
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It defines the content and structure of web content. It is often assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaScript, a programming language.
Gecko is a browser engine developed by Mozilla. It is used in the Firefox browser, the Thunderbird email client, and many other projects.
An HTML element is a type of HTML document component, one of several types of HTML nodes. The first used version of HTML was written by Tim Berners-Lee in 1993 and there have since been many versions of HTML. The current de facto standard is governed by the industry group WHATWG and is known as the HTML Living Standard.
Jakarta Faces, formerly Jakarta Server Faces and JavaServer Faces (JSF) is a Java specification for building component-based user interfaces for web applications. It was formalized as a standard through the Java Community Process as part of the Java Platform, Enterprise Edition. It is an MVC web framework that simplifies the construction of user interfaces (UI) for server-based applications by using reusable UI components in a page.
A mobile browser is a web browser designed for use on a mobile device such as a mobile phone, PDA, smartphone, or tablet. Mobile browsers are optimized to display web content most effectively on small screens on portable devices. Some mobile browsers, especially older versions, are designed to be small and efficient to accommodate the low memory capacity and low bandwidth of certain wireless handheld devices. Traditional smaller feature phones use stripped-down mobile web browsers; however, most current smartphones have full-fledged browsers that can handle the latest web technologies, such as CSS 3, JavaScript, and Ajax.
Web standards are the formal, non-proprietary standards and other technical specifications that define and describe aspects of the World Wide Web. In recent years, the term has been more frequently associated with the trend of endorsing a set of standardized best practices for building web sites, and a philosophy of web design and development that includes those methods.

The Markup Validation Service is a validator by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) that allows Internet users to check pre-HTML5 HTML and XHTML documents for well-formed markup against a document type definition (DTD). Markup validation is an important step towards ensuring the technical quality of web pages. However, it is not a complete measure of web standards conformance. Though W3C validation is important for browser compatibility and site usability, it has not been confirmed what effect it has on search engine optimization.
The Web Standards Project (WaSP) was a group of professional web developers dedicated to disseminating and encouraging the use of the web standards recommended by the World Wide Web Consortium, along with other groups and standards bodies, with a primary focus on web clients.
In HTML, the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser, <div> and <span> tags are elements used to define parts of a document, so that they are identifiable when a unique classification is necessary. Where other HTML elements such as <p> (paragraph), <em> (emphasis), and so on, accurately represent the semantics of the content, the additional use of <span> and <div> tags leads to better accessibility for readers and easier maintainability for authors. Where no existing HTML element is applicable, <span> and <div> can valuably represent parts of a document so that HTML attributes such as class, id, lang, or dir can be applied.
Scalable Inman Flash Replacement (sIFR) is an obsolete JavaScript and Adobe Flash dynamic web fonts implementation, enabling the replacement of text elements on HTML web pages with Flash equivalents. It is open-source and was initially developed by Mike Davidson and improved by Mark Wubben. It is a scalable variety of HTML text-to-flash replacement pioneered by Shaun Inman.

JavaFX is a software platform for creating and delivering desktop applications, as well as rich web applications that can run across a wide variety of devices. JavaFX has support for desktop computers and web browsers on Microsoft Windows, Linux, and macOS, as well as mobile devices running iOS and Android, through Gluon Mobile.

The Acid3 test is a web test page from the Web Standards Project that checks a web browser's compliance with elements of various web standards, particularly the Document Object Model (DOM) and JavaScript.
Extensible HyperText Markup Language (XHTML) is part of the family of XML markup languages which mirrors or extends versions of the widely used HyperText Markup Language (HTML), the language in which Web pages are formulated.

Iris Browser is a discontinued web browser for Windows Mobile smartphones and personal digital assistants (PDAs) developed by the Torch Mobile company. The first version was released in 2008. It was one of the first mobile browsers to score a perfect 100 on the Acid3 test.
Apache Cordova is a mobile application development framework created by Nitobi. Adobe Systems purchased Nitobi in 2011, rebranded it as PhoneGap, and later released an open-source version of the software called Apache Cordova. Apache Cordova enables software programmers to build hybrid web applications for mobile devices using CSS3, HTML5, and JavaScript, instead of relying on platform-specific APIs like those in Android, iOS, or Windows Phone. It enables the wrapping up of CSS, HTML, and JavaScript code depending on the platform of the device. It extends the features of HTML and JavaScript to work with the device. The resulting applications are hybrid, meaning that they are neither truly native mobile application nor purely Web-based. They are not native because all layout rendering is done via Web views instead of the platform's native UI framework. They are not Web apps because they are packaged as apps for distribution and have access to native device APIs. Mixing native and hybrid code snippets has been possible since version 1.9.
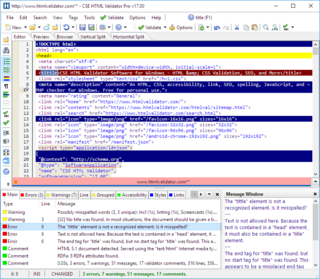
CSS HTML Validator is an HTML editor and CSS editor for Windows that helps web developers create syntactically correct and accessible HTML/HTML5, XHTML, and CSS documents by locating errors, potential problems like browser compatibility issues, and common mistakes. It is also able to check links, check spelling, suggest improvements, alert developers to deprecated, obsolete, or proprietary tags, attributes, and CSS properties, and find issues that can affect search engine optimization.

Google Chrome Experiments is an online showroom of web browser-based experiments, interactive programs, and artistic projects. Launched on March 1, 2009, Google Chrome Experiments is an official Google website that was originally meant to test the limits of JavaScript and the Google Chrome browser's performance and abilities. As the project progressed, it took on the role of showcasing and experimenting with the latest open-source web-based technologies, such as JavaScript, HTML, WebGL, Canvas, SVG, and CSS. All the projects on Chrome Experiments are user-submitted and are made using open-source technologies. As of 2024, the website continues to host a growing number of experiments, featuring over 1,500 projects.
JWt is an open-source widget-centric web application framework for the Java programming language developed by Emweb. It has an API that uses established GUI application development patterns. The programming model is component-based and event-driven, similar to Swing.
Prince is a computer program that converts XML and HTML documents into PDF files by applying Cascading Style Sheets (CSS). Prince is a commercial product, which is free to download and use for non-commercial purposes.
Next.js is an open-source web development framework created by the private company Vercel providing React-based web applications with server-side rendering and static rendering.








