Related Research Articles
A lens is a transmissive optical device that focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually arranged along a common axis. Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic, and are ground and polished or molded to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly focus or disperse waves and radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses, electron lenses, acoustic lenses, or explosive lenses.
The focal length of an optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light; it is the inverse of the system's optical power. A positive focal length indicates that a system converges light, while a negative focal length indicates that the system diverges light. A system with a shorter focal length bends the rays more sharply, bringing them to a focus in a shorter distance or diverging them more quickly. For the special case of a thin lens in air, a positive focal length is the distance over which initially collimated (parallel) rays are brought to a focus, or alternatively a negative focal length indicates how far in front of the lens a point source must be located to form a collimated beam. For more general optical systems, the focal length has no intuitive meaning; it is simply the inverse of the system's optical power.

A camera lens is an optical lens or assembly of lenses used in conjunction with a camera body and mechanism to make images of objects either on photographic film or on other media capable of storing an image chemically or electronically.
Focal point may refer to:

A hypocenter is the point of origin of an earthquake or a subsurface nuclear explosion. In seismology, it is a synonym of the focus. The term hypocenter is also used as a synonym for ground zero, the surface point directly beneath a nuclear airburst.
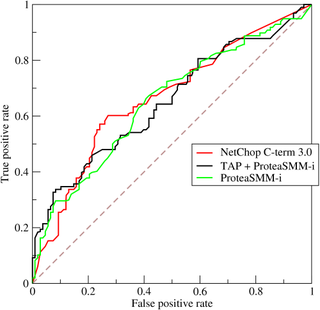
A receiver operating characteristic curve, or ROC curve, is a graphical plot that illustrates the diagnostic ability of a binary classifier system as its discrimination threshold is varied. The method was developed for operators of military radar receivers, which is why it is so named.

Macro photography, is extreme close-up photography, usually of very small subjects and living organisms like insects, in which the size of the subject in the photograph is greater than life size . By the original definition, a macro photograph is one in which the size of the subject on the negative or image sensor is life size or greater. In some senses, however, it refers to a finished photograph of a subject that is greater than life size.

In geometrical optics, a focus, also called an image point, is the point where light rays originating from a point on the object converge. Although the focus is conceptually a point, physically the focus has a spatial extent, called the blur circle. This non-ideal focusing may be caused by aberrations of the imaging optics. In the absence of significant aberrations, the smallest possible blur circle is the Airy disc, which is caused by diffraction from the optical system's aperture. Aberrations tend to get worse as the aperture diameter increases, while the Airy circle is smallest for large apertures.
FPR may refer to:
In Gaussian optics, the cardinal points consist of three pairs of points located on the optical axis of a rotationally symmetric, focal, optical system. These are the focal points, the principal points, and the nodal points. For ideal systems, the basic imaging properties such as image size, location, and orientation are completely determined by the locations of the cardinal points; in fact only four points are necessary: the focal points and either the principal or nodal points. The only ideal system that has been achieved in practice is the plane mirror, however the cardinal points are widely used to approximate the behavior of real optical systems. Cardinal points provide a way to analytically simplify a system with many components, allowing the imaging characteristics of the system to be approximately determined with simple calculations.

Ryan Clark is an American graphic designer and musician who also has performed under the stage name Maven. He is best known as the lead vocalist of the Christian metal band, Demon Hunter, which he co-founded with his brother, guitarist Don Clark. He is featured on Zao's The Lesser Lights of Heaven DVD and Mark Salomon's Podcast, Never Was.

Treasure Coast International Airport is a public airport located three miles (5 km) northwest of the central business district of Fort Pierce, a city in St. Lucie County, Florida, United States. It is owned by the St. Lucie Board of County Commissioners.
Tickford Racing is an Australian motor racing team which competes in the Virgin Australia Supercars Championship. The team currently campaigns four Ford Mustangs, driven by Lee Holdsworth, Cameron Waters, James Courtney and Jack Le Brocq. Tickford Racing also competes in the Dunlop Super2 Series with Broc Feeney. In 2020, they operated the 23Red Racing Mustang of Will Davison, but after the first two rounds 23Red withdrew from the category due to their major backing leaving as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. The team then leased the REC to continue fielding four cars, with Courtney joining the team from the third round onwards.
The formyl peptide receptors (FPR) belong to a class of G protein-coupled receptors involved in chemotaxis. In humans, there are three formyl peptide receptor isoforms, each encoded by a separate gene that are named FPR1, FPR2, and FPR3. These receptors were originally identified by their ability to bind N-formyl peptides such as N-formylmethionine produced by the degradation of either bacterial or host cells. Hence formyl peptide receptors are involved in mediating immune cell response to infection. These receptors may also act to suppress the immune system under certain conditions. The close phylogenetic relation of signaling in chemotaxis and olfaction was recently proved by detection formyl peptide receptor like proteins as a distinct family of vomeronasal organ chemosensors in mice.

N-formyl peptide receptor 2 (FPR2) is a G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) located on the surface of many cell types of various animal species. The human receptor protein is encoded by the FPR2 gene and is activated to regulate cell function by binding any one of a wide variety of ligands including not only certain N-Formylmethionine-containing oligopeptides such as N-Formylmethionine-leucyl-phenylalanine (FMLP) but also the polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolite of arachidonic acid, lipoxin A4 (LXA4). Because of its interaction with lipoxin A4, FPR2 is also commonly named the ALX/FPR2 or just ALX receptor.

N-formyl peptide receptor 3 (FPR3) is a receptor protein that in humans is encoded by the FPR3 gene.

The Micro Four Thirds system is a standard released by Olympus and Panasonic in 2008, for the design and development of mirrorless interchangeable lens digital cameras, camcorders and lenses. Camera bodies are available from Blackmagic, DJI, JVC, Kodak, Olympus, Panasonic, Sharp, and Xiaomi. MFT lenses are produced by Cosina Voigtländer, DJI, Kowa, Kodak, Mitakon, Olympus, Panasonic, Samyang, Sharp, Sigma, SLR Magic, Tamron, Tokina, Veydra, and Xiaomi, amongst others.
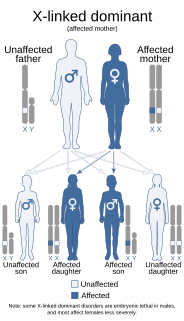
Focal dermal hypoplasia is a form of ectodermal dysplasia. It is a multisystem disorder characterized primarily by skin manifestations to the atrophic and hypoplastic areas of skin which are present at birth. These defects manifest as yellow-pink bumps on the skin and pigmentation changes. The disorder is also associated with shortness of stature and some evidence suggests that it can cause epilepsy.

The Sigma 8–16mm lens is an enthusiast-level, ultra wide-angle rectilinear zoom lens made by Sigma Corporation specifically for use with APS-C small format digital SLRs. It is the first ultrawide rectilinear zoom lens with a minimum focal length of 8 mm, designed specifically for APS-C size image sensors. The lens was introduced at the February 2010 Photo Marketing Association International Convention and Trade Show. At its release it was the widest viewing angle focal length available commercially for APS-C cameras. It is part of Sigma's DC line of lenses, meaning it was designed to have an image circle tailored to work with APS-C format cameras. The lens has a constant length regardless of optical zoom and focus with inner lens tube elements responding to these parameters. The lens has hypersonic zoom autofocus.

Formyl peptide receptor 1 is a cell surface receptor protein that in humans is encoded by the formyl peptide receptor 1 (FPR1) gene. This gene encodes a G protein-coupled receptor cell surface protein that binds and is activated by N-Formylmethionine-containing oligopeptides, particularly N-Formylmethionine-leucyl-phenylalanine (FMLP). FPR1 is prominently expressed by mammalian phagocytic and blood leukocyte cells where it functions to mediate these cells' responses to the N-formylmethionine-containing oligopeptides which are released by invading microorganisms and injured tissues. FPR1 directs these cells to sites of invading pathogens or disrupted tissues and then stimulates these cells to kill the pathogens or to remove tissue debris; as such, it is an important component of the innate immune system that operates in host defense and damage control.
References
- ↑ "Focal Point Review—FPR". Public and Commercial Services Union. Archived from the original on 24 December 2012. Retrieved 11 September 2012.
| This management-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |