
Customs is an authority or agency in a country responsible for collecting tariffs and for controlling the flow of goods, including animals, transports, personal effects, and hazardous items, into and out of a country. Traditionally, customs has been considered as the fiscal subject that charges customs duties and other taxes on import and export. In recent decades, the views on the functions of customs have considerably expanded and now covers three basic issues: taxation, security, and trade facilitation.

Border control comprises measures taken by governments to monitor and regulate the movement of people, animals, and goods across land, air, and maritime borders. While border control is typically associated with international borders, it also encompasses controls imposed on internal borders within a single state.
The Visa Waiver Program (VWP) is a program of the United States federal government that allows nationals of specific countries to travel to the United States for tourism, business, or while in transit for up to 90 days without having to obtain a visa. It applies to all fifty U.S. states, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands, as well as to Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands, which also have an additional program with waivers for more nationalities; American Samoa has a similar but separate program.

The Canada–United States border is the longest international border in the world. The boundary is 8,891 km (5,525 mi) long. The land border has two sections: Canada's border with the contiguous United States to its south, and with the U.S. state of Alaska to its west. The bi-national International Boundary Commission deals with matters relating to marking and maintaining the boundary, and the International Joint Commission deals with issues concerning boundary waters. The agencies responsible for facilitating legal passage through the international boundary are the Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA) and U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP).

The Canada Border Services Agency is a federal law enforcement agency that is responsible for border control, immigration enforcement, and customs services in Canada.

A customs officer is a law enforcement agent who enforces customs laws, on behalf of a government.

United States Customs and Border Protection (CBP) is the largest federal law enforcement agency of the United States Department of Homeland Security. It is the country's primary border control organization, charged with regulating and facilitating international trade, collecting import duties, as well as enforcing U.S. regulations, including trade, customs, and immigration. CBP is one of the largest law enforcement agencies in the United States. It has a workforce of more than 45,600 federal agents and officers. It is headquartered in Washington, D.C.
The Customs-Trade Partnership Against Terrorism (C-TPAT) is a voluntary supply-chain security program led by U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) focused on improving the security of private companies' supply chains with respect to terrorism. The program was launched in November 2001 with seven initial participants, all large U.S. companies. As of December 1, 2014, the program had 10,854 members. The 4,315 importers in the program account for approximately 54% of the value of all merchandise imported into the U.S.

Visitors to the United States must obtain a visa from one of the U.S. diplomatic missions unless they are citizens of one of the visa-exempt or Visa Waiver Program countries.

The Office of Field Operations (OFO) is a federal law enforcement agency within the U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) responsible for managing United States customs operations at 20 Field Operations offices, 328 ports of entry, and 16 pre-clearance stations in Canada, Ireland, the UAE, and the Caribbean. Headed by an Executive Assistant Commissioner, OFO directs the activities of more than 27,000 employees, including more than 22,000 CBP Officers and Agriculture Specialists. CBP Office of Field Operations is the largest component in CBP.

NEXUS is a joint Canada Border Services Agency and U.S. Customs and Border Protection-operated Trusted Traveler and expedited border control program designed for pre-approved, low-risk travelers. Members of the program can avoid waits at border entry points by using reserved lanes at land crossings into Canada and the United States, by using self-serve kiosks at airports in Canada, the US and some international locations, or by phoning border officials for a marine entry. A NEXUS membership card is a valid document under the Western Hemisphere Travel Initiative (WHTI), so it can be used in place of a passport, including by air if flying between the US and Canada. However, carrying a valid passport is still recommended, in the rare event that a flight is diverted to an airport without NEXUS support.
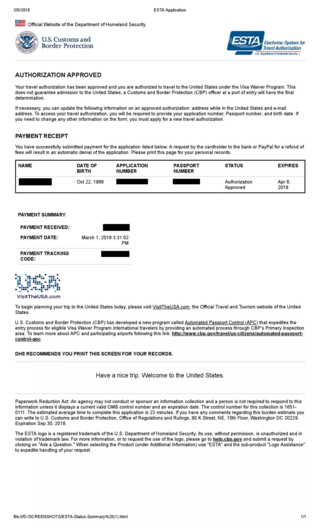
The Electronic System for Travel Authorization (ESTA) is an automated system that determines the eligibility of visitors to travel to the United States under the Visa Waiver Program (VWP). ESTA was mandated by the Implementing Recommendations of the 9/11 Commission Act of 2007. ESTA only authorizes travel to a U.S. airport, border, or port of entry, but admissibility into the United States is determined by a U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) officer upon arrival. The ESTA application collects biographic information and answers to VWP eligibility questions.
Custom brokers or Customs House Brokerages are working positions that may be employed by or affiliated with freight forwarders, independent businesses, or shipping lines, importers, exporters, trade authorities, and customs brokerage firms.

The Secure Electronic Network for Travelers Rapid Inspection (SENTRI) provides expedited U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) processing, at the U.S.–Mexico border, of pre-approved travelers considered low-risk. Voluntarily applicants must undergo a thorough background check against criminal, customs, immigration, law enforcement, and terrorist databases; a 10-fingerprint law enforcement check; and a personal interview with a CBP Officer. The total enrollment fee is $120.00, and SENTRI status is valid for 5 years.
The Canadian Passenger Accelerated Service System (CANPASS) is a Canada Border Services Agency program in place to streamline customs and immigration clearance for travellers flying on corporate and private aircraft. The CANPASS Corporate Aircraft program and the CANPASS Private Aircraft program allow company and private aircraft that frequently fly directly into Canada from the United States to access more airports and receive expedited clearance. Enrolment in each program costs CA$40 for a validity period of five years.
According to the World Customs Organization (WCO), an authorized economic operator (AEO) is
"a party involved in the international movement of goods in whatever function that has been approved by or on behalf of a national Customs administration as complying with WCO or equivalent supply chain security standards. Authorized Economic Operators include inter alia manufacturers, importers, exporters, brokers, carriers, consolidators, intermediaries, ports, airports, terminal operators, integrated operators, warehouses and distributors"

Global Entry is a program of the U.S. Customs and Border Protection service that allows pre-approved, low-risk travelers to receive expedited clearance upon arrival into the United States through automatic kiosks at select airports and via the SENTRI and NEXUS lanes by land and sea. As of May 4, 2018, Global Entry was available at 53 U.S. airports and 15 preclearance locations. By April 2018 more than five million people were enrolled in Global Entry and approximately 50,000 new applications for the program were being filed each month.

U.S. citizens and permanent residents entering Canada by land are required to possess the requisite documentation, such as a passport, driver's license, and other valid identification documents. They must also meet other criteria, such as passing security measures, before they are allowed entry into Canada. Consequently, travelers must also meet the requirements for re-entering the U.S. at the end of their visit.

The APEC Business Travel Card (ABTC) is a travel document issued to business travelers who are citizens of APEC participating economies. It is valid for five years. The card waives the need for a visa when visiting other APEC participating economies, provided the bearer has obtained the corresponding pre-clearance during the application process.
The United States imposes tariffs on imports of goods. The duty is levied at the time of import and is paid by the importer of record. Customs duties vary by country of origin and product. Goods from many countries are exempt from duty under various trade agreements. Certain types of goods are exempt from duty regardless of source. Customs rules differ from other import restrictions. Failure to properly comply with customs rules can result in seizure of goods and criminal penalties against involved parties. The United States Customs and Border Protection (CBP) enforces customs rules.












