Related Research Articles

The Circus Maximus is an ancient Roman chariot-racing stadium and mass entertainment venue in Rome, Italy. In the valley between the Aventine and Palatine hills, it was the first and largest stadium in ancient Rome and its later Empire. It measured 621 m (2,037 ft) in length and 118 m (387 ft) in width and could accommodate over 150,000 spectators. In its fully developed form, it became the model for circuses throughout the Roman Empire. The site is now a public park.

Proserpina or Proserpine is an ancient Roman goddess whose cult, myths and mysteries were combined from those of Libera, an early Roman goddess of wine. In Greek she is known as Persephone and her mother is Demeter, goddesses of grain and agriculture. The originally Roman goddess Libera was daughter of the agricultural goddess Ceres and wife to Liber, god of wine and freedom. In 204 BCE, a new "Greek-style" cult to Ceres and Proserpina as "Mother and Maiden" was imported from southern Italy, along with Greek priestesses to serve it, and was installed in Libera and Ceres' temple on Rome's Aventine Hill. The new cult and its priesthood were actively promoted by Rome's religious authorities as morally desirable for respectable Roman women, and may have partly subsumed the temple's older, native cult to Ceres, Liber and Libera; but the new rites seem to have functioned alongside the old, rather than replaced them.

In ancient Roman religion, Ceres was a goddess of agriculture, grain crops, fertility and motherly relationships. She was originally the central deity in Rome's so-called plebeian or Aventine Triad, then was paired with her daughter Proserpina in what Romans described as "the Greek rites of Ceres". Her seven-day April festival of Cerealia included the popular Ludi Ceriales. She was also honoured in the May lustratio of the fields at the Ambarvalia festival, at harvest-time, and during Roman marriages and funeral rites. She is usually depicted as a mature woman.

In ancient Roman religion and mythology, Liber, also known as Liber Pater, was a god of viticulture and wine, fertility and freedom. He was a patron deity of Rome's plebeians and was part of their Aventine Triad. His festival of Liberalia became associated with free speech and the rights attached to coming of age. His cult and functions were increasingly associated with Romanised forms of the Greek Dionysus/Bacchus, whose mythology he came to share.

Bona Dea was a goddess in ancient Roman religion. She was associated with chastity and fertility in Roman women, healing, and the protection of the state and people of Rome. According to Roman literary sources, she was brought from Magna Graecia at some time during the early or middle Republic, and was given her own state cult on the Aventine Hill.

The Roman Forum, also known by its Latin name Forum Romanum, is a rectangular forum (plaza) surrounded by the ruins of several important ancient government buildings at the center of the city of Rome. Citizens of the ancient city referred to this space, originally a marketplace, as the Forum Magnum, or simply the Forum.

The Aventine Hill is one of the Seven Hills on which ancient Rome was built. It belongs to Ripa, the modern twelfth rione, or ward, of Rome.

The decemviri or decemvirs were any of several 10-man commissions established by the Roman Republic.
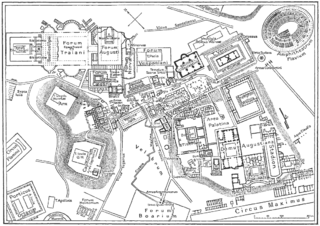
Vicus Tuscus was an ancient street in the city of Rome, running southwest out of the Roman Forum between the Basilica Julia and the Temple of Castor and Pollux towards the Forum Boarium and Circus Maximus via the west side of the Palatine Hill and Velabrum.

Festivals in ancient Rome were a very important part of Roman religious life during both the Republican and Imperial eras, and one of the primary features of the Roman calendar. Feriae were either public (publicae) or private (privatae). State holidays were celebrated by the Roman people and received public funding. Games (ludi), such as the Ludi Apollinares, were not technically feriae, but the days on which they were celebrated were dies festi, holidays in the modern sense of days off work. Although feriae were paid for by the state, ludi were often funded by wealthy individuals. Feriae privatae were holidays celebrated in honor of private individuals or by families. This article deals only with public holidays, including rites celebrated by the state priests of Rome at temples, as well as celebrations by neighborhoods, families, and friends held simultaneously throughout Rome.

The Forum Boarium was the cattle forum venalium of ancient Rome. It was located on a level piece of land near the Tiber between the Capitoline, the Palatine and Aventine hills. As the site of the original docks of Rome, the Forum Boarium experienced intense commercial activity.
The Pons Sublicius is the earliest known bridge of ancient Rome, spanning the Tiber River near the Forum Boarium downstream from the Tiber Island, near the foot of the Aventine Hill. According to tradition, its construction was ordered by Ancus Marcius around 642 BC, but this date is approximate because there is no ancient record of its construction. Marcius wished to connect the newly fortified Janiculum Hill on the Etruscan side to the rest of Rome, augmenting the ferry that was there. The bridge was part of public works projects that included building a port at Ostia, at the time the location of worked salt deposits.
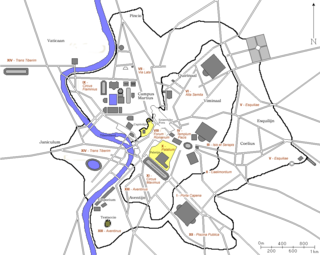
In 7 BC, Augustus divided the city of Rome into 14 administrative regions. These replaced the four regiones — or "quarters" — traditionally attributed to Servius Tullius, sixth king of Rome. They were further divided into official neighborhoods.
Secessio plebis was an informal exercise of power by Rome's plebeian citizens, similar in concept to the general strike. During the secessio plebis, the plebs would abandon the city en masse in a protest emigration and leave the patrician order to themselves. Therefore, a secessio meant that all shops and workshops would shut down and commercial transactions would largely cease. This was an effective strategy in the Conflict of the Orders due to strength in numbers; plebeian citizens made up the vast majority of Rome's populace and produced most of its food and resources, while a patrician citizen was a member of the minority upper class, the equivalent of the landed gentry of later times. Authors report different numbers for how many secessions there were. Cary & Scullard state there were five between 494 BC and 287 BC.

The Porta Trigemina was one of the main gates in the ancient 4th century Servian Wall of Rome, Italy. The gate no longer exists, but it is frequently mentioned by ancient authors as standing between the north end of the Aventine Hill and the Tiber River, placing it near the southeastern end of the Forum Boarium. The Clivus Publicius descended from the Aventine to the Porta Trigemina.

The Via Ostiensis was an important road in ancient Rome. It ran west 30 kilometres (19 mi) from the city of Rome to its important sea port of Ostia Antica, from which it took its name. The road began near the Forum Boarium, ran between the Aventine Hill and the Tiber River along its left (eastern) bank, and left the city's Servian Walls through the Porta Trigemina. When the later Aurelian Walls were built, the road left the city through the Porta Ostiensis. In the late Roman Empire, trade suffered under an economic crisis, and Ostia declined as an important port. With the accompanying growth of importance of the Via Portuensis from the time of Constantine onwards, that of the Via Ostiensis correspondingly decreased. Modern Via Ostiense, following a similar path, is the main connection of Rome to Ostia together with the Via del Mare. On its way to Ostia, the road passes by the important basilica of Saint Paul Outside the Walls.

Murus Romuli is the name given to a wall built to protect the Palatine Hill, the centermost of the Seven Hills of Rome, in one of the oldest parts of the city of Rome. Ancient tradition holds that this wall was built by Romulus.
During the Middle Ages, Rome was divided into a number of administrative regions, usually numbering between twelve and fourteen, which changed over time.

Aventine is the second studio album by Danish singer-songwriter Agnes Obel, released on 30 September 2013 by PIAS Recordings. The album received positive reviews from music critics. It was also a commercial success, charting inside the top 40 of the charts in nine countries.
References
- ↑ John Henry Parker (1876). The Forum Romanum: and the Via Sacra. James Parker and Company. pp. 36–.