
The first written records of the region come from Arab traders in the 9th and 10th centuries. In medieval times, the region was dominated by the Trans-Saharan trade and was ruled by the Mali Empire. In the 16th century, the region came to be ruled by the Songhai Empire. The first Europeans to visit the Gambia River were the Portuguese in the 15th century, in 1447, who attempted to settle on the river banks, but no settlement of significant size was established. Descendants of the Portuguese settlers remained until the 18th century. In the late 16th century, English merchants attempted to begin a trade with the Gambia, reporting that it was "a river of secret trade and riches concealed by the Portuguese."

The Province of Georgia was one of the Southern Colonies in colonial-era British America. In 1775 it was the last of the Thirteen Colonies to support the American Revolution.

Jekyll Island is located off the coast of the U.S. state of Georgia, in Glynn County. It is one of the Sea Islands and one of the Golden Isles of Georgia barrier islands. The island is owned by the State of Georgia and run by a self-sustaining, self-governing body.

The Battle of Bloody Marsh took place on 7 July 1742 between Spanish and British forces on St. Simons Island, part of the Province of Georgia, resulting in a victory for the British. Part of the War of Jenkins' Ear, the battle was for the British fortifications of Fort Frederica and Fort St. Simons, with the strategic goal the sea routes and inland waters they controlled. With the victory, the Province of Georgia established undisputed claim to the island. The British also won the Battle of Gully Hole Creek, which took place on the island the same day.

Ayuba Suleiman Diallo (1701–1773), also known as Job Ben Solomon, was a prominent Fulani Muslim prince from West Africa who was kidnapped and trafficked to the Americas during the Atlantic slave trade, having previously owned and sold slaves himself.
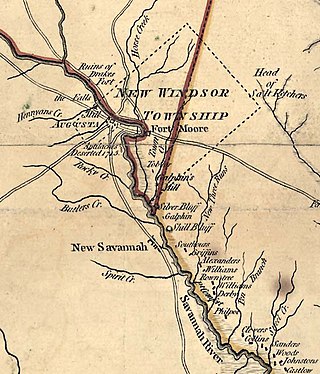
Savannah Town, South Carolina is a defunct settlement that was located in the colonial years on the Savannah River below the Fall Line in present-day Aiken County. In the 1670s the Westo had a village here, but they were displaced by the Savannah in a trade war, and it became known by 1685 as Savannah Town. The English colony had traders who did a lucrative business in dressed skins with the Savannah Shawnee. Fortified as a frontier post, the settlement developed and ferry service was established across the river. The town was gradually overtaken by its competitor of Augusta, Georgia, established in 1735 five miles upriver and closer to Indian settlements. Traders here intercepted commerce, sending it to their port of Savannah on the coast. By 1740 Savannah Town was declining, and by 1765 the village was abandoned and the fort closed.

Fort King George State Historic Site is a fort located in the U.S. state of Georgia in McIntosh County, adjacent to Darien. The fort was built in 1721 along what is now known as the Darien River and served as the southernmost outpost of the British Empire in the Americas until 1727. The fort was constructed in what was then considered part of the colony of South Carolina, but was territory later settled as Georgia. It was part of a defensive line intended to encourage settlement along the colony's southern frontier, from the Savannah River to the Altamaha River. Great Britain, France, and Spain were competing to control the American Southeast, especially the Savannah-Altamaha River region.
The city of Savannah, Georgia, the largest city and the county seat of Chatham County, Georgia, was established in 1733, and was the first colonial and state capital of Georgia. It is known as Georgia's first planned city and attracts millions of visitors, who enjoy the city's architecture and historic structures such as the birthplace of Juliette Gordon Low, the Telfair Academy of Arts and Sciences, the First African Baptist Church, Congregation Mickve Israel, and the Central of Georgia Railway roundhouse complex. Today, Savannah's downtown area is one of the largest National Historic Landmark Districts in the United States .[A]
Mary Musgrove was a leading figure in early Georgia history. She was the daughter of Edward Griffin, an English-born trader from Charles Town in the Province of Carolina, and a Muscogee Creek mother. Fluent in local Creek languages as well as English, Mary became an important intermediary between Muscogee Creek Natives and the early colonists. Musgrove carved out a life that merged both cultures, making a significant contribution to the development of colonial Georgia.
Trustee Georgia is the name of the period covering the first twenty years of Georgia history, from 1732–1752, because during that time the English Province of Georgia was governed by a board of trustees. England's King George II, for whom the colony was named, signed a charter establishing the colony and creating its governing board on July 7, 1732. His action culminated a lengthy process. Tomochichi was a Native American that resides along the Savannah River that allowed Oglethorpe to settle on the Yamacraw Bluff.

John Pine (1690–1756) was an English designer, engraver, and cartographer notable for his artistic contribution to the Augustan style and Newtonian scientific paradigm that flourished during the British Enlightenment.

Lieutenant-General James Edward Oglethorpe was a British Army officer, Tory politician and colonial administrator best known for founding the Province of Georgia in British North America. As a social reformer, he hoped to resettle Britain's "worthy poor" in the New World, initially focusing on those in debtors' prisons.
John Gordon was a Loyalist British merchant and trader of Scottish origin who lived in South Carolina for many years. He settled in Charles Town about 1760, and from 1759 to 1773 he was a major exporter of deerskins supplied by Native American hunters. Gordon also participated in the transatlantic slave trade but was not a major importer of captive Africans.
The Georgia Experiment was the colonial-era policy prohibiting the ownership of slaves in the Georgia Colony. At the urging of Georgia's proprietor, General James Oglethorpe, and his fellow colonial trustees, the British Parliament formally codified prohibition in 1735, three years after the colony's founding. The ban remained in effect until 1751, when the diminution of the Spanish threat and economic pressure from Georgia's emergent planter class forced Parliament to reverse itself.

Johann Martin Boltzius was a German-born American Lutheran minister. He is most known for his association with the Salzburger emigrants, a group of German-speaking Protestant refugees who migrated to the British colony of Georgia in 1734. They founded the city of Ebenezer, Georgia to escape persecution in the Archbishopric of Salzburg and other Roman Catholic authorities for their religious views.

Fort St. Andrews was a British colonial coastal fortification built on Cumberland Island, Georgia, in 1736. The fort was built by the British as part of a buffer against Spanish Florida and the colonies to the north. The fort was abandoned and later destroyed by the Spanish in mid-1742.

Fort San Francisco de Pupo was an 18th-century Spanish fort on the west bank of the St. Johns River in Florida, about eighteen miles from St. Augustine, the capital of Spanish Florida. Lying on the old trail to the Spanish province of Apalachee in western Florida, Fort Pupo and its sister outpost, Fort Picolata on the opposite shore of the river, controlled all traffic on the ferry crossing. The remains of Fort Pupo are situated about three miles south of Green Cove Springs in Clay County, near the end of Bayard Point opposite Picolata. The surrounding area is a hammock of southern live oak, southern magnolia, pignut hickory and other typical trees native to the region.
Abraham Minis was a European immigrant to the newly settled colony of Savannah, Province of Georgia, in 1733. Despite their not knowing if they would be received, General James Oglethorpe, founder of the Savannah colony, allowed Minis and his family entry and granted them land. Their descendants have lived in Savannah ever since.

Audience Given by the Trustees of Georgia to a Delegation of Creek Indians is an oil-on-canvas group portrait created by English painter William Verelst (1704–1752). It was painted in London in 1734 or 1735. A bequest from Henry Francis du Pont, the painting is held in the permanent collection of the Winterthur Museum, Garden and Library. The painting depicts a Lower Creek Yamacraw delegation meeting with the governing body of the English Province of Georgia.













