Related Research Articles
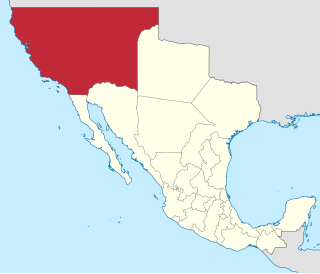
Alta California, also known as Nueva California, among other names, was a province of New Spain, formally established in 1804. Along with the Baja California peninsula, it had previously comprised the province of Las Californias, but was split off into a separate province in 1804. Following the Mexican War of Independence, it became a territory of Mexico in April 1822 and was renamed Alta California in 1824. The claimed territory included all of the modern US states of California, Nevada and Utah, and parts of Arizona, Wyoming, Colorado and New Mexico. In the 1836 Siete Leyes government reorganization, the two Californias were once again combined. That change was undone in 1846, but rendered moot by the U.S. military occupation of California in the Mexican-American War.

Human history in California began when indigenous Americans first arrived some 13,000 years ago. Coastal exploration by Europeans began in the 16th century, and settlement by Europeans along the coast and in the inland valleys began in the 18th century. California was ceded to the United States under the terms of the 1848 Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo following the defeat of Mexico in the Mexican–American War. American westward expansion intensified with the California Gold Rush, beginning in 1848. California joined the Union as a free state in 1850, due to the Compromise of 1850. By the end of the 19th century, California was still largely rural and agricultural, but had a population of about 1.4 million.
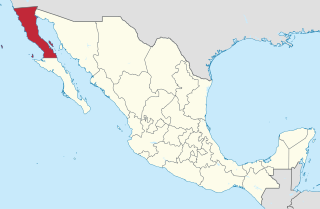
Baja California (Spanish pronunciation: [ˈbaxa kaliˈfoɾnja];, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California, is a state in Mexico. It is the northernmost and westernmost of the 32 federal entities of Mexico. Before becoming a state in 1952, the area was known as the North Territory of Baja California. It has an area of 70,113 km2 and comprises the northern half of the Baja California Peninsula, north of the 28th parallel, plus oceanic Guadalupe Island. The mainland portion of the state is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean; on the east by Sonora, the U.S. state of Arizona, and the Gulf of California ; and on the south by Baja California Sur. Its northern limit is the U.S. state of California.

Raúl Héctor Castro was a Mexican American politician, diplomat and judge. In 1964, Castro was selected to be U.S. Ambassador to El Salvador, a position he held until 1968 when he was appointed U.S. Ambassador to Bolivia. In 1974, Castro was elected to serve as the 14th governor of Arizona, and resigned two years into his term to become U.S. Ambassador to Argentina. Prior to his entry into public service, Castro was a lawyer and a judge for Pima County, Arizona. He was a member of the Democratic Party.
José María de Echeandía (?–1871) was twice Mexican governor of Alta California from 1825 to 1831 and again from 1832 to 1833. He was the only governor of California that lived in San Diego.

José Antonio Castro was a Californio politician, statesman, and military leader who served as acting governor of Alta California in 1835, and military commander under governor Juan Bautista Alvarado after November, 1836. He was also Commandante General in northern California during the Bear Flag Revolt.

José de Gálvez y Gallardo, 1st Marquess of Sonora was a Spanish lawyer and Visitador generál in New Spain (1764–1772); later appointed to the Council of the Indies (1775–1787). He was one of the prime figures behind the Bourbon Reforms. He belonged to an important political family that included his brother Matías de Gálvez and nephew Bernardo de Gálvez.

Francisco Rafael Arellano Félix was a Mexican drug lord and former leader of the Tijuana Cartel, a drug trafficking organization. He was the oldest of seven brothers and headed the criminal organization early in the 1990s alongside them. Through his brother Benjamín, Francisco Rafael joined the Tijuana Cartel in 1989 following the arrest of Miguel Ángel Félix Gallardo, one of the most prominent drug czars in Mexico during the 1980s. When the Arellano Félix took control of the organization in the early 1990s, tensions with the rival Sinaloa Cartel prompted violent attacks and slayings from both fronts.

Fernando Jorge "El Diablo" Castro Trenti is a Mexican politician affiliated with the Institutional Revolutionary Party (PRI) who served in the LX and the LXI Legislatures as senator representing the State of Baja California.
Fernando Castro may refer to:

The Californias, occasionally known as the Three Californias or Two Californias, are a region of North America spanning the United States and Mexico, consisting of the U.S. state of California and the Mexican states of Baja California and Baja California Sur. Historically, the term Californias was used to define the vast northwestern region of Spanish America, as the Province of the Californias, and later as a collective term for Alta California and the Baja California Peninsula.

The Rock Paintings of Sierra de San Francisco are prehistoric rock art pictographs found in the Sierra de San Francisco mountain range in Mulegé Municipality of the northern region of Baja California Sur state, in Mexico.
The Spanish and Mexican governments made many concessions and land grants in Alta California from 1785 to 1846. The Spanish Concessions of land were made to retired soldiers as an inducement for them to remain in the frontier. These Concessions reverted to the Spanish crown upon the death of the recipient. The Mexican government later encouraged settlement by issuing much larger land grants to both native-born and naturalized Mexican citizens. The grants were usually two or more square leagues, or 35 square kilometres (14 sq mi) in size. Unlike Spanish Concessions, Mexican land grants provided permanent, unencumbered ownership rights. Most ranchos granted by Mexico were located along the California coast around San Francisco Bay, inland along the Sacramento River, and within the San Joaquin Valley.
The California Land Act of 1851, enacted following the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo and the admission of California as a state in 1850, established a three-member Public Land Commission to determine the validity of prior Spanish and Mexican land grants. It required landowners who claimed title under the Mexican government to file their claim with a commission within two years. Contrary to the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, which guaranteed full protection of all property rights for Mexican citizens, it placed the burden on landholders to prove their title.
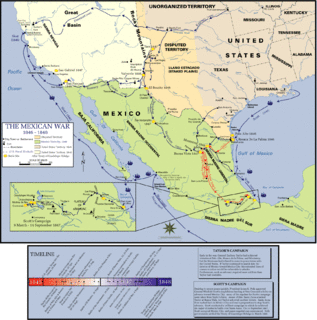
The Pacific Coast Campaign refers to United States naval operations against targets along Mexico's Pacific Coast during the Mexican–American War. It excludes engagements of the California Campaign in areas of The Californias north of the Baja California Peninsula. The objective of the campaign was to secure the Baja Peninsula of Mexico, and to blockade/capture west-coast ports of Mexico—especially Mazatlan, a major port-of-entry for imported supplies. The resistance of Mexican forces to the north in the Los Angeles area and the lack of ships, soldiers and logistical support prevented an early occupation of the peninsula and the west-coast Mexican seaports. The U.S. Navy attempted blockades of the ports three times before being able to successfully blockade and/or occupy them.

Baja California Territory was a Mexican territory from 1824 to 1931, that encompassed the Baja California Peninsula of present-day northwestern Mexico. It replaced the Baja California Province (1773–1824) of the Spanish colonial Viceroyalty of New Spain, after Mexican independence. Along with Alta California, the two territories were split from the Spanish The Californias region.

Francisco Vega de Lamadrid, also known as Kiko Vega is a Mexican politician of the National Action Party who was the 15th Governor of Baja California, for the term from 2013-2019. He previously served as the Municipal President of Tijuana, from 1998 to 2001. He later served as a member of Mexico's Chamber of Deputies as part of the LXI Legislature of the Mexican Congress from 2009 to 2012. He succeeded José Guadalupe Osuna Millán, having taken office on 1 November 2013.
Francisco Palacios Miranda was the Governor and Military Commandant of the Baja California Territory from 1844 to 1847. He is known for his cooperation with the Americans during the Mexican American War, accepting neutrality of his Territory in 1846 and making the abject surrender of La Paz to the Americans in 1847. For this he was declared a traitor and forced into exile at the end of the war.
References
- ↑ Anuncian cambios en la PGJE , SignOnSanDiego, January 17, 2006.
- ↑ Balacera entre ministeriales y sospechosos, SignOnSanDiego.com, October 12, 2005.
| This article about an Institutional Revolutionary Party politician is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |