
Until independence in 1975, São Tomé and Príncipe had few ties abroad except those that passed through Portugal. Following independence, the new government sought to expand its diplomatic relationships. A common language, tradition, and colonial legacy have led to close collaboration between São Tomé and other ex-Portuguese colonies in Africa, particularly Angola. São Toméan relations with other African countries in the region, such as Gabon and the Republic of the Congo, are also good. In December 2000, São Tomé signed the African Union treaty; it was later ratified by the National Assembly.

The Community of Portuguese Language Countries, also known as the Lusophone Community, is an international organization and political association of Lusophone nations across five continents, where Portuguese is an official language. The CPLP operates as a privileged, multilateral forum for the mutual cooperation of the governments, economies, non-governmental organizations, and peoples of the Lusofonia. The CPLP consists of 9 member states and 33 associate observers, located in Europe, South America, Asia, Africa and Oceania, totaling 38 countries and 4 organizations.

Banco Nacional Ultramarino is a Macau banking and financial services corporation. It was historically a Portuguese bank with operations throughout the world, especially in Portugal's former overseas provinces. It ceased existence as an independent legal entity in Portugal following its merger in 2001 with Caixa Geral de Depósitos, the government-owned savings bank.

The Ministry of Commerce (MOFCOM) is a executive department of the State Council of the People's Republic of China that is responsible for formulating policy on foreign trade, export and import regulations, foreign direct investments, consumer protection, market competition and negotiating bilateral and multilateral trade agreements. it is the 20th-ranking department of the State Council. The current minister is Wang Wentao.

Portuguese is spoken in a number of African countries and is the official language in six African countries: Angola, Cape Verde, Equatorial Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Mozambique and São Tomé and Príncipe. There are Portuguese-speaking communities in most countries of Southern Africa, a mixture of Portuguese settlers and Angolans and Mozambicans who left their countries during the civil wars. A rough estimate has it that there are about 14 million people who use Portuguese as their sole mother tongue across Africa, but depending on the criteria applied, the number might be considerably higher, since many Africans speak Portuguese as a second language, in countries like Angola and Mozambique, where Portuguese is an official language, but also in countries like South Africa and Senegal, thanks to migrants coming from Portuguese-speaking countries. Some statistics claim that there are over 60 million Portuguese speakers in the continent.

Under the Basic Law, Macau's diplomatic relations and defence are the responsibility of the central government of China. Except diplomatic relations and defence, nonetheless, Macau has retained considerable autonomy in all aspects, including economic and commercial relations, customs control.
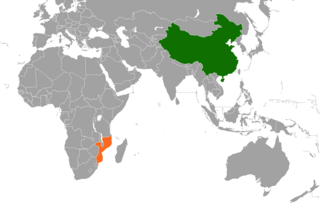
China–Mozambique relations date back to the 1960s, when China began to support the struggle of Mozambique's Marxist-oriented FRELIMO party against Portuguese colonialism. Diplomatic relations were formally established on 25 June 1975, soon after Mozambique gained independence from Portugal. In November 2006, Mozambique became the thirteenth African country to be added to China's official list of tourism destinations.

São Tomé and Príncipe, officially the Democratic Republic of São Tomé and Príncipe, is an island country in the Gulf of Guinea, off the western equatorial coast of Central Africa. It consists of two archipelagos around the two main islands of São Tomé and Príncipe, about 150 km (93.21 mi) apart and about 250 and 225 km off the northwestern coast of Gabon. With a population of 201,800, São Tomé and Príncipe is the second-smallest and second-least populous African sovereign state after Seychelles.
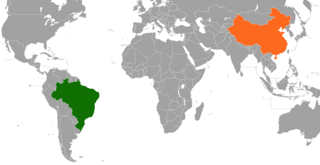
Brazil–China relations are the current and historical relationship between Brazil and China. Relations between Brazil and China began in the early nineteenth century and continued until 1949, when they were disrupted by the creation of the People's Republic of China (PRC). Diplomatic relations between the PRC and Brazil officially began in 1974 with agreement on the establishment and operation of Brazil's embassy in Beijing and China's embassy in Brasília. Since then, bilateral ties have developed mostly based on non-interference, equality, and mutual benefit (win-win).

Cape Verde–People's Republic of China relations refers to the current and historical relationship between the People's Republic of China and Cape Verde. The two states established bilateral relations on April 25, 1976, shortly after Cape Verde gained independence from the Portuguese Empire. Cape Verde is an adherent to PR China's One China Policy. In the mid-1990s, a number of Chinese capitalists began investing in the island nation and relations grew during the 2000s as a result.

China-East Timor relations were established shortly following East Timor's independence on May 20, 2002. However, China had established a representative office in Dili in 2000, when it was still under United Nations administration.

People's Republic of China – Guinea-Bissau relations refers to the current and historical relationship between the People's Republic of China (PRC) and Guinea-Bissau. Relations were established in March 1974, several months before Guinea-Bissau's September 1974 independence. From 1990 to 1998, Guinea-Bissau maintained diplomatic relations with the Republic of China (Taiwan) rather than with the People's Republic. Relations were reestablished in 1998 and maintained since.

Portugal–São Tomé and Príncipe relations refers to the diplomatic relations between the Portuguese Republic and São Tomé and Príncipe. Both nations are members of the Community of Portuguese Language Countries and the United Nations.

Visitors to São Tomé and Príncipe must obtain a visa online or from one of the diplomatic missions of São Tomé and Príncipe prior to arrival unless they come from one of the visa exempt countries.
The Taipei Economic and Cultural Centre; represents the interests of Taiwan in Portugal in the absence of formal diplomatic relations, functioning as a de facto embassy.

India–São Tomé and Príncipe relations refers to the international relations that exist between India and São Tomé and Príncipe (STP). India has an embassy in São Tomé. STP maintains an Honorary Consul in New Delhi.

The People's Republic of China (PRC) and São Tomé and Príncipe are both members of the United Nations.
The Belt and Road Forum for International Cooperation is an international political and economic forum of the Belt and Road Initiative.
The China–Arab States Cooperation Forum is a formal dialogue initiative between China and the Arab League established in 2004. It serves as the primary multilateral coordination mechanism between China and the Arab states.














