
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of 70,550.19 km2 (27,239.58 sq mi), it is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total land area of Germany, and with over 13.08 million inhabitants, it is the second most populous German state, behind only North Rhine-Westphalia; however, due to its large land area, its population density is below the German average. Major cities include Munich, Nuremberg, and Augsburg.

Franconia is a region of Germany, characterised by its culture and East Franconian dialect. Franconia is made up of the three Regierungsbezirke of Lower, Middle and Upper Franconia in Bavaria, the adjacent, Franconian-speaking South Thuringia, south of the Thuringian Forest—which constitutes the language boundary between Franconian and Thuringian—and the eastern parts of Heilbronn-Franconia in Baden-Württemberg.

The Palatinate, or the Rhenish Palatinate (Rheinpfalz), is a historical region of Germany. The Palatinate occupies most of the southern quarter of the German federal state of Rhineland-Palatinate (Rheinland-Pfalz), covering an area of 2,105 square miles (5,450 km2) with about 1.4 million inhabitants. Its residents are known as Palatines (Pfälzer).

Swabia is one of the seven administrative regions of Bavaria, Germany. It consists of ten districts and 340 municipalities with Augsburg being the administrative capital. It is the only German region officially named Swabia in the principle of spatiality.

Bavarian, alternately Austro-Bavarian, is a major group of Upper German varieties spoken in the south-east of the German language area, including the German state of Bavaria, most of Austria and the Italian region of South Tyrol. Prior to 1945, Bavarian was also prevalent in parts of the southern Sudetenland and western Hungary. Bavarian is spoken by approximately 12 million people in an area of around 125,000 square kilometres (48,000 sq mi), making it the largest of all German dialects. In 2008, 45 percent of Bavarians claimed to use only dialect in everyday communication.
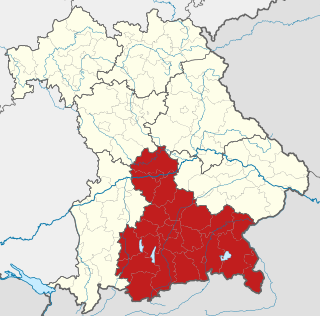
Upper Bavaria is one of the seven administrative regions of Bavaria, Germany.

Lower Bavaria is one of the seven administrative regions of Bavaria, Germany, located in the east of the state. It consists of nine districts and 258 municipalities.

The Upper Palatinate is an administrative district in the east of Bavaria, Germany. It consists of seven districts and 226 municipalities, including three cities.
Altötting is a Landkreis (district) in Bavaria, Germany. It is bounded by Austria and the Bavarian districts of Traunstein, Mühldorf and Rottal-Inn.
Cham is a Landkreis (district) in Bavaria, Germany. It is bounded by the districts of Regen, Straubing-Bogen, Regensburg and Schwandorf and by the Czech Plzeň Region.
The Regen is a river in Bavaria, Germany, and for a short distance in the Czech Republic. It is a left tributary of the Danube, at Regensburg, Germany.

The Bavarian Alps is a collective name for several mountain ranges of the Northern Limestone Alps within the German state of Bavaria.

Bavarians are an ethnographic group of Germans of the Bavaria region, a state within Germany. The group's dialect or speech is known as the Bavarian language, native to Altbayern, roughly the territory of the Electorate of Bavaria in the 17th century.

The Duchy of Bavaria was a frontier region in the southeastern part of the Merovingian kingdom from the sixth through the eighth century. It was settled by Bavarian tribes and ruled by dukes (duces) under Frankish overlordship. A new duchy was created from this area during the decline of the Carolingian Empire in the late ninth century. It became one of the stem duchies of the East Frankish realm, which evolved as the Kingdom of Germany and the Holy Roman Empire.

The Tauber is a river in Franconia, Germany. It is a left tributary of the Main and is 132 km (82 mi) in length. The name derives from the Celtic word for water.

The Kingdom of Bavaria was a German state that succeeded the former Electorate of Bavaria in 1806 and continued to exist until 1918. With the unification of Germany into the German Empire in 1871, the kingdom became a federated state of the new empire and was second in size, power, and wealth only to the leading state, the Kingdom of Prussia.
Southern Germany is a region of Germany that included the areas in which Upper German dialects are spoken, which includes the stem duchies of Bavaria and Swabia in present-day Bavaria, Baden-Württemberg, and the southern portion of Hesse and Rhineland-Palatinate that were part of the Duchy of Franconia.

The Bavarian State Police is the state police force of the German state of Bavaria under the umbrella of the Bavarian Ministry of the Interior. It has approximately 33,500 armed officers and roughly 8,500 other civilian employees.

The Itz is a river of Thuringia and Bavaria, Germany.

The Kahl is a river in the northern Spessart in Bavaria and Hesse, Germany. It is a right tributary of the Main and is 35.6 km (22.1 mi) long. The name Kahl comes from the Old High German word kaldaha, which means cool and clear. The Kahl rises from two sources left and right of the road at the foot of the Spessart hills, near Kleinkahl. These springs produce 50–60 litres per second. The Kahl flows into the river Main in Kahl am Main. The mouth is near the old Kahl Nuclear Power Plant. The largest tributaries are Westerbach, Sommerkahl, Reichenbach and Geiselbach.


















