
Free software is computer software distributed under terms that allow users to run the software for any purpose as well as to study, change, and distribute it and any adapted versions. Free software is a matter of liberty, not price; all users are legally free to do what they want with their copies of a free software regardless of how much is paid to obtain the program. Computer programs are deemed "free" if they give end-users ultimate control over the software and, subsequently, over their devices.

Theodor Holm Nelson is an American pioneer of information technology, philosopher, and sociologist. He coined the terms hypertext and hypermedia in 1963 and published them in 1965. Nelson coined the terms transclusion, virtuality, and intertwingularity. According to a 1997 Forbes profile, Nelson "sees himself as a literary romantic, like a Cyrano de Bergerac, or 'the Orson Welles of software'."

A screen reader is a form of assistive technology (AT) that renders text and image content as speech or braille output. Screen readers are essential to people who are blind, and are useful to people who are visually impaired, illiterate, or have a learning disability. Screen readers are software applications that attempt to convey what people with normal eyesight see on a display to their users via non-visual means, like text-to-speech, sound icons, or a braille device. They do this by applying a wide variety of techniques that include, for example, interacting with dedicated accessibility APIs, using various operating system features, and employing hooking techniques.
An application program is a computer program designed to carry out a specific task other than one relating to the operation of the computer itself, typically to be used by end-users. Word processors, media players, and accounting software are examples. The collective noun refers to all applications collectively. The other principal classifications of software are system software, relating to the operation of the computer, and utility software ("utilities").
JAWS is a computer screen reader program for Microsoft Windows that allows blind and visually impaired users to read the screen either with a text-to-speech output or by a refreshable Braille display. JAWS is produced by the Blind and Low Vision Group of Freedom Scientific.
Ted Henter is an American computer programmer and businessperson known for having invented the JAWS screen reader for the blind. He studied engineering, but learned computer programming and started his own business after becoming blind in a car accident in 1978, which put an end to a promising career as an international motorcycle racer.

Free and open-source software (FOSS) is software that is both free software and open-source software where anyone is freely licensed to use, copy, study, and change the software in any way, and the source code is openly shared so that people are encouraged to voluntarily improve the design of the software. This is in contrast to proprietary software, where the software is under restrictive copyright licensing and the source code is usually hidden from the users.
ZoomText is a screen magnifier for Microsoft Windows, developed by Ai Squared which was acquired by Freedom Scientific in 2016. The first version was released for DOS in 1988, and the first version for Windows was released in 1991. ZoomText is available in two editions: ZoomText Magnifier and ZoomText Magnifier/Reader, which includes a built-in screen reader.
SpeedTree is a group of vegetation programming and modeling software products developed and sold by Interactive Data Visualization, Inc. (IDV) that generates virtual foliage for animations, architecture and in real time for video games and demanding real time simulations.

Richard Matthew Stallman, also known by his initials, rms, is an American free software movement activist and programmer. He campaigns for software to be distributed in a manner such that its users receive the freedoms to use, study, distribute, and modify that software. Software that ensures these freedoms is termed free software. Stallman launched the GNU Project, founded the Free Software Foundation, developed the GNU Compiler Collection and GNU Emacs, and wrote the GNU General Public License.
NonVisual Desktop Access (NVDA) is a free and open-source, portable screen reader for Microsoft Windows. The project was started by Michael Curran in 2006.

Orca is a free and open-source, flexible, extensible screen reader from the GNOME project for individuals who are blind or visually impaired. Using various combinations of speech synthesis and braille, Orca helps provide access to applications and toolkits that support the AT-SPI.
Braille technology is assistive technology which allows blind or visually impaired people to do common tasks such as writing, browsing the Internet, typing in Braille and printing in text, engaging in chat, downloading files, music, using electronic mail, burning music, and reading documents. It also allows blind or visually impaired students to complete all assignments in school as the rest of sighted classmates and allows them take courses online. It enables professionals to do their jobs and teachers to lecture using hardware and software applications. The advances of Braille technology are meaningful because blind people can access more texts, books and libraries and it also facilitates the printing of Braille texts.
The GNU General Public License is a series of widely used free software licenses that guarantee end users the four freedoms to run, study, share, and modify the software. The licenses were originally written by Richard Stallman, founder of the Free Software Foundation (FSF), for the GNU Project, and grant the recipients of a computer program the rights of the Free Software Definition. The GPL series are all copyleft licenses, which means that any derivative work must be distributed under the same or equivalent license terms. This is in distinction to permissive software licenses, of which the BSD licenses and the MIT License are widely used, less restrictive examples. GPL was the first copyleft license for general use.
The Free Software Foundation (FSF) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization founded by Richard Stallman on October 4, 1985, to support the free software movement, which promotes the universal freedom to study, distribute, create, and modify computer software, with the organization's preference for software being distributed under copyleft terms, such as with its own GNU General Public License. The FSF was incorporated in Boston, Massachusetts, US, where it is also based.

Opera is a multi-platform web browser developed by its namesake company Opera. Opera is nowadays a Chromium-based browser. It distinguishes itself from other browsers through its user interface and other features.

LibreOffice is a free and open-source office productivity software suite, a project of The Document Foundation (TDF). It was forked in 2010 from OpenOffice.org, an open-sourced version of the earlier StarOffice. The LibreOffice suite consists of programs for word processing, creating and editing of spreadsheets, slideshows, diagrams and drawings, working with databases, and composing mathematical formulae. It is available in 115 languages.
Software categories are groups of software. They allow software to be understood in terms of those categories, instead of the particularities of each package. Different classification schemes consider different aspects of software.
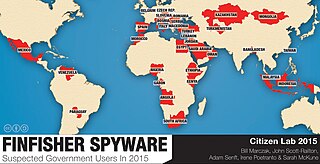
FinFisher, also known as FinSpy, is surveillance software marketed by Lench IT Solutions plc, which markets the spyware through law enforcement channels.







