See also
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Freedom of Religion Act. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Freedom of Religion Act may refer to:
| This disambiguation page lists articles associated with the title Freedom of Religion Act. If an internal link led you here, you may wish to change the link to point directly to the intended article. |
Religious conversion is the adoption of a set of beliefs identified with one particular religious denomination to the exclusion of others. Thus "religious conversion" would describe the abandoning of adherence to one denomination and affiliating with another. This might be from one to another denomination within the same religion, for example, from Baptist to Catholic Christianity or from Sunni Islam to Shi’a Islam. In some cases, religious conversion "marks a transformation of religious identity and is symbolized by special rituals".

Freedom of religion or religious liberty is a principle that supports the freedom of an individual or community, in public or private, to manifest religion or belief in teaching, practice, worship, and observance. It also includes the freedom to change one's religion or beliefs, "the right not to profess any religion or belief" or "not to practise a religion".
Religious intolerance is intolerance of another's religious beliefs or practices or lack thereof.

A state religion is a religious body or creed officially endorsed by the state. A state with an official religion, while not secular, is not necessarily a theocracy, a country whose rulers have both secular and spiritual authority. State religions are official or government-sanctioned establishments of a religion, but the state does not need be under the control of the religion nor is the state-sanctioned religion necessarily under the control of the state.

Muslims constitute over 17.3 per cent of Mauritius population. Muslims of Mauritius are mostly of Indian descent. Large numbers of Muslims arrived to Mauritius during the British regime starting in 1834 as part of the large scale indentured labor force from India.
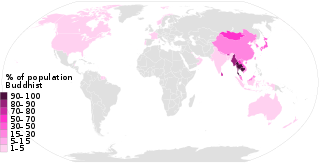
This list of Buddhism by country shows the distribution of the Buddhist religion, practiced by about 500 million people as of the 2010s, representing 7% to 8% of the world's total population.
Freedom of religion in India is a fundamental right guaranteed by Article 25-28 of the Constitution of India. Modern India came into existence in 1947 and the Indian constitution's preamble was amended in 1976 to state that India is a secular state. However, in S.R Bommai v. Union of India, Supreme Court of India ruled that India was already a secular state from the time it adopted its constitution, what actually was done through this amendment is to state explicitly what was earlier contained implicitly under article 25 to 28. Every citizen of India has a right to practice and promote their religion peacefully. However, there have been numerous incidents of religious intolerance that resulted in riots and violence, notably, the 1984 Anti-Sikh Massacre in Delhi, 1990 Anti-Hindu riots in Kashmir, 2002 Gujarat Riots and the 2008 Anti-Christian riots in Odisha. Some perpetrators of the 1984 Anti-Sikh Massacre in Delhi have not been brought to justice despite widespread condemnation.

The Fundamental Rights, Directive Principles of State Policy and Fundamental Duties are sections of the Constitution of India that prescribe the fundamental obligations of the states to its citizens and the duties and the rights of the citizens to the State. These sections comprise a constitutional bill of rights for government policy-making and the behaviour and conduct of citizens. These sections are considered vital elements of the constitution, which was developed between 1947 and 1949 by the Constituent Assembly of India.
With the Forty-second Amendment of the Constitution of India enacted in 1976, the Preamble to the Constitution asserted that India is a secular nation. However, the Supreme Court of India in S. R. Bommai v. Union of India established the fact that India was secular since the formation of the republic. The judgement established that there is separation of state and religion. It stated "In matters of State, religion has no place. And if the Constitution requires the State to be secular in thought and action, the same requirement attaches to political parties as well. The Constitution does not recognize, it does not permit, mixing religion and State power. That is the constitutional injunction. None can say otherwise so long as this Constitution governs this country. Politics and religion cannot be mixed. Any State government which pursues nonsecular policies or nonsecular course of action acts contrary to the constitutional mandate and renders itself amenable to action under Article 356". Furthermore, constitutionally, state-owned educational institutions are prohibited from imparting religious instructions.Officially, secularism has always inspired modern India. However, India's secularism does not completely separate religion and state. The Indian Constitution has allowed extensive interference of the state in religious affairs. In matters of law in modern India, however, the applicable code of law is unequal, and India's personal laws – on matters such as marriage, divorce, inheritance, alimony – varies with an individual's religion. The Indian Constitution permits partial financial support for religious schools, as well as the financing of religious buildings and infrastructure by the state. The Islamic Central Wakf Council and many Hindu temples of great religious significance are administered and managed by the Indian government. The attempt to respect unequal, religious law has created a number of issues in India such as acceptability of polygamy, unequal inheritance rights, extra judicial unilateral divorce rights favorable to some males, and conflicting interpretations of religious books.
The Gujarat Freedom of Religion Act (2003) requires religious conversions in Gujarat, India, to be approved by a district magistrate.

The United States Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF) is a U.S. federal government commission created by the International Religious Freedom Act (IRFA) of 1998. USCIRF Commissioners are appointed by the President and the leadership of both political parties in the Senate and the House of Representatives. USCIRF's principal responsibilities are to review the facts and circumstances of violations of religious freedom internationally and to make policy recommendations to the President, the Secretary of State, and the Congress.
Jainism is considered to be a legally distinct religion in India. A section of scholars earlier considered it as a Hindu sect or a Buddhist heresy, but it is one of the three ancient Indian religions. On 30 January 2014, the Government of India explicitly awarded the status of a "minority religion" to the Jain community in India, as per Section 2(c) of the National Commission for Minorities (NCM) Act (NCM), 1992.

Religion in India is characterised by a diversity of religious beliefs and practices. The preamble of Indian constitution states that India is a secular state. The Indian subcontinent is the birthplace of four of the world's major religions; namely Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism. They are of the Moksh-aligned dharms (religions) that believe Moksha is the most supreme state of the atma (soul). According to the 2011 census, 79.8% of the population of India practices Hinduism, 14.2% adheres to Islam, 2.3% adheres to Christianity, 1.7% adheres to Sikhism, 0.7% adheres to Buddhism and 0.4% adheres to Jainism. Zoroastrianism, Yungdrung Bon, Baha'i, Sanamahism and Judaism also have a history in India, and each has several thousands of Indian adherents

Finland is a predominantly Christian nation where 68.7% of the 5.5 million overall population are members of the Evangelical Lutheran Church of Finland (Protestant), 28.5% are unaffiliated, 1.1% are Orthodox Christians and 0.8% follow other religions like Islam, Hinduism, Buddhism, Judaism, folk religion etc.
Rev Stanislaus vs Madhya Pradesh, 1977 SCR (2) 611, is a matter where the Supreme Court of India considered the issue whether the fundamental right to practise and propagate religion includes the right to convert, held that the right to propagate does not include the right to convert and therefore upheld the constitutional validity of the laws enacted by Madhya Pradesh and Odisha legislatures prohibiting conversion by force, fraud or allurement.
Himachal Pradesh Freedom of Religion Act 2006 is a bill unanimously passed by the Legislature of Himachal Pradesh state in India on 19 December 2006.

Anti-Christian violence in India is religiously-motivated violence against Christians in India. Violence against Christians has been seen by the organization Human Rights Watch as a tactic used to meet political ends. The acts of violence include arson of churches, conversion of Christians by force and threats of physical violence, sexual assaults, murder of Christian priests and destruction of Christian schools, colleges, and cemeteries.

Religious violence in Odisha consists of civil unrest and riots in the remote forest region surrounding the Kandhamal district in the western parts of the Indian state of Odisha.

Bal Patil was a Jain scholar, journalist, social activist and Jain minority status advocate from Mumbai, Maharashtra. He was appointed as a member of State Minority Commission by the Govt. of Maharashtra from 2001 to 2004. He was the Secretary-General of All India Jain Minority Forum, New Delhi—a position he held till his death—and was an ardent advocate of minority status for Jainism. The Jain minority cause gained prominence when he petitioned the Supreme Court of India for the recognition of Jain religious minority status on par with other Indian minorities as per the two recommendations by the National Minorities Commission. He was also the first non-medical President of the National Society for the Prevention of Heart Disease & Rehabilitation, Mumbai. He has also authored many books on Jainism and presented several papers at various seminars and conferences.

Amit Anilchandra Shah is an Indian politician currently serving as the Minister of Home Affairs. He served as the President of the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) from 2014 to 2020. He was elected to the lower house of Parliament, Lok Sabha, in the 2019 Indian general elections from Gandhinagar. Earlier, he had been elected as a member of the upper house of Parliament, Rajya Sabha, from Gujarat in 2017. Sworn in at the age of 54, he is the youngest serving full-time Home Minister. He is the chief strategist of the BJP and a close aide to Narendra Modi.