
Nancy Catherine Greene Raine is a former Canadian Senator for British Columbia and an Olympic alpine skier voted as Canada's Female Athlete of the 20th Century. She was born in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. Greene Raine won the giant slalom in the 1968 Winter Olympics in Grenoble, France.

The Doukhobors or Dukhobors are a Spiritual Christian ethnoreligious group of Russian origin. They are known for their pacifism and tradition of oral history, hymn-singing, and verse. They reject the Russian Orthodox priesthood and associated rituals, believing that personal revelation is more important than the Bible. Facing persecution by the Russian government for their nonorthodox beliefs, many migrated to Canada between 1899 and 1938, where most currently reside.

Alice Stokes Paul was an American Quaker, suffragist, feminist, and women's rights activist, and one of the foremost leaders and strategists of the campaign for the Nineteenth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution, which prohibits sex discrimination in the right to vote. Paul initiated, and along with Lucy Burns and others, strategized events such as the Woman Suffrage Procession and the Silent Sentinels, which were part of the successful campaign that resulted in the amendment's passage in August 1920.

The Salt march, also known as the Salt Satyagraha, Dandi March, and the Dandi Satyagraha, was an act of nonviolent civil disobedience in colonial India, led by Mahatma Gandhi. The 24-day march lasted from 12 March 1930 to 5 April 1930 as a direct action campaign of tax resistance and nonviolent protest against the British salt monopoly. Another reason for this march was that the Civil Disobedience Movement needed a strong inauguration that would inspire more people to follow Gandhi's example. Gandhi started this march with 78 of his trusted volunteers. The march spanned 387 kilometres (240 mi), from Sabarmati Ashram to Dandi, which was called Navsari at that time. Growing numbers of Indians joined them along the way. When Gandhi broke the British Raj salt laws at 8:30 am on 6 April 1930, it sparked large-scale acts of civil disobedience against the salt laws by millions of Indians.

The Silent Sentinels, also known as the Sentinels of Liberty, were a group of over 2,000 women in favor of women's suffrage organized by Alice Paul and the National Woman's Party, who nonviolently protested in front of the White House during Woodrow Wilson's presidency starting on January 10, 1917. Nearly 500 were arrested, and 168 served jail time. They were the first group to picket the White House. Later, they also protested in Lafayette Square, not stopping until June 4, 1919 when the Nineteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution was passed both by the House of Representatives and the Senate.

New Denver is a village in the Central Kootenay region of British Columbia, Canada at the mouth of Carpenter Creek, on the east shore of Slocan Lake, in the West Kootenay region of southeastern British Columbia. The village is 47 kilometres (29 mi) west of Kaslo on Highway 31A, and 47 kilometres (29 mi) southeast of Nakusp and 32 kilometres (20 mi) northeast of Slocan on Highway 6.
The Freedomite movement split-off from the Doukhobors, a community of Spiritual Christians who began a mass migration from Russia to Canada in 1898. The Freedomite movement first appeared in 1902 in what is now Saskatchewan, and later most moved to the Kootenay and Boundary Districts of British Columbia.

Lieutenant Colonel Robert William Bonner was a Canadian lawyer, politician, and corporate executive. He pursued his career working in the British Columbia government and in B.C.-based companies.

Marion Wallace Dunlop was a Scottish artist, author and illustrator of children's books, and Suffragette. She was the first and one of the most well known British suffrage activists to go on hunger strike on 5 July 1909, after being arrested in July 1909 for militancy. She said she would not take any food unless she was treated as a political prisoner instead of as a common criminal. Wallace Dunlop's mode of protest influenced suffragettes after her and other leaders like M. K. Gandhi and James Connolly, who also used fasting to protest British rule. She was at the centre of the Women's Social and Political Union and designed some of the most influential processions of the UK suffrage campaign, as well as designing banners for them.

Frances Crowe was an American peace activist and pacifist from the Pioneer Valley of Western Massachusetts.
Gloria Blackwell, also known as Gloria Rackley, was an African-American civil rights activist and educator. She was at the center of the Civil Rights Movement in Orangeburg, South Carolina during the 1960s, attracting some national attention and a visit by Dr. Martin Luther King of the Southern Christian Leadership Conference. Her activities were widely covered by the local press.
In Canada, topfreedom has primarily been an attempt to combat the interpretation of indecency laws that considered a woman's breasts to be indecent, and therefore their exhibition in public an offence. In British Columbia, it is a historical issue dating back to the 1930s and the public protests against the materialistic lifestyle held by the radical religious sect of the Freedomites, whose pacifist beliefs led to their exodus from Russia to Canada at the end of the 19th century. The Svobodniki became famous for their public nudity: primarily for their nude marches in public and the acts of arson committed also in the nude.
Ghoncheh Ghavami, also spelled as Goncheh Ghavami, is a British-Iranian law graduate of the School of Oriental and African Studies, University of London who was held in solitary confinement in Evin Prison for protesting for equal access to sporting events in Iran.
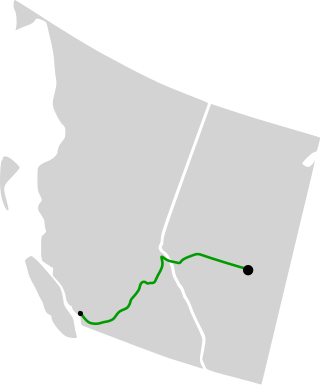
The Trans Mountain Pipeline System, or simply the Trans Mountain Pipeline(TMPL), is a multiple product pipeline system that carries crude and refined products from Edmonton, Alberta, to the coast of British Columbia, Canada.
The Girls of Enghelab protests are protests against the compulsory hijab in Iran, part of the wider Iranian Democracy Movement. The protests were inspired by Vida Movahed, an Iranian woman known as the Girl of Enghelab Street, who stood in the crowd on a utility box on Enghelab Street in Tehran on 27 December 2017 during the 2017–2018 Iranian protests who tied a white headscarf, to a stick, and waved it to the crowd as a flag. She was arrested on that day and was released temporary on bail a month later, on 28 January 2018. Some people interpreted Movahed's action as being based on Masih Alinejad's call for White Wednesdays, a protest movement that the presenter at VOA Persian Television started in early 2017. Other women later re-enacted her protest and posted photos of their actions on social media. These women are described as the "Girls of Enghelab Street" and the "Girls of Revolution Street" in English sources. Some of the protesters however claim that they were not following Masih Alinejad's call. The protests intensified in 2022 due to the death of Mahsa Amini.

Edith Hudson was a British nurse and suffragette. She was an active member of the Edinburgh branch of the Women's Social and Political Union (WSPU) and was arrested several times for her part in their protests in Scotland and London. She engaged in hunger strikes while in prison and was forcibly fed. She was released after the last of these strikes under the so-called Cat and Mouse Act. Hudson was awarded a Hunger Strike Medal 'for Valour' by the WSPU.
Elizabethand Agnes Thomson were Scottish suffragettes and members of the Edinburgh branch of the Women's Social and Political Union. They were arrested for their involvement in WSPU protests in Scotland and London. The sisters were involved in the first arson attempt in Scotland as part of the WSPU arson campaign in 1913. Elizabeth was imprisoned for her role and went on hunger strike. She was later released under the Prisoners Act 1913, so-called Cat and Mouse Act. Elizabeth was awarded a Hunger Strike Medal 'for Valour' by the WSPU.
Prior to the civil rights movement in South Carolina, African Americans in the state had very few political rights. South Carolina briefly had a majority-black government during the Reconstruction era after the Civil War, but with the 1876 inauguration of Governor Wade Hampton III, a Democrat who supported the disenfranchisement of blacks, African Americans in South Carolina struggled to exercise their rights. Poll taxes, literacy tests, and intimidation kept African Americans from voting, and it was virtually impossible for someone to challenge the Democratic Party, which ran unopposed in most state elections for decades. By 1940, the voter registration provisions written into the 1895 constitution effectively limited African-American voters to 3,000—only 0.8 percent of those of voting age in the state.
Muriel Eleanor Scott (1888–1963), was a Scottish suffragette, hunger striker, and protest organiser. Her sister Arabella Scott was force-fed many times, and Muriel Scott led protests about this cruel treatment.

Krestova is an unincorporated community of about 150 people in the Kootenay region of British Columbia, Canada. The community was established by members of the Doukhobor religious group, who originally immigrated from Ukraine and Russia, in 1911-12. The name comes from the Russian "Dolina Krestova ", meaning "valley of the cross". The area is still home to the "Sons of Freedom" movement, which split from the Doukhobor community in the early 1900s.











