Related Research Articles

Ion implantation is a low-temperature process by which ions of one element are accelerated into a solid target, thereby changing the physical, chemical, or electrical properties of the target. Ion implantation is used in semiconductor device fabrication and in metal finishing, as well as in materials science research. The ions can alter the elemental composition of the target if they stop and remain in the target. Ion implantation also causes chemical and physical changes when the ions impinge on the target at high energy. The crystal structure of the target can be damaged or even destroyed by the energetic collision cascades, and ions of sufficiently high energy can cause nuclear transmutation.
Isotope separation is the process of concentrating specific isotopes of a chemical element by removing other isotopes. The use of the nuclides produced is varied. The largest variety is used in research. By tonnage, separating natural uranium into enriched uranium and depleted uranium is the largest application. In the following text, mainly uranium enrichment is considered. This process is crucial in the manufacture of uranium fuel for nuclear power plants and is also required for the creation of uranium-based nuclear weapons. Plutonium-based weapons use plutonium produced in a nuclear reactor, which must be operated in such a way as to produce plutonium already of suitable isotopic mix or grade.

A cyclotron is a type of particle accelerator invented by Ernest Lawrence in 1929–1930 at the University of California, Berkeley, and patented in 1932. A cyclotron accelerates charged particles outwards from the center of a flat cylindrical vacuum chamber along a spiral path. The particles are held to a spiral trajectory by a static magnetic field and accelerated by a rapidly varying electric field. Lawrence was awarded the 1939 Nobel Prize in Physics for this invention.

The GSI Helmholtz Centre for Heavy Ion Research is a federally and state co-funded heavy ion (Schwerion) research center in the Wixhausen suburb of Darmstadt, Germany. It was founded in 1969 as the Society for Heavy Ion Research, abbreviated GSI, to conduct research on and with heavy-ion accelerators. It is the only major user research center in the State of Hesse.

A linear particle accelerator is a type of particle accelerator that accelerates charged subatomic particles or ions to a high speed by subjecting them to a series of oscillating electric potentials along a linear beamline. The principles for such machines were proposed by Gustav Ising in 1924, while the first machine that worked was constructed by Rolf Widerøe in 1928 at the RWTH Aachen University. Linacs have many applications: they generate X-rays and high energy electrons for medicinal purposes in radiation therapy, serve as particle injectors for higher-energy accelerators, and are used directly to achieve the highest kinetic energy for light particles for particle physics.

Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a mass spectrum, a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures.
FRS may also refer to:

Neutron generators are neutron source devices which contain compact linear particle accelerators and that produce neutrons by fusing isotopes of hydrogen together. The fusion reactions take place in these devices by accelerating either deuterium, tritium, or a mixture of these two isotopes into a metal hydride target which also contains deuterium, tritium or a mixture of these isotopes. Fusion of deuterium atoms results in the formation of a helium-3 ion and a neutron with a kinetic energy of approximately 2.5 MeV. Fusion of a deuterium and a tritium atom results in the formation of a helium-4 ion and a neutron with a kinetic energy of approximately 14.1 MeV. Neutron generators have applications in medicine, security, and materials analysis.

Spallation is a process in which fragments of material (spall) are ejected from a body due to impact or stress. In the context of impact mechanics it describes ejection of material from a target during impact by a projectile. In planetary physics, spallation describes meteoritic impacts on a planetary surface and the effects of stellar winds and cosmic rays on planetary atmospheres and surfaces. In the context of mining or geology, spallation can refer to pieces of rock breaking off a rock face due to the internal stresses in the rock; it commonly occurs on mine shaft walls. In the context of metal oxidation, spallation refers to the breaking off of the oxide layer from a metal. For example, the flaking off of rust from iron. In the context of anthropology, spallation is a process used to make stone tools such as arrowheads by knapping. In nuclear physics, spallation is the process in which a heavy nucleus emits numerous nucleons as a result of being hit by a high-energy particle, thus greatly reducing its atomic weight. In industrial processes and bioprocessing the loss of tubing material due to the repeated flexing of the tubing within a peristaltic pump is termed spallation.

The ISOLDE Radioactive Ion Beam Facility, is an on-line isotope separator facility located at the centre of the CERN accelerator complex on the Franco-Swiss border. Created in 1964, the ISOLDE facility started delivering radioactive ion beams (RIBs) to users in 1967. Originally located at the Synchro-Cyclotron (SC) accelerator, the facility has been upgraded several times most notably in 1992 when the whole facility was moved to be connected to CERN's ProtonSynchroton Booster (PSB). ISOLDE is currently the longest-running facility in operation at CERN, with continuous developments of the facility and its experiments keeping ISOLDE at the forefront of science with RIBs. ISOLDE benefits a wide range of physics communities with applications covering nuclear, atomic, molecular and solid-state physics, but also biophysics and astrophysics, as well as high-precision experiments looking for physics beyond the Standard Model. The facility is operated by the ISOLDE Collaboration, comprising CERN and sixteen (mostly) European countries. As of 2019, close to 1,000 experimentalists around the world are coming to ISOLDE to perform typically 50 different experiments per year.

A sector instrument is a general term for a class of mass spectrometer that uses a static electric (E) or magnetic (B) sector or some combination of the two as a mass analyzer. Popular combinations of these sectors have been the EB, BE, three-sector BEB and four-sector EBEB (electric-magnetic-electric-magnetic) instruments. Most modern sector instruments are double-focusing instruments in that they focus the ion beams both in direction and velocity.

The Argonne Tandem Linac Accelerator System (ATLAS) is a U.S. Department of Energy scientific user facility at Argonne National Laboratory. ATLAS is the first superconducting linear accelerator (linac) for heavy ions at energies in the vicinity of the Coulomb barrier and is open to scientists from all over the world.
Electron-beam physical vapor deposition, or EBPVD, is a form of physical vapor deposition in which a target anode is bombarded with an electron beam given off by a charged tungsten filament under high vacuum. The electron beam causes atoms from the target to transform into the gaseous phase. These atoms then precipitate into solid form, coating everything in the vacuum chamber with a thin layer of the anode material.
Gas cluster ion beams (GCIB) is a technology for nano-scale modification of surfaces. It can smooth a wide variety of surface material types to within an angstrom of roughness without subsurface damage. It is also used to chemically alter surfaces through infusion or deposition.

Time-of-flight mass spectrometry (TOFMS) is a method of mass spectrometry in which an ion's mass-to-charge ratio is determined by a time of flight measurement. Ions are accelerated by an electric field of known strength. This acceleration results in an ion having the same kinetic energy as any other ion that has the same charge. The velocity of the ion depends on the mass-to-charge ratio. The time that it subsequently takes for the ion to reach a detector at a known distance is measured. This time will depend on the velocity of the ion, and therefore is a measure of its mass-to-charge ratio. From this ratio and known experimental parameters, one can identify the ion.
Photofragment ion imaging or, more generally, Product Imaging is an experimental technique for making measurements of the velocity of product molecules or particles following a chemical reaction or the photodissociation of a parent molecule. The method uses a two-dimensional detector, usually a microchannel plate, to record the arrival positions of state-selected ions created by resonantly enhanced multi-photon ionization (REMPI). The first experiment using photofragment ion imaging was performed by David W Chandler and Paul L Houston in 1987 on the phototodissociation dynamics of methyl iodide (iodomethane, CH3I).
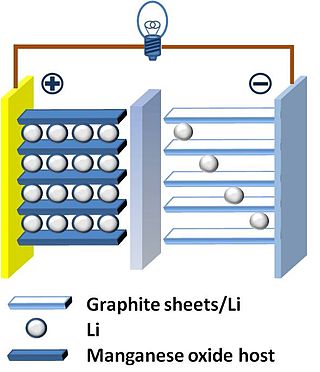
The thin-film lithium-ion battery is a form of solid-state battery. Its development is motivated by the prospect of combining the advantages of solid-state batteries with the advantages of thin-film manufacturing processes.
The program LISE++ is designed to predict the intensity and purity of radioactive ion beams (RIB) produced by In-flight separators. LISE++ also facilitates the tuning of experiments where its results can be quickly compared to on-line data. The program is constantly expanding and evolving from the feedback of its users around the world.
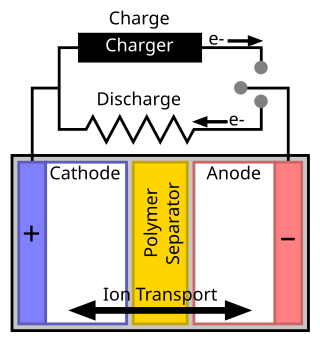
A separator is a permeable membrane placed between a battery's anode and cathode. The main function of a separator is to keep the two electrodes apart to prevent electrical short circuits while also allowing the transport of ionic charge carriers that are needed to close the circuit during the passage of current in an electrochemical cell.
Heavy ion fusion is a fusion energy concept that uses a stream of high-energy ions from a particle accelerator to rapidly heat and compress a small pellet of fusion fuel. It is a subclass of the larger inertial confinement fusion (ICF) approach, replacing the more typical laser systems with an accelerator.
References
- ↑ "NEXT GENERATION FRAGMENT SEPARATORS" (PDF). Northern Illinois University. Retrieved 2009-08-01.
- ↑ "The program LISE: a simulation of fragment separators". [{Research Gate]}. 12 June 2001.