
Anthony is an incorporated town in El Paso County, Texas, United States. The population was 5,011 at the 2010 census. It is the first town encountered in Texas when traveling eastbound on Interstate 10 from New Mexico.

Tap water is water supplied to a tap (valve). Its uses include drinking, washing, cooking, and the flushing of toilets. Indoor tap water is distributed through "indoor plumbing", which has existed since antiquity but was available to very few people until the second half of the 19th century when it began to spread in popularity in what are now developed countries. Tap water became common in many regions during the 20th century, and is now lacking mainly among people in poverty, especially in developing countries.

Water treatment is any process that improves the quality of water to make it more acceptable for a specific end-use. The end use may be drinking, industrial water supply, irrigation, river flow maintenance, water recreation or many other uses, including being safely returned to the environment. Water treatment removes contaminants and undesirable components, or reduces their concentration so that the water becomes fit for its desired end-use. This treatment is crucial to human health and allows humans to benefit from both drinking and irrigation use.

Raising Cane's Chicken Fingers is a fast-food restaurant chain specializing in chicken fingers, that was founded in Baton Rouge, Louisiana, by Todd Graves and Craig Silvey on August 26, 1996. While company headquarters remain in Louisiana, a second restaurant support office was opened in Plano, Texas in 2009, followed by a third in August 2018 in North Platte, Nebraska.

Fresh Pond is a reservoir and park in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Prior to the Pond's use exclusively as a reservoir, its ice had been harvested by Boston's "Ice King", Frederic Tudor, and others, for shipment to North American cities and to tropical areas around the world.

The Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) is the principal federal law in the United States intended to ensure safe drinking water for the public. Pursuant to the act, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is required to set standards for drinking water quality and oversee all states, localities, and water suppliers that implement the standards.

Lake Casitas is a reservoir in Ventura County, California, built by the United States Bureau of Reclamation and completed in 1959. The project provides drinking water and water for irrigation. A secondary benefit is flood control.

Arsenic contamination of groundwater is a form of groundwater pollution which is often due to naturally occurring high concentrations of arsenic in deeper levels of groundwater. It is a high-profile problem due to the use of deep tubewells for water supply in the Ganges Delta, causing serious arsenic poisoning to large numbers of people. A 2007 study found that over 137 million people in more than 70 countries are probably affected by arsenic poisoning of drinking water. The problem became serious health concern after mass poisoning of water in Bangladesh. Arsenic contamination of ground water is found in many countries throughout the world, including the US.

A rainwater tank is a water tank used to collect and store rain water runoff, typically from rooftops via pipes. Rainwater tanks are devices for collecting and maintaining harvested rain. A rainwater catchment or collection system can yield 2,358 litres (623 US gal) of water from 2.54 cm (1.00 in) of rain on a 92.9 m2 (1,000 sq ft) roof.
Rainfall Catchment Equation: Catchment Area x Event Rainfall Depth (in) x 0.623 Conversion Factor =Gallonsof Potential Rainwater Collected
*Note this equation is for U.S., imperial measurements; i.e. calculations and conversion factor is for distance in feet and inches, and volume in gallons.

Houston, the most populous city in the Southern United States, is located along the upper Texas Gulf Coast, approximately 50 miles (80 km) northwest of the Gulf of Mexico at Galveston. The city, which is the ninth-largest in the United States by area, covers 601.7 square miles (1,558 km2), of which 579.4 square miles (1,501 km2), or 96.3%, is land and 22.3 square miles (58 km2), or 3.7%, is water.

Lavon Lake is a fresh water reservoir located in southeast Collin County, Texas on the East Fork of the Trinity River near Wylie, off of State Highway 78. It is commonly called Lake Lavon for commercial and recreational purposes but Lavon Lake is its official name according to the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. It was originally called Lavon Reservoir.

Water scarcity is the lack of fresh water resources to meet water demand. It affects every continent and was listed in 2019 by the World Economic Forum as one of the largest global risks in terms of potential impact over the next decade. It is manifested by partial or no satisfaction of expressed demand, economic competition for water quantity or quality, disputes between users, irreversible depletion of groundwater, and negative impacts on the environment. One-third of the global population live under conditions of severe water scarcity at least 1 month of the year. Half a billion people in the world face severe water scarcity all year round. Half of the world’s largest cities experience water scarcity.

Peak water is a concept that underlines the growing constraints on the availability, quality, and use of freshwater resources.
Drinking water supply and sanitation in Pakistan is characterized by some achievements and many challenges. Despite high population growth the country has increased the share of the population with access to an improved water source from 85% in 1990 to 92% in 2010, although this does not necessarily mean that the water from these sources is safe to drink. The share with access to improved sanitation increased from 27% to 48% during the same period, according to the Joint Monitoring Program for Water Supply and Sanitation. There has also been considerable innovation at the grass-root level, in particular concerning sanitation. The Orangi Pilot Project in Karachi and community-led total sanitation in rural areas are two examples of such innovation.
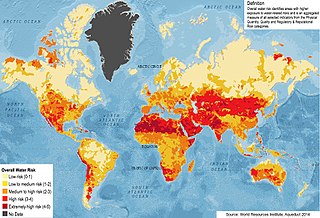
Water security has been defined as "the reliable availability of an acceptable quantity and quality of water for health, livelihoods and production, coupled with an acceptable level of water-related risks". It is realised to the degree that water scarcity is non-existent, or has been decreased or eliminated, and to the degree that floods and contamination of freshwater supplies are non-threatening.
"Sustainable development will not be achieved without a water secure world. A water secure world integrates a concern for the intrinsic value of water with a concern for its use for human survival and well-being. A water secure world harnesses water's productive power and minimises its destructive force. Water security also means addressing environmental protection and the negative effects of poor management. It is also concerned with ending fragmented responsibility for water and integrating water resources management across all sectors—finance, planning, agriculture, energy, tourism, industry, education and health. A water secure world reduces poverty, advances education, and increases living standards. It is a world where there is an improved quality of life for all, especially for the most vulnerable—usually women and children—who benefit most from good water governance."
A water district is a special district given the task of supplying water and sewer needs to a community. This term is commonly used in the United States.

Navo is an unincorporated community in east central Denton County, Texas, United States, located along U.S. Highway 380 about 10 miles east of Denton, Texas.
















