
The Rubik's Cube is a 3D combination puzzle invented in 1974 by Hungarian sculptor and professor of architecture Ernő Rubik. Originally called the Magic Cube, the puzzle was licensed by Rubik to be sold by Pentangle Puzzles in the UK in 1978, and then by Ideal Toy Corp in 1980 via businessman Tibor Laczi and Seven Towns founder Tom Kremer. The cube was released internationally in 1980 and became one of the most recognized icons in popular culture. It won the 1980 German Game of the Year special award for Best Puzzle. As of January 2024, around 500 million cubes had been sold worldwide, making it the world's bestselling puzzle game and bestselling toy. The Rubik's Cube was inducted into the US National Toy Hall of Fame in 2014.
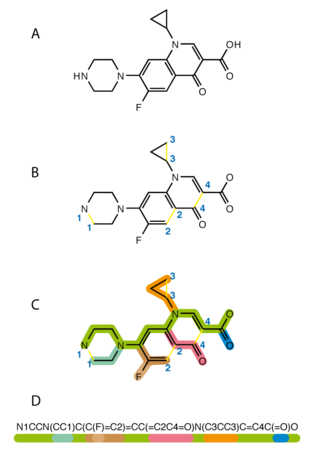
The simplified molecular-input line-entry system (SMILES) is a specification in the form of a line notation for describing the structure of chemical species using short ASCII strings. SMILES strings can be imported by most molecule editors for conversion back into two-dimensional drawings or three-dimensional models of the molecules.

A polyomino is a plane geometric figure formed by joining one or more equal squares edge to edge. It is a polyform whose cells are squares. It may be regarded as a finite subset of the regular square tiling.

In four-dimensional geometry, the 24-cell is the convex regular 4-polytope (four-dimensional analogue of a Platonic solid) with Schläfli symbol {3,4,3}. It is also called C24, or the icositetrachoron, octaplex (short for "octahedral complex"), icosatetrahedroid, octacube, hyper-diamond or polyoctahedron, being constructed of octahedral cells.

The Rubik's Revenge is a 4×4×4 version of the Rubik's Cube. It was released in 1981. Invented by Péter Sebestény, the cube was nearly called the Sebestény Cube until a somewhat last-minute decision changed the puzzle's name to attract fans of the original Rubik's Cube. Unlike the original puzzle, it has no fixed faces: the center faces are free to move to different positions.

In computer science, a state space is a discrete space representing the set of all possible configurations of a "system". It is a useful abstraction for reasoning about the behavior of a given system and is widely used in the fields of artificial intelligence and game theory.
In computer science, tree traversal is a form of graph traversal and refers to the process of visiting each node in a tree data structure, exactly once. Such traversals are classified by the order in which the nodes are visited. The following algorithms are described for a binary tree, but they may be generalized to other trees as well.

The Pocket Cube is a 2×2×2 combination puzzle invented in 1970 by American puzzle designer Larry D. Nichols. The cube consists of 8 pieces, all corners.

The Megaminx or Mégaminx is a dodecahedron-shaped puzzle similar to the Rubik's Cube. It has a total of 50 movable pieces to rearrange, compared to the 20 movable pieces of the Rubik's Cube.

Nurikabe is a binary determination puzzle named for Nurikabe, an invisible wall in Japanese folklore that blocks roads and delays foot travel. Nurikabe was apparently invented and named by the publisher Nikoli; other names for the puzzle include Cell Structure and Islands in the Stream.
Induction puzzles are logic puzzles, which are examples of multi-agent reasoning, where the solution evolves along with the principle of induction.

Hitori is a type of logic puzzle published by Nikoli.

Slitherlink is a logic puzzle developed by publisher Nikoli.
Light Up, also called Akari is a binary-determination logic puzzle published by Nikoli. As of 2011, three books consisting entirely of Light Up puzzles have been published by Nikoli.

In mathematics, and more specifically in graph theory, a directed graph is a graph that is made up of a set of vertices connected by directed edges, often called arcs.
In graph theory, a cop-win graph is an undirected graph on which the pursuer (cop) can always win a pursuit–evasion game against a robber, with the players taking alternating turns in which they can choose to move along an edge of a graph or stay put, until the cop lands on the robber's vertex. Finite cop-win graphs are also called dismantlable graphs or constructible graphs, because they can be dismantled by repeatedly removing a dominated vertex or constructed by repeatedly adding such a vertex. The cop-win graphs can be recognized in polynomial time by a greedy algorithm that constructs a dismantling order. They include the chordal graphs, and the graphs that contain a universal vertex.

The Challenge: Invasion of the Champions is the 29th season of the MTV reality game show, The Challenge. The new individual format was filmed in Krabi, Thailand during October and November 2016, and features alumni from The Real World, Road Rules, The Challenge, and Are You the One? competing.

The Challenge: Champs vs. Pros is a special mini-series of MTV's long-running reality game show, The Challenge. In the six-week event, ten Challenge greats competed against ten professional athletes. The series premiered on Tuesday, May 16, 2017, and concluded on June 20, 2017. The series was hosted by NFL wide receiver Victor Cruz. Contestants competed to win $50,000 to donate to the charity of their choice. In 2017 the series format was changed to include celebrities and was renamed Champs vs. Stars.
The Challenge: War of the Worlds is the thirty-third season of the MTV reality competition series The Challenge. This season featured alumni from The Real World, The Challenge, Are You the One?, The Bachelor Canada, The Bachelorette, Big Brother, Celebrity Big Brother UK, Love Island UK, Survivor Turkey, American Ninja Warrior, Party Down South, Geordie Shore, Ex on the Beach, Telemundo, and Floribama Shore competing for a share of a $1 million prize. The season had a "Basic Training" launch special on January 30, 2019, and premiered on February 6, 2019 on MTV.

The first season of The Challenge: USA premiered on CBS on July 6, 2022. The season featured twenty-eight cast members from Big Brother, Love Island, Survivor, and The Amazing Race competing for a monetary prize.
















