Related Research Articles

The Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) is a Eurasian political, economic, international security and defence organization established by China and Russia in 2001. It is the world's largest regional organization in terms of geographic scope and population, covering approximately 80% of the area of Eurasia and 40% of the world population. As of 2023, its combined GDP based on PPP was around 32% of the world's total.

A major non-NATO ally (MNNA) is a designation given by the United States government to countries that have strategic working relationships with the U.S. Armed Forces while not being members of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). While the status does not automatically constitute a mutual defense pact with the United States, it does confer a variety of military and financial advantages that are otherwise unobtainable by non-NATO countries. There are currently 20 major non-NATO allies across four continents: 11 in Asia, 4 in Africa, 3 in South America, and 2 in Oceania.

Relations between India and the United States date back to India's independence movement and have continued well after independence from the United Kingdom in 1947. Currently, India and the United States enjoy close relations and have deepened collaboration on issues such as counterterrorism and countering Chinese influence in the Indo-Pacific.

The United States has friendly relations with the Republic of Maldives since the nation's independence from the United Kingdom in 1966. The U.S. ambassador and some Embassy staff in Sri Lanka are accredited to the Maldives and make periodic visits. On the other hand, Maldives is represented in U.S. through its Permanent Mission to the UN at New York City.

India has enjoyed close bilateral ties with the Russian Federation since the independence of India in 1947. During the Cold War, India and the USSR formed a strong and strategic relationship; this diplomatic unity was further strengthened with both nations’ shared military ideals, as well as their overall economic policies. After the dissolution of the Soviet Union, Russia kept the same close ties to India; in international terms, both nations share a special relationship. Russia and India, both, consider their mutual affinity to be a "special and privileged strategic partnership". Their governments support the creation of a multipolar world order in which both nations are "poles".

Kenneth Ian Juster is a veteran American diplomat, who served as the United States Ambassador to India from 2017 to 2021. He is currently senior counselor at the global law firm Freshfields Bruckhaus Deringer, senior adviser at the institutional investor CDPQ, strategic adviser at the software company Salesforce, and distinguished fellow at the Council on Foreign Relations.

India and Maldives are neighbours sharing a maritime border. India continues to contribute to maintaining security as well as providing financial aid on the island nation.

India-Singapore relations, also known as the Indo-Singaporeanrelations, are the bilateral relations between India and Singapore. Relations between the two countries have traditionally been strong and friendly, with the two nations enjoying extensive cultural and commercial relations. India and Singapore have signed the Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) and strategic-relationship agreement in order to increase trade, investments and economic cooperation, and expanded bilateral cooperation on maritime security, training forces, joint naval exercises, developing military technology and fighting terrorism.

Indo-Polish relations are the bilateral relations between the Republic of Poland and the Republic of India. Historically, relations have generally been friendly, characterised by understanding and cooperation on an international front.
The Australian Defence Satellite Communications Station (ADSCS), an Earth station in Australia is located at Kojarena 30 km (19 mi) east of Geraldton, Western Australia. The ADSCS is part of the US signals intelligence and analysis network ECHELON.
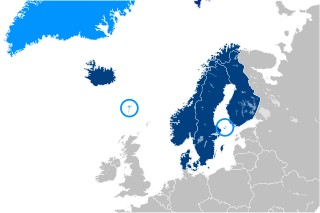
The Nordic Defence Cooperation (NORDEFCO) is a collaboration among the Nordic countries in the area of defence. Its five members are Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden.
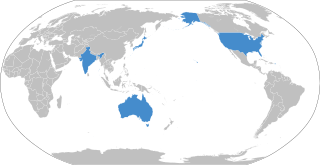
The Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (QSD), commonly known as the Quad, is a strategic security dialogue between Australia, India, Japan, and the United States that is maintained by talks between member countries. The dialogue was initiated in 2007 by Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe, with the support of Australian Prime Minister John Howard, Indian Prime Minister Manmohan Singh and U.S. Vice President Dick Cheney. The dialogue was paralleled by joint military exercises of an unprecedented scale, titled Exercise Malabar. The diplomatic and military arrangement was widely viewed as a response to increased Chinese economic and military power.

Subrahmanyam Jaishankar is an Indian diplomat and politician, who is the thirtieth Minister of External Affairs of the Government of India since 31 May 2019. He is a member of the Bharatiya Janata Party and has been a Member of Parliament in the Rajya Sabha since 5 July 2019. He previously served as the Foreign Secretary from January 2015 to January 2018. He is the second diplomat to be appointed India's External Affairs minister, after Natwar Singh.

The military budget or defence budget of India is the portion of the overall budget of Union budget of India that is allocated for the funding of the Indian Armed Forces. The military budget finances employee salaries and training costs, maintenance of equipment and facilities, support of new or ongoing operations, and development and procurement of new technologies, weapons, equipment, and vehicles.
The Field Artillery Rationalisation Plan is a procurement and development plan of the Indian Army. The programme was drafted in 1999 in the aftermath of the Kargil war, emboldened by the success of the 155 mm Bofors guns in its inventory. The programme was slated to replace the weapons of 169 artillery regiments with modern weapon systems, predominantly of 155mm calibre. The procurement involves direct import, manufacture under license, as well as inhouse development of artillery weapon systems.

The 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue is a diplomatic summit that has been held every year since 2018 initially between the Minister of External Affairs or Foreign Minister, and Defence Minister of India with the Secretary of State and Secretary of Defense of the United States to discuss and work on common issues of concern to improve and strengthen India–United States relations.
References
- ↑ Jain 2018, p. 114–116.
- ↑ Philip, Snehesh Alex (2020-10-27). "The 3 foundational agreements with US and what they mean for India's military growth". ThePrint. Retrieved 2020-10-28.
- ↑ Roy, Shubhajit (2020-10-28). "BECA — and importance of three foundational pacts of India-US military cooperation". The Indian Express. Retrieved 2020-10-28.
- ↑ Ragi, Sangit K.; Sondhi, Sunil; Pathak, Vidhan (2017-07-28). Imagining India as a Global Power: Prospects and Challenges. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-351-60915-9.
- ↑ Jha, Lalit K (13 May 2015). "Foundational Agreements Facilitate Better Defence Ties: US". Outlook India. Retrieved 2020-10-28.
- ↑ Editorial (2020-10-28). "Back to Future". The Indian Express. Retrieved 2020-10-28.
- ↑ Joshi, Manoj (28 October 2020). "Building upon the American connection". ORF. Retrieved 2020-10-28.
- ↑ "Watch | India and U.S. sign BECA". The Hindu. 2020-10-28. ISSN 0971-751X . Retrieved 2020-10-28.
- ↑ Tomar, Dr Ravi (25 June 2002). "India-US Relations in a Changing Strategic Environment". www.aph.gov.au. Retrieved 2020-10-28.
- ↑ Philip, Snehesh Alex (2024-08-23). "SOSA done, India & US now aim for RDP. A look at these two critical defence agreements". ThePrint. Retrieved 2024-08-24.
Bibliography
- Jain, Bhupesh (2018). "LSA, CISMOA, and BECA: The Future of US-India Defence Ties" (PDF). CLAWS Journal. Summer 2018: 114–126.