
Plate tectonics is the scientific theory that Earth's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving since 3–4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of continental drift, an idea developed during the first decades of the 20th century. Plate tectonics came to be accepted by geoscientists after seafloor spreading was validated in the mid-to-late 1960s.

Scaffolding, also called scaffold or staging, is a temporary structure used to support a work crew and materials to aid in the construction, maintenance and repair of buildings, bridges and all other human-made structures. Scaffolds are widely used on site to get access to heights and areas that would be otherwise hard to get to. Unsafe scaffolding has the potential to result in death or serious injury. Scaffolding is also used in adapted forms for formwork and shoring, grandstand seating, concert stages, access/viewing towers, exhibition stands, ski ramps, half pipes and art projects.

The keel is the bottom-most longitudinal structural element of a watercraft. On some sailboats, it may have a hydrodynamic and counterbalancing purpose as well. The laying of the keel is often the initial step in the construction of a ship. In the British and American shipbuilding traditions, this event marks the beginning date of a ship's construction.

A strut is a structural component commonly found in engineering, aeronautics, architecture and anatomy. Struts generally work by resisting longitudinal compression, but they may also serve in tension.

Timber framing and "post-and-beam" construction are traditional methods of building with heavy timbers, creating structures using squared-off and carefully fitted and joined timbers with joints secured by large wooden pegs. If the structural frame of load-bearing timber is left exposed on the exterior of the building it may be referred to as half-timbered, and in many cases the infill between timbers will be used for decorative effect. The country most known for this kind of architecture is Germany, where timber-framed houses are spread all over the country.

Seismic retrofitting is the modification of existing structures to make them more resistant to seismic activity, ground motion, or soil failure due to earthquakes. With better understanding of seismic demand on structures and with recent experiences with large earthquakes near urban centers, the need of seismic retrofitting is well acknowledged. Prior to the introduction of modern seismic codes in the late 1960s for developed countries and late 1970s for many other parts of the world, many structures were designed without adequate detailing and reinforcement for seismic protection. In view of the imminent problem, various research work has been carried out. State-of-the-art technical guidelines for seismic assessment, retrofit and rehabilitation have been published around the world – such as the ASCE-SEI 41 and the New Zealand Society for Earthquake Engineering (NZSEE)'s guidelines. These codes must be regularly updated; the 1994 Northridge earthquake brought to light the brittleness of welded steel frames, for example.
A load-bearing wall or bearing wall is a wall that is an active structural element of a building, which holds the weight of the elements above it, by conducting its weight to a foundation structure below it.

Jettying is a building technique used in medieval timber-frame buildings in which an upper floor projects beyond the dimensions of the floor below. This has the advantage of increasing the available space in the building without obstructing the street. Jettied floors are also termed jetties. In the U.S., the most common surviving colonial version of this is the garrison house. Most jetties are external, but some early medieval houses were built with internal jetties.

Framing, in construction, is the fitting together of pieces to give a structure support and shape. Framing materials are usually wood, engineered wood, or structural steel. The alternative to framed construction is generally called mass wall construction, where horizontal layers of stacked materials such as log building, masonry, rammed earth, adobe, etc. are used without framing.
A tie, strap, tie rod, eyebar, guy-wire, suspension cables, or wire ropes, are examples of linear structural components designed to resist tension. It is the opposite of a strut or column, which is designed to resist compression. Ties may be made of any tension resisting material.

A plate or wall plate is a horizontal, structural, load-bearing member in wooden building framing.
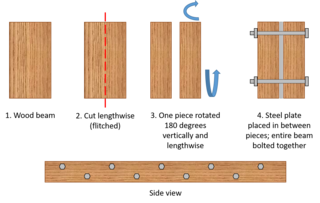
A flitch beam is a compound beam used in the construction of houses, decks, and other primarily wood-frame structures. Typically, the flitch beam is made up of a vertical steel plate sandwiched between two wood beams, the three layers being held together with bolts. In that common form it is sometimes referenced as a steel flitch beam. Further alternating layers of wood and steel can be used to produce an even stronger beam. The metal plates within the beam are known as flitch plates.[1] Flitch beams were used as a cost-effective way to strengthen long-span wooden beams, and have been largely supplanted by more recent technology.

A bressummer, breastsummer, summer beam is a load-bearing beam in a timber-framed building. The word summer derived from sumpter or French sommier, "a pack horse", meaning "bearing great burden or weight". "To support a superincumbent wall", "any beast of burden", and in this way is similar to a wall plate.

Admiral Fetterman Field is a multi-use park in Pensacola, Florida that includes a stadium, commercial buildings, a waterfront public park and amphitheater. The mixed use stadium holds 5,038 people and can be used for a number of events year-round, including baseball, soccer, football, festivals, graduations, and similar events. The multi-use stadium was originally designed to be the home field of the Pensacola Pelicans; it hosts the Miami Marlins Double-A affiliate, the Pensacola Blue Wahoos of the Southern League. The stadium is situated facing the Pensacola Bay.

The Cube is a 24-storey mixed-use development in the centre of Birmingham, England. Designed by Ken Shuttleworth of Make Architects, it contains 244 flats, 111,500 square feet (10,359 m2) of offices, shops, a hotel and a 'skyline' restaurant. It is the final phase of The Mailbox development.

An anchor plate, floor plate or wall washer is a large plate or washer connected to a tie rod or bolt. Anchor plates are used on exterior walls of masonry buildings, for structural reinforcement against lateral bowing. Anchor plates are made of cast iron, sometimes wrought iron or steel, and are often made in a decorative style.

Earthquake-resistant or aseismic structures are designed to protect buildings to some or greater extent from earthquakes. While no structure can be entirely impervious to earthquake damage, the goal of earthquake engineering is to erect structures that fare better during seismic activity than their conventional counterparts. According to building codes, earthquake-resistant structures are intended to withstand the largest earthquake of a certain probability that is likely to occur at their location. This means the loss of life should be minimized by preventing collapse of the buildings for rare earthquakes while the loss of the functionality should be limited for more frequent ones.

The Blue Condominium, also known as the Blue Tower, is located in the Lower East Side neighborhood of New York City at 105 Norfolk Street. Designed by Bernard Tschumi, it is his first residential and first high-rise structure. At 16 stories tall, it opened in 2007 with 32 condominium apartments, a ground floor commercial space occupied by the Thierry Goldberg Gallery, and a third floor roof terrace for residents. Commercial at the ground floor with residential above is a common method of programming space in urban residential projects. The tower is not LEED certified. The faceted pixelated form, a reaction to the zoning and set back requirements, is clad in a blue panel and window curtain wall system, contrasting with the low rise brick buildings that typify the neighborhood.

The Castle of Santo Estêvão is a medieval castle located in the civil parish of Santo Estêvão, municipality of Chaves, in the Portuguese district of Vila Real. Located in a dominant position over the village, the castle is within walking distance of the course of the river Tamega and the border with Spain.

Al-Akbar National Mosque of Surabaya, also known as Al-Akbar Mosque or Great Mosque of Surabaya, is a national mosque located in Surabaya, East Java. It is the second largest mosque in Indonesia after the Istiqlal Mosque in Jakarta in terms of maximum capacity. The location of the mosque is beside the Surabaya-Gempol Highway. Its most distinctive feature is its large vertical dome, accompanied by four small blue domes. It also has a minaret with a height of 99 meters, an ode to the 99 names of Allah.

















