
Assisi is a town and comune of Italy in the Province of Perugia in the Umbria region, on the western flank of Monte Subasio.

Todi is a town and comune (municipality) of the province of Perugia in central Italy. It is perched on a tall two-crested hill overlooking the east bank of the river Tiber, commanding distant views in every direction.

Saint Rita of Cascia was an Italian widow and Augustinian nun venerated as a saint in the Roman Catholic Church. Rita was a child bride, married before the age of 12. The marriage lasted for eighteen years, during which she is remembered for her Christian values as a model wife and mother who made efforts to convert her husband from his abusive behaviour. Upon the murder of her husband by another feuding family, she sought to dissuade her sons from revenge.

Norcia, traditionally known in English by its Latin name of Nursia, is a town and comune in the province of Perugia (Italy) in southeastern Umbria. Unlike many ancient towns, it is located in a wide plain abutting the Monti Sibillini, a subrange of the Apennines with some of its highest peaks, near the Sordo River, a small stream that eventually flows into the Nera. The town is popularly associated with the Valnerina.

Benozzo Gozzoli was an Italian Renaissance painter from Florence. He is best known for a series of murals in the Magi Chapel of the Palazzo Medici-Riccardi, depicting festive, vibrant processions with fine attention to detail and a pronounced International Gothic influence. The chapel's fresco cycle reveals a new Renaissance interest in nature with its realistic depiction of landscapes and vivid human portraits. Gozzoli is considered one of the most prolific fresco painters of his generation. While he was mainly active in Tuscany, he also worked in Umbria and Rome.
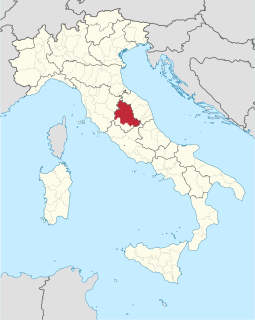
The Province of Perugia is the larger of the two provinces in the Umbria region of Italy, comprising two-thirds of both the area and population of the region. Its capital is the city of Perugia. The province covered all of Umbria until 1927, when the province of Terni was carved out of its southern third. The province of Perugia has an area of 6,334 km² covering two-thirds of Umbria, and a total population of about 660,000. There are 59 comunes in the province. The province has numerous tourist attractions, especially artistic and historical ones, and is home to the Lake Trasimeno, the largest lake of Central Italy. It historically the ancestral origin of the Umbri, while later it was a Roman province and then part of the Papal States until the late 19th century.
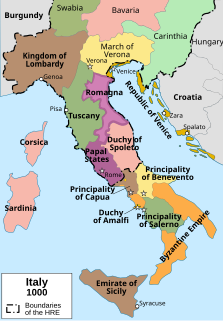
The Duchy of Spoleto was a Lombard territory founded about 570 in central Italy by the Lombard dux Faroald. Its capital was the city of Spoleto.

Saint Gabriel of Our Lady of Sorrows C.P was an Italian Passionist clerical student. Born to a professional family, he gave up ambitions of a secular career to enter the Passionist Congregation. His life in the monastery was not extraordinary, yet he followed the rule of the congregation perfectly and was known for his great devotion to the sorrows of the Virgin Mary. He died from tuberculosis at the age of 23 in Isola del Gran Sasso, in the province of Teramo. He was canonized by Pope Benedict XV in 1920.

Saint Constantius is one of the patron saints of Perugia, Italy.

Saint Clare of Montefalco, also called Saint Clare of the Cross, was an Augustinian nun and abbess. Before becoming a nun, St. Clare was a member of the Third Order of St. Francis (Secular). She was canonized by Pope Leo XIII on December 8, 1881.

Ubald of Gubbio was a medieval bishop of Gubbio, in Umbria, today venerated as a saint by the Catholic Church. Saint Ubaldo Day is still celebrated at the Basilica of Sant'Ubaldo in Gubbio in his honor, as well as at Jessup, Pennsylvania.

Our Lady of Graces or St Mary of Graces is a devotion to the Virgin Mary in the Roman Catholic Church. Churches with this dedication often owe their foundation to thankfulness for graces received from the Virgin Mary, and are particularly numerous in Italy, India, Australia, United States, France and the Italian-speaking region of Switzerland.
Saint Fortunatus was a 6th-century bishop of Todi. According to tradition, he defended Todi during a Gothic siege. He is the patron saint of Todi. He is praised by Gregory the Great, who calls him a man of great virtue who took great care in attending to the sick. Gregory, who was born around the time that Fortunatus died, was greatly interested in Fortunatus' life. Gregory writes that "a certain poor old man was brought to me –because I always love to talk with such men- of whom I inquired his country, and hearing that he was of the city of Todi, I asked him whether he knew Bishop Fortunatus. He said he knew him very well. 'Then I beseech you,' said I, 'tell me whether you know of any miracles that he did, and, since I am very desirous to know, explained to me what manner of man he was.'"
Saint Fortunatus of Casei is venerated as a saint by the Catholic Church. Tradition makes him a member of the Theban Legion, and thus martyred at Agaunum. However, his relics were situated in the catacombs of Saint Callixtus in Rome until 1746, when Cardinal Guadagni, Roman vicar to Benedict XIV, re-exhumed and displayed Fortunatus’ relics in the collegiate church of Santa Maria in Via Lata in Rome. It is unclear how the relics of Fortunatus reached Rome from the saint’s supposed place of death in the Swiss Alps.
Saint Crispoldus is venerated as a 1st-century Christian martyr. He is the patron saint of Bettona, in Umbria, and said to have been the first bishop of that city, although the dioceses of Nocera and Foligno also include his name in episcopal lists.
Blessed Giacomo Bianconi was an Italian Roman Catholic priest and a professed member of the Order of Preachers. Bianconi - who hailed from Umbria - joined the order in his adolescence and dedicated his pastoral career to his flock and on one notable occasion aided refugees when Frederick II sacked the area in 1248. He also combatted heresies and managed to convert one of their chief propagators while also distinguishing himself through his life of extreme poorness that went past the Dominican standards.
Blessed Andrea Caccioli was an Italian Roman Catholic priest and a professed member from the Order of Friars Minor. He became the first priest to enter the Franciscans and served as one of the disciples of Saint Francis of Assisi himself - the priest was at his deathbed and attended his canonization. The friar preached across Italian cities such as Rome and Padua as well as in France and he became noted for miracles performed during his lifetime.
















