Related Research Articles

Atari ST is a line of personal computers from Atari Corporation and the successor to the company's 8-bit home computers. The initial model, the Atari 520ST, had limited release in April–June 1985, and it was widely available in July. The ST was the first personal computer with a bitmapped color graphical user interface, using a version of Digital Research's GEM interface / operating system, from February 1985.

Commodore International Corporation was a Bahamian home computer and electronics manufacturer with executive offices in the United States founded by Jack Tramiel and Irving Gould. Commodore International (CI), along with its subsidiary Commodore Business Machines (CBM), was a significant participant in the development of the home computer industry in the 1970s to early 1990s. In 1982, the company developed and marketed the world's second-best selling computer, the Commodore 64, and released its Amiga computer line in July 1985. Commodore was one of the world's largest personal computer manufacturers, with sales peaking in the last quarter of 1983 at $49 million.
A disk operating system (DOS) is a computer operating system that resides on and can use a disk storage device, such as a floppy disk, hard disk drive, or optical disc. A disk operating system provides a file system for organizing, reading, and writing files on the storage disk, and a means for loading and running programs stored on that disk. Strictly speaking, this definition does not include any other functionality, so it does not apply to more complex OSes, such as Microsoft Windows, and is more appropriately used only for older generations of operating systems.
A "Hello, World!" program is generally a simple computer program which outputs to the screen a message similar to "Hello, World!" while ignoring any user input. A small piece of code in most general-purpose programming languages, this program is used to illustrate a language's basic syntax. A "Hello, World!" program is often the first written by a student of a new programming language, but such a program can also be used as a sanity check to ensure that the computer software intended to compile or run source code is correctly installed, and that its operator understands how to use it.

The Atari 8-bit computers, formally launched as the Atari Home Computer System, are a series of 8-bit home computers introduced by Atari, Inc. in 1979 with the Atari 400 and Atari 800. It is the first home computer architecture with coprocessors, enabling more advanced graphics and sound than most of its contemporaries. Video games are key to its software library, and the 1980 first-person space combat simulator Star Raiders is considered the platform's killer app.

Atari BASIC is an interpreter for the BASIC programming language that shipped with Atari 8-bit computers. Unlike most American BASICs of the home computer era, Atari BASIC is not a derivative of Microsoft BASIC and differs in significant ways. It includes keywords for Atari-specific features and lacks support for string arrays.

Christopher Crawford is an American video game designer and writer. Hired by Alan Kay to work at Atari, Inc., he wrote the computer wargame Eastern Front (1941) for Atari 8-bit computers which was sold through the Atari Program Exchange and later Atari's official product line. After leaving Atari, he wrote a string of games beginning with Balance of Power for Macintosh. Writing about the process of developing games, he became known among other creators in the nascent home computer game industry for his passionate advocacy of game design as an art form. He self-published The Journal of Computer Game Design and founded the Computer Game Developers Conference.

Boulder Dash is a 2D maze-puzzle video game released in 1984 by First Star Software for Atari 8-bit computers. It was created by Canadian developers Peter Liepa and Chris Gray. The player controls Rockford, who collects treasures while evading hazards.
The Atari Microsoft BASIC and Atari Microsoft BASIC II variants of the 6502-version of Microsoft BASIC ported to the Atari 8-bit computers. The first version, released 1981, required 32 KB of RAM and was supplied on floppy disk. The second version, released the next year, had most of the code on a ROM cartridge with additional functions on an optional floppy.
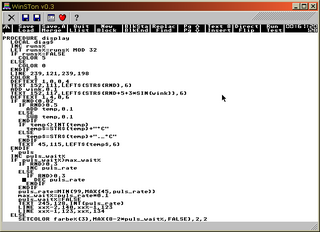
GFA BASIC is a dialect of the BASIC programming language, by Frank Ostrowski. The name is derived from the company, which distributed the software. In the mid-1980s to the 1990s it enjoyed popularity as an advanced BASIC dialect, but has been mostly superseded by several other programming languages. Official support ended in the early 2000s.

Turbo-BASIC XL is an enhanced version of the BASIC programming language for Atari 8-bit computers. It is a compatible superset of the Atari BASIC that shipped with the Atari 8-bit systems. Turbo-Basic XL was developed by Frank Ostrowski and published in the December 1985 issue of German computer magazine Happy Computer. A version for the 400/800 models was released shortly after as Frost Basic 1.4. Several modified versions working with different DOS systems have been released by other authors.

Atari DOS is the disk operating system used with the Atari 8-bit computers. Operating system extensions loaded into memory were required in order for an Atari computer to manage files stored on a disk drive. These extensions to the operating system added the disk handler and other file management features.
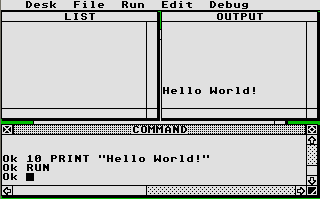
Atari ST BASIC was the first dialect of BASIC that was produced for the Atari ST line of computers. This BASIC interpreter was bundled with all new STs in the early years of the ST's lifespan, and quickly became the standard BASIC for that platform. However, many users disliked it, and improved dialects of BASIC quickly came out to replace it.
Optimized Systems Software (OSS) was a company that produced disk operating systems, programming languages with integrated development environments, and applications primarily for Atari 8-bit computers. The founders of OSS previously developed Atari DOS, Atari BASIC, and the Atari Assembler Editor for Atari, Inc., and many OSS products are substantially improved versions. OS A+ and DOS XL are based on Atari DOS. BASIC A+, BASIC XL, and BASIC XE are based on Atari BASIC. EASMD and MAC/65 are modeled on the Atari Assembler Editor. Action! is an ALGOL-inspired compiled programming language with an integrated full-screen editor. OSS also sold some software for the Apple II.

Frank James "Jim" Butterfield, was a Toronto-based computer programmer, author, and television personality known for his work with early microcomputers. He is particularly noted for associations with Commodore Business Machines and the Toronto PET Users Group, for many books and articles on machine language programming, and for educational videos and TV programs.

Many games, utilities, and educational programs were available for Atari 8-bit computers. Atari, Inc. was primarily the publisher following the launch of the Atari 400/800 in 1979, then increasingly by third parties. Atari also distributed "user written" software through the Atari Program Exchange from 1981 to 1984. After APX folded, many titles were picked up by Antic Software.
Maxon Computer GmbH is a German software company that produces software for content creators. The company’s product lines include the 3D software Cinema 4D, the Red Giant tools for editing, motion design and filmmaking, Redshift renderer and the digital sculpting and painting software ZBrush as well as the mobile sculpting app Forger. The company’s cross-platform benchmarking application Cinebench is used by developers, reviewers and users to evaluate hardware performance.
The Rugg/Feldman benchmarks are a series of seven short BASIC programming language programs that are used to test the performance of BASIC implementations on various microcomputers. They were published by Tom Rugg and Phil Feldman in the June 1977 issue of the US computer magazine, Kilobaud.
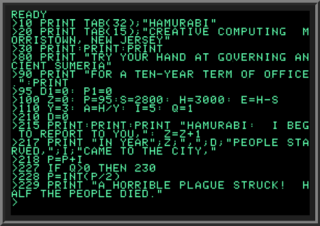
A BASIC interpreter is an interpreter that enables users to enter and run programs in the BASIC language and was, for the first part of the microcomputer era, the default application that computers would launch. Users were expected to use the BASIC interpreter to type in programs or to load programs from storage.
References
- ↑ AtariWiki: Turbo-BASIC XL. Retrieved 10 December 2020
- ↑ "Historie vývoje počítačových her (145. část – další textovky na Amigách)". Root CZ. Retrieved 13 October 2018.