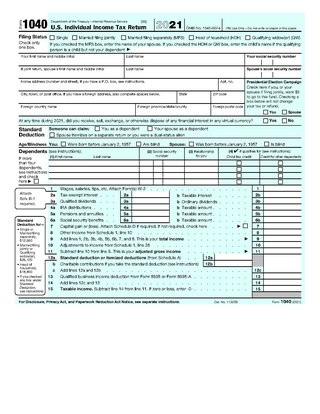
Form 1040, officially, the U.S. Individual Income Tax Return, is an IRS tax form used for personal federal income tax returns filed by United States residents. The form calculates the total taxable income of the taxpayer and determines how much is to be paid to or refunded by the government.

The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 is a United States Act of Congress enacted by the 104th United States Congress and signed into law by President Bill Clinton on August 21, 1996. It aimed to alter the transfer of healthcare information, stipulated the guidelines by which personally identifiable information maintained by the healthcare and healthcare insurance industries should be protected from fraud and theft, and addressed some limitations on healthcare insurance coverage. It generally prohibits healthcare providers and businesses called covered entities from disclosing protected information to anyone other than a patient and the patient's authorized representatives without their consent. The bill does not restrict patients from receiving information about themselves. Furthermore, it does not prohibit patients from voluntarily sharing their health information however they choose, nor does it require confidentiality where a patient discloses medical information to family members, friends or other individuals not employees of a covered entity.
Tax returns in the United States are reports filed with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) or with the state or local tax collection agency containing information used to calculate income tax or other taxes. Tax returns are generally prepared using forms prescribed by the IRS or other applicable taxing authority.
Three key types of withholding tax are imposed at various levels in the United States:
A tax refund is a payment to the taxpayer due because the taxpayer has paid more tax than owed.
Form 1099 is one of several IRS tax forms used in the United States to prepare and file an information return to report various types of income other than wages, salaries, and tips. The term information return is used in contrast to the term tax return although the latter term is sometimes used colloquially to describe both kinds of returns.
Tax withholding, also known as tax retention, pay-as-you-earn tax or tax deduction at source, is income tax paid to the government by the payer of the income rather than by the recipient of the income. The tax is thus withheld or deducted from the income due to the recipient. In most jurisdictions, tax withholding applies to employment income. Many jurisdictions also require withholding taxes on payments of interest or dividends. In most jurisdictions, there are additional tax withholding obligations if the recipient of the income is resident in a different jurisdiction, and in those circumstances withholding tax sometimes applies to royalties, rent or even the sale of real estate. Governments use tax withholding as a means to combat tax evasion, and sometimes impose additional tax withholding requirements if the recipient has been delinquent in filing tax returns, or in industries where tax evasion is perceived to be common.
A direct debit or direct withdrawal is a financial transaction in which one organisation withdraws funds from a payer's bank account. Formally, the organisation that calls for the funds instructs their bank to collect an amount directly from another's bank account designated by the payer and pay those funds into a bank account designated by the payee. Before the payer's banker will allow the transaction to take place, the payer must have advised the bank that they have authorized the payee to directly draw the funds. It is also called pre-authorized debit (PAD) or pre-authorized payment (PAP). After the authorities are set up, the direct debit transactions are usually processed electronically.
A payment is the tender of something of value, such as money or its equivalent, by one party to another in exchange for goods or services provided by them, or to fulfill a legal obligation or philanthropy desire. The party making the payment is commonly called the payer, while the payee is the party receiving the payment. Whilst payments are often made voluntarily, some payments are compulsory, such as payment of a fine.
Debt settlement is a settlement negotiated with a debtor's unsecured creditor. Commonly, creditors agree to forgive a large part of the debt: perhaps around half, though results can vary widely. When settlements are finalized, the terms are put in writing. It is common that the debtor makes one lump-sum payment in exchange for the creditor agreeing that the debt is now cancelled and the matter closed. Some settlements are paid out over a number of months. In either case, as long as the debtor does what is agreed in the negotiation, no outstanding debt will appear on the former debtor's credit report.

Form W-9 is used in the United States income tax system by a third party who must file an information return with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). It requests the name, address, and taxpayer identification information of a taxpayer.
In tax administration in the United States, backup withholding is the sending of a portion of a payment to a tax authority instead of to the payee. This applies to the US IRS and the tax authorities of some states. For the IRS, it applies to some payments reported on Form 1099 which must be submitted to the IRS by financial institutions and businesses making certain income payments. Factors that necessitate backup withholding include:
- Incorrect taxpayer identification number (TIN)/ITIN/ATIN on Form W-9
- An IRS backup withholding order
- Certain types of payments
The United States Internal Revenue Service (IRS) uses forms for taxpayers and tax-exempt organizations to report financial information, such as to report income, calculate taxes to be paid to the federal government, and disclose other information as required by the Internal Revenue Code (IRC). There are over 800 various forms and schedules. Other tax forms in the United States are filed with state and local governments.
E-file is a system for submitting tax documents to the US Internal Revenue Service through the Internet or direct connection, usually without the need to submit any paper documents. Tax preparation software with e-filing capabilities includes stand-alone programs or websites. Tax professionals use tax preparation software from major software vendors for commercial use.
Tax information reporting in the United States is a requirement for organizations to report wage and non-wage payments made in the course of their trade or business to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). This area of government reporting and corporate responsibility is continuously growing, carrying with it a large number of regulatory requirements established by the federal government and the states. There are currently more than 30 types of tax information returns required by the federal government, and they provide the primary cross-checking measure the IRS has to verify accuracy of tax returns filed by individual taxpayers.
In the United States, Form 1099-MISC is a variant of Form 1099 used to report miscellaneous income. One notable use of Form 1099-MISC was to report amounts paid by a business to a non-corporate US resident independent contractor for services, but starting tax year 2020, this use was moved to the separate Form 1099-NEC. The ubiquity of the form has also led to use of the phrase "1099 workers" or "the 1099 economy" to refer to the independent contractors themselves. Other uses of Form 1099-MISC include rental income, royalties, and Native American gaming profits.
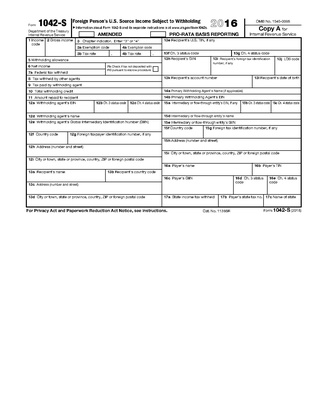
Forms 1042, 1042-S and 1042-T are United States Internal Revenue Service tax forms dealing with payments to foreign persons, including nonresident aliens, foreign partnerships, foreign corporations, foreign estates, and foreign trusts.

In the United States, Form 1099-R is a variant of Form 1099 used for reporting on distributions from pensions, annuities, retirement or profit sharing plans, IRAs, charitable gift annuities and Insurance Contracts. Form 1099-R is filed for each person who has received a distribution of $10 or more from any of the above.
The Individual Master File (IMF) is the system currently used by the United States Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to store and process tax submissions and used as the main data input to process the IRS's transactions. It is a running record of all of a person's individual tax events including refunds, payments, penalties and tax payer status. It is a batch-driven application that uses VSAM files.
The Central Electronic System of Payments (CESOP) regime is an automatic exchange of information regime being introduced in the European Union from 1 January 2024. The rules were introduced by Council Directive 2020/284, amending the EU's Value-added tax Directive.





