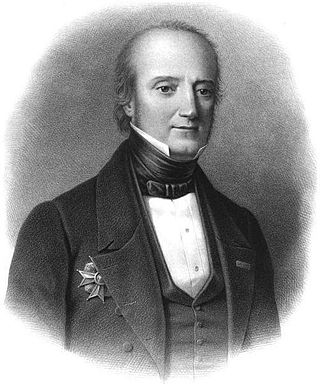Marie Henri Daniel Gauthier, comte de Rigny was the commander of the French squadron at the Battle of Navarino in the Greek War of Independence.

Jean de Vienne was a French light cruiser of the La Galissonnière class. During World War II, she remained with Vichy France. She was named for Jean de Vienne, a 14th-century French knight, general and admiral during the Hundred Years' War.

Marseillaise was a French light cruiser of the La Galissonnière class. During the Second World War, she remained with Vichy France.

HMS Pompee was a 74-gun ship of the line of the British Royal Navy. Built as Pompée, a Téméraire-class ship of the French Navy, she was handed over to the British at Spithead by French royalists who had fled France after the Siege of Toulon by the French Republic, only a few months after being completed. After reaching Great Britain, Pompée was registered and recommissioned as HMS Pompee and spent the entirety of her active career with the Royal Navy until she was broken up in 1817.

The Romulus was a Téméraire class 74-gun ship of the line of the French Navy.

The Iéna was a Commerce de Paris class 110-gun ship of the line of the French Navy.

Marengo was a Téméraire class 74-gun ship of the line of the French Navy.

Ville de Marseille was a Téméraire-class 74-gun ship of the line of the French Navy.

Provence was a Téméraire class 74-gun ship of the line of the French Navy.

HMS Volage was a Laurel-class sixth-rate post-ship of the Royal Navy. She served during the Napoleonic War, capturing four privateers and participating in the Battle of Lissa (1811). She was sold in 1818. Her new owners renamed her Rochester and she served in a commercial capacity for another 12 years, first sailing between England and India, and then making two voyages to the South Seas as a whaler. She was last listed in Lloyd's List in 1831.

Sibylle was a 38-gun Hébé-class frigate of the French Navy. She was launched in 1791 at the dockyards in Toulon and placed in service in 1792. After the 50-gun fourth rate HMS Romney captured her in 1794, the British took her into service as HMS Sybille. She served in the Royal Navy until disposed of in 1833. While in British service Sybille participated in three notable single ship actions, in each case capturing a French vessel. On anti-slavery duties off West Africa from July 1827 to June 1830, Sybille captured numerous slavers and freed some 3,500 slaves. She was finally sold in 1833 in Portsmouth.

The Pallas class constituted the standard design of 40-gun frigates of the French Navy during the Napoleonic Empire period. Jacques-Noël Sané designed them in 1805, as a development of his seven-ship Hortense class of 1802, and over the next eight years the Napoléonic government ordered in total 62 frigates to be built to this new design. Of these some 54 were completed, although ten of them were begun for the French Navy in shipyards within the French-occupied Netherlands or Italy, which were then under French occupation; these latter ships were completed for the Netherlands or Austrian navies after 1813.

The Adrienne was a Pallas-class 46-gun frigate of the French Navy.
HMS Montreal was a 32-gun Niger-class fifth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy. She was launched in 1761 and served in the Seven Years' War and the American War of Independence. The French captured her in 1779 and she then served with them under the name Montréal. An Anglo-Spanish force destroyed her during the occupation of Toulon early in the French Revolutionary Wars.

Sphinx was a paddle steamer, initially rated as a corvette, of the French Navy, and lead ship of her class. She was the first operational French naval steamer. She took part in the Invasion of Algiers in 1830, pioneering the role of steamers in navies of the mid-19th century, and later took part in the transfer of the Luxor Obelisk from Egypt to Paris.
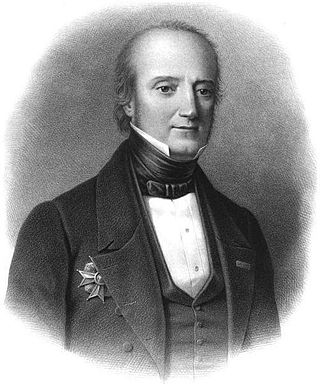
Jean Marguerite Tupinier was a French naval engineer and politician. In 1839 he was briefly Minister of Navy and Colonies.

HMS Proserpine was a 32-gun Amphion-class frigate built for the Royal Navy during the Napoleonic Wars. The French Navy captured her off Toulon about a year after her commissioning and took her into service as Proserpine. She served in various capacities such as a frigate, troopship, hospital ship, and prison hulk until 1865.

The French destroyer Panthère was a Chacal-class destroyer built for the French Navy during the 1920s. Aside from cruises to the English Channel and the French West Indies, she spent her entire career in the Mediterranean Sea. The ship was assigned to the Torpedo School at Toulon in 1932 and remained there until World War II began in September 1939. She was then assigned convoy escort duties in the Atlantic and was being refitted when the Battle of France began in May 1940. After the surrender of France a month later, Panthère was reduced to reserve. When the Germans attempted to seize the French fleet there in November 1942, she was one of the few ships that was not scuttled and was captured virtually intact.

Agamemnon was a Téméraire-class 74-gun ship of the line of the French Navy. She served during the later days of the First French Empire, notably taking part in the action of 5 November 1813. During the Bourbon Restoration, she was razéed into a 58-gun frigate and renamed Amphitrite.

Superbe was a Téméraire-class 74-gun ship of the line of the French Navy.