
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity.

Protein biosynthesis is a core biological process, occurring inside cells, balancing the loss of cellular proteins through the production of new proteins. Proteins perform a number of critical functions as enzymes, structural proteins or hormones. Protein synthesis is a very similar process for both prokaryotes and eukaryotes but there are some distinct differences.

Protein folding is the physical process where a protein chain is translated into its native three-dimensional structure, typically a "folded" conformation, by which the protein becomes biologically functional. Via an expeditious and reproducible process, a polypeptide folds into its characteristic three-dimensional structure from a random coil. Each protein exists first as an unfolded polypeptide or random coil after being translated from a sequence of mRNA into a linear chain of amino acids. At this stage, the polypeptide lacks any stable three-dimensional structure. As the polypeptide chain is being synthesized by a ribosome, the linear chain begins to fold into its three-dimensional structure.

In biochemistry, globular proteins or spheroproteins are spherical ("globe-like") proteins and are one of the common protein types. Globular proteins are somewhat water-soluble, unlike the fibrous or membrane proteins. There are multiple fold classes of globular proteins, since there are many different architectures that can fold into a roughly spherical shape.

In biology and biochemistry, the active site is the region of an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The active site consists of amino acid residues that form temporary bonds with the substrate, the binding site, and residues that catalyse a reaction of that substrate, the catalytic site. Although the active site occupies only ~10–20% of the volume of an enzyme, it is the most important part as it directly catalyzes the chemical reaction. It usually consists of three to four amino acids, while other amino acids within the protein are required to maintain the tertiary structure of the enzymes.
In biochemistry, the native state of a protein or nucleic acid is its properly folded and/or assembled form, which is operative and functional. The native state of a biomolecule may possess all four levels of biomolecular structure, with the secondary through quaternary structure being formed from weak interactions along the covalently-bonded backbone. This is in contrast to the denatured state, in which these weak interactions are disrupted, leading to the loss of these forms of structure and retaining only the biomolecule's primary structure.
In polymer chemistry, a random coil is a conformation of polymers where the monomer subunits are oriented randomly while still being bonded to adjacent units. It is not one specific shape, but a statistical distribution of shapes for all the chains in a population of macromolecules. The conformation's name is derived from the idea that, in the absence of specific, stabilizing interactions, a polymer backbone will "sample" all possible conformations randomly. Many unbranched, linear homopolymers — in solution, or above their melting temperatures — assume (approximate) random coils.
Self-assembly is a process in which a disordered system of pre-existing components forms an organized structure or pattern as a consequence of specific, local interactions among the components themselves, without external direction. When the constitutive components are molecules, the process is termed molecular self-assembly.
Supramolecular chemistry refers to the branch of chemistry concerning chemical systems composed of a discrete number of molecules. The strength of the forces responsible for spatial organization of the system range from weak intermolecular forces, electrostatic charge, or hydrogen bonding to strong covalent bonding, provided that the electronic coupling strength remains small relative to the energy parameters of the component. While traditional chemistry concentrates on the covalent bond, supramolecular chemistry examines the weaker and reversible non-covalent interactions between molecules. These forces include hydrogen bonding, metal coordination, hydrophobic forces, van der Waals forces, pi–pi interactions and electrostatic effects.
In chemistry, a non-covalent interaction differs from a covalent bond in that it does not involve the sharing of electrons, but rather involves more dispersed variations of electromagnetic interactions between molecules or within a molecule. The chemical energy released in the formation of non-covalent interactions is typically on the order of 1–5 kcal/mol. Non-covalent interactions can be classified into different categories, such as electrostatic, π-effects, van der Waals forces, and hydrophobic effects.

In chemistry, a foldamer is a discrete chain molecule (oligomer) that folds into a conformationally ordered state in solution. They are artificial molecules that mimic the ability of proteins, nucleic acids, and polysaccharides to fold into well-defined conformations, such as α-helices and β-sheets. The structure of a foldamer is stabilized by noncovalent interactions between nonadjacent monomers. Foldamers are studied with the main goal of designing large molecules with predictable structures. The study of foldamers is related to the themes of molecular self-assembly, molecular recognition, and host–guest chemistry.

DNA origami is the nanoscale folding of DNA to create arbitrary two- and three-dimensional shapes at the nanoscale. The specificity of the interactions between complementary base pairs make DNA a useful construction material, through design of its base sequences. DNA is a well-understood material that is suitable for creating scaffolds that hold other molecules in place or to create structures all on its own.

The folding funnel hypothesis is a specific version of the energy landscape theory of protein folding, which assumes that a protein's native state corresponds to its free energy minimum under the solution conditions usually encountered in cells. Although energy landscapes may be "rough", with many non-native local minima in which partially folded proteins can become trapped, the folding funnel hypothesis assumes that the native state is a deep free energy minimum with steep walls, corresponding to a single well-defined tertiary structure. The term was introduced by Ken A. Dill in a 1987 article discussing the stabilities of globular proteins.
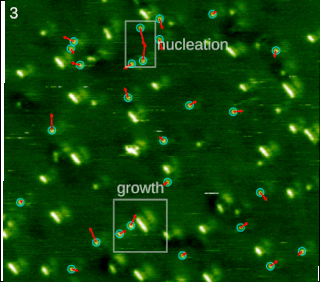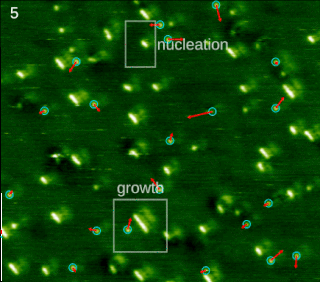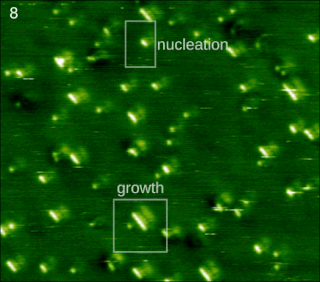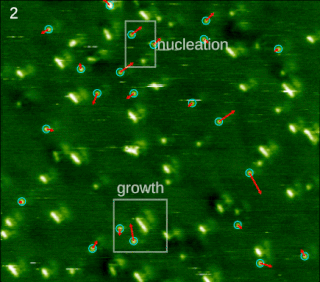
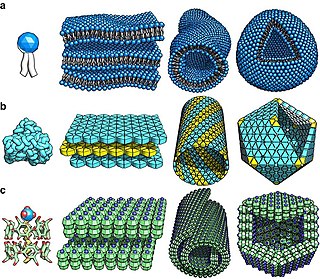
In chemistry and materials science, molecular self-assembly is the process by which molecules adopt a defined arrangement without guidance or management from an outside source. There are two types of self-assembly: intramolecular and intermolecular. Commonly, the term molecular self-assembly refers to the former, while the latter is more commonly called folding.
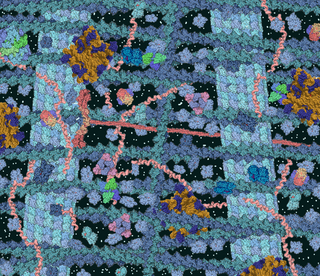
The phenomenon of macromolecular crowding alters the properties of molecules in a solution when high concentrations of macromolecules such as proteins are present. Such conditions occur routinely in living cells; for instance, the cytosol of Escherichia coli contains about 300–400 mg/ml of macromolecules. Crowding occurs since these high concentrations of macromolecules reduce the volume of solvent available for other molecules in the solution, which has the result of increasing their effective concentrations. Crowding can promote formation of a biomolecular condensate by colloidal phase separation.
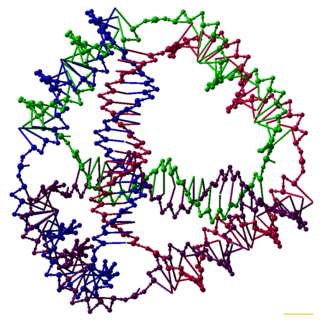
DNA nanotechnology is the design and manufacture of artificial nucleic acid structures for technological uses. In this field, nucleic acids are used as non-biological engineering materials for nanotechnology rather than as the carriers of genetic information in living cells. Researchers in the field have created static structures such as two- and three-dimensional crystal lattices, nanotubes, polyhedra, and arbitrary shapes, and functional devices such as molecular machines and DNA computers. The field is beginning to be used as a tool to solve basic science problems in structural biology and biophysics, including applications in X-ray crystallography and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins to determine structures. Potential applications in molecular scale electronics and nanomedicine are also being investigated.
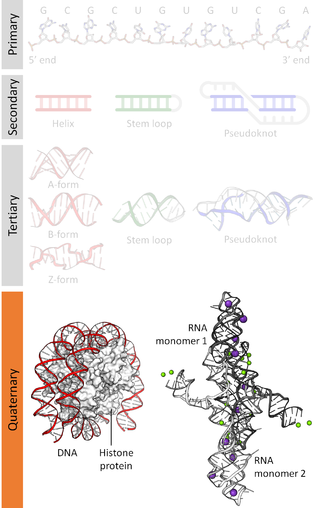
Nucleic acidquaternary structure refers to the interactions between separate nucleic acid molecules, or between nucleic acid molecules and proteins. The concept is analogous to protein quaternary structure, but as the analogy is not perfect, the term is used to refer to a number of different concepts in nucleic acids and is less commonly encountered. Similarly other biomolecules such as proteins, nucleic acids have four levels of structural arrangement: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure. Primary structure is the linear sequence of nucleotides, secondary structure involves small local folding motifs, and tertiary structure is the 3D folded shape of nucleic acid molecule. In general, quaternary structure refers to 3D interactions between multiple subunits. In the case of nucleic acids, quaternary structure refers to interactions between multiple nucleic acid molecules or between nucleic acids and proteins. Nucleic acid quaternary structure is important for understanding DNA, RNA, and gene expression because quaternary structure can impact function. For example, when DNA is packed into heterochromatin, therefore exhibiting a type of quaternary structure, gene transcription will be inhibited.
A depletion force is an effective attractive force that arises between large colloidal particles that are suspended in a dilute solution of depletants, which are smaller solutes that are preferentially excluded from the vicinity of the large particles. One of the earliest reports of depletion forces that lead to particle coagulation is that of Bondy, who observed the separation or "creaming" of rubber latex upon addition of polymer depletant molecules to solution. More generally, depletants can include polymers, micelles, osmolytes, ink, mud, or paint dispersed in a continuous phase.
Chemical chaperones are a class of small molecules that function to enhance the folding and/or stability of proteins. Chemical chaperones are a broad and diverse group of molecules, and they can influence protein stability and polypeptide organization through a variety of mechanisms. Chemical chaperones are used for a range of applications, from production of recombinant proteins to treatment of protein misfolding in vivo.

RNA origami is the nanoscale folding of RNA, enabling the RNA to create particular shapes to organize these molecules. It is a new method that was developed by researchers from Aarhus University and California Institute of Technology. RNA origami is synthesized by enzymes that fold RNA into particular shapes. The folding of the RNA occurs in living cells under natural conditions. RNA origami is represented as a DNA gene, which within cells can be transcribed into RNA by RNA polymerase. Many computer algorithms are present to help with RNA folding, but none can fully predict the folding of RNA of a singular sequence.














