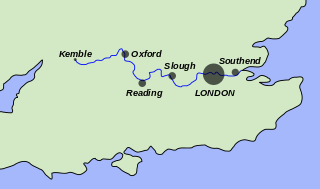
The River Thames, known alternatively in parts as the River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At 215 miles (346 km), it is the longest river entirely in England and the second-longest in the United Kingdom, after the River Severn.

The Thames Barrier is a retractable barrier system built to protect the floodplain of most of Greater London from exceptionally high tides and storm surges moving up from the North Sea. It has been operational since 1982. When needed, it is closed (raised) during high tide; at low tide, it can be opened to restore the river's flow towards the sea. Built about 2 miles east of the Isle of Dogs, its northern bank is in Silvertown in the London Borough of Newham and its southern bank is in the New Charlton area of the Royal Borough of Greenwich.

Wapping is an area in London, England and is located in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. It is in East London and part of the East End. Wapping is on the north bank of the River Thames between St Katharine Docks to the west, and Shadwell to the east. This position gives the district a strong maritime character.

A mudlark is someone who scavenges the banks and shores of rivers for items of value, a term used especially to describe those who scavenged this way in London during the late 18th and 19th centuries. The practice of searching the banks of rivers for items continues in the modern era, with newer technology such as metal detectors sometimes being employed to search for metal valuables that may have washed ashore.

The SS Richard Montgomery is a wrecked American Liberty cargo ship that was built during World War II. She was named after Richard Montgomery, an Irish officer who fought in the American Revolutionary War.

The Bristol Channel is a major inlet in the island of Great Britain, separating South Wales and South West England. It extends from the smaller Severn Estuary of the River Severn to the North Atlantic Ocean. It takes its name from the English city and port of Bristol.

Swansea Bay is a bay on the southern coast of Wales. The River Neath, River Tawe, River Afan, River Kenfig and Clyne River flow into the bay. Swansea Bay and the upper reaches of the Bristol Channel experience a large tidal range. The shipping ports in Swansea Bay are Swansea Docks, Port Talbot Docks and Briton Ferry wharfs.

The Thames Estuary is where the River Thames meets the waters of the North Sea, in the south-east of Great Britain.

The Severn Estuary is the estuary of the River Severn, flowing into the Bristol Channel between South West England and South Wales. Its very high tidal range, approximately 50 feet (15 m), creates valuable intertidal habitats and has led to the area being at the centre of discussions in the UK regarding renewable tidal energy.

The Thames Path is a National Trail following the River Thames from one of its sources near Kemble in Gloucestershire to the Woolwich foot tunnel, south east London. It is about 185 miles (298 km) long. A path was first proposed in 1948 but it only opened in 1996.

The public trust doctrine is the principle that the sovereign holds in trust for public use some resources such as shoreline between the high and low tide lines, regardless of private property ownership.

Chiswick Eyot is a 3.266-acre (1.3 ha) narrow, uninhabited ait of the Thames. It is a tree- and reed-covered rise on the Tideway by Chiswick, in London, England and is overlooked by Chiswick Mall and by some of the Barnes riverside on the far bank.

Watermen's stairs were semipermanent structures that formed part of a complex transport network of public stairs, causeways and alleys in use from the 14th century to access the waters of the tidal River Thames in England. They were used by watermen, who taxied passengers across and along the river in London.

Isleworth Ait, also known as Isleworth Eyot, is a between 3.5-hectare (8.6-acre) and 9.370-acre (3.792 ha) teardrop-shaped island in the River Thames in England. The long ait is on the Tideway facing Old Isleworth and the towpath alongside the Royal Mid-Surrey Golf Club. These places are in the London Boroughs of Hounslow and Richmond upon Thames. The island faces Heron's Place and a number of commercial buildings.

Corporation Island is a small island on the River Thames in London. The island is between Richmond Bridge and Richmond Railway Bridge, where it forms part of the celebrated view from the Richmond waterfront. Its name seems to derive from its owners, the Corporation of Richmond, now the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames. It is uninhabited and heavily wooded, and was formerly known as Richmond Ait.

The Thames Discovery Programme is a community archaeology project, focusing on the archaeology of the River Thames on the Tideway. The Thames Discovery Programme (TDP) was launched in October 2008 and until September 2011, the project was supported by the National Lottery and a grant from the Heritage Lottery Fund. The project is designed to communicate an understanding and informed enjoyment of the historic Thames to the widest possible audience, and to train and support members of the public to monitor and record the archaeology of the foreshore during the lifetime of the project, and into the future.

Lara Maiklem FSA is a British author, editor and publishing consultant, known for her writing and speaking on mudlarking. She was elected a Fellow of the Society of Antiquaries of London in 2022.

The River Hull tidal surge barrier is a flood control gate located on the River Hull in the city of Kingston upon Hull, in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. The barrier impounds the river in times of tidal surges, preventing water moving upstream of the river from the Humber Estuary, and flooding the areas of the city which are near to the river, or susceptible to flooding. It is held horizontal when not in use, and turns 90 degrees before being lowered to the riverbed in the event of a tidal surge. It is the second largest flood barrier in the United Kingdom after the Thames Barrier in London.

Lagoon Hull is a proposed £1.5 billion development on the Humber Estuary foreshore between Hessle and Kingston upon Hull, in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. The proposed lagoon would be formed from a stone causeway and will provide an outer lock gate in the Humber Estuary which would effectively dam the River Hull, making it a non-tidal waterway. The 11-kilometre (6.8 mi) long causeway would also provide a dual carriageway from the A63 at Hessle which would run to Hull Docks, taking traffic away from the city centre. The scheme is being vaunted as one that will prevent future flooding in Hull when sea levels rise, and contribute to less flooding in the wider Humber Estuary.
Tower Beach was an urban beach on the north bank of the River Thames in London, England, adjacent to the Tower of London, which was open to the public from 1934 to 1971.



















