External links
- Foundry Discovery Protocol (FDP) Archived 2015-02-07 at the Wayback Machine , Multi-Service IronWare Feature and RFC Support Matrix, product documentation by Brocade Communications Systems, January 24, 2014
The Foundry Discovery Protocol (FDP) is a proprietary data link layer protocol. It was developed by Foundry Networks.
Although Foundry Networks was acquired by Brocade Communications Systems, the protocol is still supported.
The Internet protocol suite, commonly known as TCP/IP, is a framework for organizing the set of communication protocols used in the Internet and similar computer networks according to functional criteria. The foundational protocols in the suite are the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), the User Datagram Protocol (UDP), and the Internet Protocol (IP). Early versions of this networking model were known as the Department of Defense (DoD) model because the research and development were funded by the United States Department of Defense through DARPA.

Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol is an open communication protocol designed for instant messaging (IM), presence information, and contact list maintenance. Based on XML, it enables the near-real-time exchange of structured data between two or more network entities. Designed to be extensible, the protocol offers a multitude of applications beyond traditional IM in the broader realm of message-oriented middleware, including signalling for VoIP, video, file transfer, gaming and other uses.
FDP may refer to:
Zero-configuration networking (zeroconf) is a set of technologies that automatically creates a usable computer network based on the Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP) when computers or network peripherals are interconnected. It does not require manual operator intervention or special configuration servers. Without zeroconf, a network administrator must set up network services, such as Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Domain Name System (DNS), or configure each computer's network settings manually.
Foundry Networks, Inc. was a networking hardware vendor selling high-end Ethernet switches and routers. The company was acquired by Brocade Communications Systems on December 18, 2008.
Brocade is an American technology company specializing in storage networking products, now a subsidiary of Broadcom Inc. The company is known for its Fibre Channel storage networking products and technology. Prior to the acquisition, the company expanded into adjacent markets including a wide range of IP/Ethernet hardware and software products. Offerings included routers and network switches for data center, campus and carrier environments, IP storage network fabrics; Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) and software-defined networking (SDN) markets such as a commercial edition of the OpenDaylight Project controller; and network management software that spans physical and virtual devices.
The Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) is a vendor-neutral link layer protocol used by network devices for advertising their identity, capabilities, and neighbors on a local area network based on IEEE 802 technology, principally wired Ethernet. The protocol is formally referred to by the IEEE as Station and Media Access Control Connectivity Discovery specified in IEEE 802.1AB with additional support in IEEE 802.3 section 6 clause 79.

Zeus Technology, Ltd. was a software company founded in 1995 and based in Cambridge, England, known for its web server. In July 2011, Zeus Technology was acquired by Riverbed Technology. In March 2015, Riverbed Technology sold the SteelApp business unit to Brocade Communications Systems. In June 2017, Brocade Communications Systems sold the vADC business unit to Pulse Secure. In December 2020 Pulse Secure, including the vADC business unit, was acquired by Ivanti.
Vyatta is a software-based virtual router, virtual firewall and VPN products for Internet Protocol networks. A free download of Vyatta has been available since March 2006. The system is a specialized Debian-based Linux distribution with networking applications such as Quagga, OpenVPN, and many others. A standardized management console, similar to Juniper JUNOS or Cisco IOS, in addition to a web-based GUI and traditional Linux system commands, provides configuration of the system and applications. In recent versions of Vyatta, web-based management interface is supplied only in the subscription edition. However, all functionality is available through KVM, serial console or SSH/telnet protocols. The software runs on standard x86-64 servers.

A core router is a router designed to operate in the Internet backbone, or core. To fulfill this role, a router must be able to support multiple telecommunications interfaces of the highest speed in use in the core Internet and must be able to forward IP packets at full speed on all of them. It must also support the routing protocols being used in the core. A core router is distinct from an edge router: edge routers sit at the edge of a backbone network and connect to core routers.
Windows Rally is a set of technologies from Microsoft intended to simplify the setup and maintenance of wired and wireless network-connected devices. They aim to increase reliability and security of connectivity for users who connect the devices to the Internet or to computers running Microsoft Windows. These technologies provide control of network quality of service (QoS) and diagnostics for data sharing, communications, and entertainment. Windows Rally technologies provide provisioning for the following devices:
The Virtual Switch Redundancy Protocol (VSRP) is a proprietary network resilience protocol developed by Foundry Networks and currently being sold in products manufactured by both Brocade Communications Systems and Hewlett Packard. The protocol differs from many others in use as it combines Layer 2 and Layer 3 resilience – effectively doing the jobs of both Spanning tree protocol and the Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol at the same time. Whilst the restrictions on the physical topologies able to make use of VSRP mean that it is less flexible than STP and VRRP, it does significantly improve on the failover times provided by either of those protocols.
The Metro Ring Protocol (MRP) is a Layer 2 resilience protocol developed by Foundry Networks and currently being delivered in products manufactured by Brocade Communications Systems and Hewlett Packard. The protocol quite tightly specifies a topology in which layer 2 devices, usually at the core of a larger network, are configured and as such is able to achieve much faster failover times than other Layer 2 protocols such as Spanning Tree.
The Nortel Discovery Protocol (NDP) is a data link layer network protocol for discovery of Nortel networking devices and certain products from Avaya and Ciena. The device and topology information may be graphically displayed network management software.
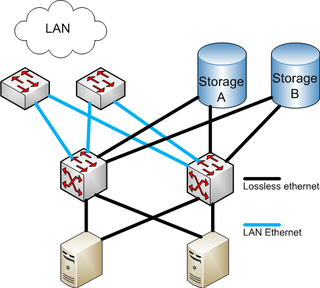
Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) is a computer network technology that encapsulates Fibre Channel frames over Ethernet networks. This allows Fibre Channel to use 10 Gigabit Ethernet networks while preserving the Fibre Channel protocol. The specification was part of the International Committee for Information Technology Standards T11 FC-BB-5 standard published in 2009.

A10 Networks is an American public company specializing in the manufacturing of application delivery controllers. Founded in 2004 by Lee Chen, co-founder of Foundry Networks, A10 originally serviced just the identity management market with its line of ID Series products. In early 2007, they added bandwidth management appliances. The company had its initial public offering on March 21, 2014, raising $187.5 million.
Data center bridging (DCB) is a set of enhancements to the Ethernet local area network communication protocol for use in data center environments, in particular for use with clustering and storage area networks.
OpenFlow is a communications protocol that gives access to the forwarding plane of a network switch or router over the network.
TRILL is an Internet Standard implemented by devices called TRILL switches. TRILL combines techniques from bridging and routing, and is the application of link-state routing to the VLAN-aware customer-bridging problem. Routing bridges (RBridges) are compatible with and can incrementally replace previous IEEE 802.1 customer bridges. TRILL Switches are also compatible with IPv4 and IPv6, routers and end systems. They are invisible to current IP routers, and like conventional routers, RBridges terminate the broadcast, unknown-unicast and multicast traffic of DIX Ethernet and the frames of IEEE 802.2 LLC including the bridge protocol data units of the Spanning Tree Protocol.