types of financial instruments, including stocks, exchange-traded funds, insurance, forward contracts, swaps, options, gambles, many types of over-the-counter and derivative products, and futures contracts.
An exchange-traded fund (ETF) is a type of investment fund and exchange-traded product, i.e. they are traded on stock exchanges. ETFs are similar in many ways to mutual funds, except that ETFs are bought and sold from other owners throughout the day on stock exchanges whereas mutual funds are bought and sold from the issuer based on their price at day's end. An ETF holds assets such as stocks, bonds, currencies, futures contracts, and/or commodities such as gold bars, and generally operates with an arbitrage mechanism designed to keep it trading close to its net asset value, although deviations can occasionally occur. Most ETFs are index funds: that is, they hold the same securities in the same proportions as a certain stock market index or bond market index. The most popular ETFs in the U.S. replicate the S&P 500 Index, the total market index, the NASDAQ-100 index, the price of gold, the "growth" stocks in the Russell 1000 Index, or the index of the largest technology companies. With the exception of non-transparent actively managed ETFs, in most cases, the list of stocks that each ETF owns, as well as their weightings, is posted daily on the website of the issuer. The largest ETFs have annual fees of 0.03% of the amount invested, or even lower, although specialty ETFs can have annual fees well in excess of 1% of the amount invested. These fees are paid to the ETF issuer out of dividends received from the underlying holdings or from selling assets.

In finance, cornering the market consists of obtaining sufficient control of a particular stock, commodity, or other asset in an attempt to manipulate the market price. One definition of cornering a market is "having the greatest market share in a particular industry without having a monopoly".

West Texas Intermediate (WTI) can refer to a grade or a mix of crude oil, and/or the spot price, the futures price, or the assessed price for that oil; colloquially WTI usually refers to the price of the New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX) WTI Crude Oil futures contract or the contract itself. The WTI oil grade is also known as Texas light sweet, although oil produced from any location can be considered WTI if the oil meets required qualifications. Spot and futures prices of WTI are used as a benchmark in oil pricing. This grade is described as light crude oil because of its relatively low density, and sweet because of its low sulfur content.
In economics, overproduction, oversupply, excess of supply or glut refers to excess of supply over demand of products being offered to the market. This leads to lower prices and/or unsold goods along with the possibility of unemployment.

The price of oil, or the oil price, generally refers to the spot price of a barrel of benchmark crude oil—a reference price for buyers and sellers of crude oil such as West Texas Intermediate (WTI), Brent Crude, Dubai Crude, OPEC Reference Basket, Tapis crude, Bonny Light, Urals oil, Isthmus and Western Canadian Select (WCS).

Coffee is a popular beverage and an important commodity. Tens of millions of small producers in developing countries make their living growing coffee. Over 2.25 billion cups of coffee are consumed in the world daily. Over 90 percent of coffee production takes place in developing countries—mainly South America—while consumption happens primarily in industrialized economies. There are 25 million small producers who rely on coffee for a living worldwide. In Brazil, where almost a third of the world's coffee is produced, over five million people are employed in the cultivation and harvesting of over three billion coffee plants; it is a more labour-intensive culture than alternative cultures of the same regions, such as sugar cane or cattle, as its cultivation is not automated, requiring frequent human attention.
Market manipulation is a type of market abuse where there is a deliberate attempt to interfere with the free and fair operation of the market; the most blatant of cases involve creating false or misleading appearances with respect to the price of, or market for, a product, security or commodity.

The Onion Futures Act is a United States law banning the trading of futures contracts on onions as well as "motion picture box office receipts".
In economics, an excess supply, economic surplus market surplus or briefly surply is a situation in which the quantity of a good or service supplied is more than the quantity demanded, and the price is above the equilibrium level determined by supply and demand. That is, the quantity of the product that producers wish to sell exceeds the quantity that potential buyers are willing to buy at the prevailing price. It is the opposite of an economic shortage.
Vincent W. Kosuga was an American onion farmer and commodity trader best known for manipulating the onion futures market. Public outcry over his practices led to the passing of the Onion Futures Act, which banned the trading of futures contracts on onions.

The Essential Commodities Act (ECA) is an act of the Parliament of India that was established to ensure the delivery of certain commodities or products, the supply of which, if obstructed due to hoarding or black marketing, would affect the normal life of the people. This includes foodstuff, drugs, fuel etc.
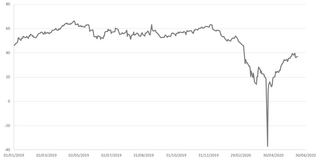
In economics, negative pricing can occur when demand for a product drops or supply increases to an extent that owners or suppliers are prepared to pay others to accept it, in effect setting the price to a negative number. This can happen because it costs money to transport, store, and dispose of a product even when there is little demand to buy it.










