Related Research Articles

Kim Eric Drexler is an American engineer best known for introducing molecular nanotechnology (MNT), and his studies of its potential from the 1970s and 1980s. His 1991 doctoral thesis at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) was revised and published as the book Nanosystems: Molecular Machinery Manufacturing and Computation (1992), which received the Association of American Publishers award for Best Computer Science Book of 1992. He has been called the "godfather of nanotechnology".
Nanotechnology was defined by the National Nanotechnology Initiative as the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). At this scale, commonly known as the nanoscale, surface area and quantum mechanical effects become important in describing properties of matter. The definition of nanotechnology is inclusive of all types of research and technologies that deal with these special properties. It is therefore common to see the plural form "nanotechnologies" as well as "nanoscale technologies" to refer to the broad range of research and applications whose common trait is size. An earlier description of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal of precisely manipulating atoms and molecules for fabrication of macroscale products, also now referred to as molecular nanotechnology.

Erwin Chargaff was an Austro-Hungarian-born American biochemist, writer, Bucovinian Jew who emigrated to the United States during the Nazi era, and professor of biochemistry at Columbia University medical school. He wrote a well-reviewed autobiography, Heraclitean Fire: Sketches from a Life Before Nature.

Nanoid robotics, or for short, nanorobotics or nanobotics, is an emerging technology field creating machines or robots, which are called nanorobots or simply nanobots, whose components are at or near the scale of a nanometer. More specifically, nanorobotics refers to the nanotechnology engineering discipline of designing and building nanorobots with devices ranging in size from 0.1 to 10 micrometres and constructed of nanoscale or molecular components. The terms nanobot, nanoid, nanite, nanomachine and nanomite have also been used to describe such devices currently under research and development.

Molecular machines are a class of molecules typically described as an assembly of a discrete number of molecular components intended to produce mechanical movements in response to specific stimuli, mimicking macromolecular devices such as switches and motors. Naturally occurring or biological molecular machines are responsible for vital living processes such as DNA replication and ATP synthesis. Kinesins and ribosomes are examples of molecular machines, and they often take the form of multi-protein complexes. For the last several decades, scientists have attempted, with varying degrees of success, to miniaturize machines found in the macroscopic world. The first example of an artificial molecular machine (AMM) was reported in 1994, featuring a rotaxane with a ring and two different possible binding sites. In 2016 the Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Jean-Pierre Sauvage, Sir J. Fraser Stoddart, and Bernard L. Feringa for the design and synthesis of molecular machines.

Armand Paul Alivisatos is an American etymologist, chemist and academic administrator who has served as the 14th president of the University of Chicago since September 2021. He is a pioneer in nanomaterials development and an authority on the fabrication of nanocrystals and their use in biomedical and renewable energy applications. He was ranked fifth among the world's top 100 chemists for the period 2000–2010 in the list released by Thomson Reuters.

Patrick Cramer is a German chemist, structural biologist, and molecular systems biologist. In 2020, he was honoured to be an international member of the National Academy of Sciences. He became president of the Max Planck Society in June 2023.

DNA origami is the nanoscale folding of DNA to create arbitrary two- and three-dimensional shapes at the nanoscale. The specificity of the interactions between complementary base pairs make DNA a useful construction material, through design of its base sequences. DNA is a well-understood material that is suitable for creating scaffolds that hold other molecules in place or to create structures all on its own.

David Haussler is an American bioinformatician known for his work leading the team that assembled the first human genome sequence in the race to complete the Human Genome Project and subsequently for comparative genome analysis that deepens understanding the molecular function and evolution of the genome.

Joachim Wilhelm "Jo" Messing was a German-American biologist who was a professor of molecular biology and the fourth director of the Waksman Institute of Microbiology at Rutgers University.
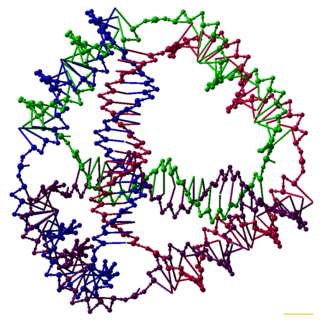
DNA nanotechnology is the design and manufacture of artificial nucleic acid structures for technological uses. In this field, nucleic acids are used as non-biological engineering materials for nanotechnology rather than as the carriers of genetic information in living cells. Researchers in the field have created static structures such as two- and three-dimensional crystal lattices, nanotubes, polyhedra, and arbitrary shapes, and functional devices such as molecular machines and DNA computers. The field is beginning to be used as a tool to solve basic science problems in structural biology and biophysics, including applications in X-ray crystallography and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins to determine structures. Potential applications in molecular scale electronics and nanomedicine are also being investigated.

Nadrian C. "Ned" Seeman was an American nanotechnologist and crystallographer known for inventing the field of DNA nanotechnology.

Mark Christopher Hersam is a professor of Chemistry and Materials Science Engineering at Northwestern University (2000–present) who, according to the National Science Foundation, has made "major breakthrough[s]" in the field of nanotechnology. He is a 2014 recipient of the MacArthur "Genius" Award and a 1996 Marshall Scholar. He is also an Executive Editor of ACS Nano. As of October 2023, he has been cited over 68,000 times according to Google Scholar.
The International Society for Nanoscale Science, Computation, and Engineering is a scientific society specializing in nanotechnology and DNA computing. It was started in 2004 by Nadrian Seeman, founder of the field of DNA nanotechnology. According to the society, its purpose is "to promote the study of the control of the arrangement of the atoms in matter, examine the principles that lead to such control, to develop tools and methods to increase such control, and to investigate the use of these principles for molecular computation, and for engineering on the finest possible scales."

Burkhard Rost is a scientist leading the Department for Computational Biology & Bioinformatics at the Faculty of Informatics of the Technical University of Munich (TUM). Rost chairs the Study Section Bioinformatics Munich involving the TUM and the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (LMU) in Munich. From 2007-2014 Rost was President of the International Society for Computational Biology (ISCB).
Alejandro Strachan is a scientist in the field of computational materials and the Reilly Professor of Materials Engineering at Purdue University. Before joining Purdue University, he was a staff member at Los Alamos National Laboratory.

Kwang Soo Kim is a South Korean professor in chemistry, an adjunct professor in physics, and the director of Center for Superfunctional Materials (CSM), of Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) in South Korea. He received his B.S. and M.S. degrees in Applied Chemistry from Seoul National University and also an M.S. degree in Physics from Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) (1975). He obtained his Ph.D. degree from University of California, Berkeley (1982). His research fields include Theoretical/Computational Chemistry/Physics and Experimental Nanosciences.
Franz-Josef Ulm is a structural engineer, an engineering scientist and a professor since 1999. He is Professor of Civil & Environmental Engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), the Faculty Director of the Concrete Sustainability Hub (CSHub@MIT). He is credited for discovering the nanogranular structure of Calcium-Silicate-Hydrates (C-S-H), the binding phase of concrete, and for the development of concepts of nanoengineering of concrete which combine advanced nanomechanics experiments with molecular simulation results. He speaks up for an environmental sustainable engineering, with “greener” concrete with lower CO2 footprint, to reduce the carbon footprint of concrete; to enhance concrete's resilience; and reduce its impact on global warming.
Lulu Qian is a Chinese-American biochemist who is a professor at the California Institute of Technology. Her research uses DNA-like molecules to build artificial machines.
Hendrik Dietz is a German physicist known for his contributions in the field of DNA origami. He is a full-professor for biophysics at the Technical University of Munich.
References
- ↑ Yurke, Bernard (2000), "A DNA-fuelled molecular machine made of DNA", Nature , 406 (6796): 605–8, Bibcode:2000Natur.406..605Y, doi:10.1038/35020524, PMID 10949296, S2CID 2064216 .
- ↑ Franco, Elisa (2011), "Timing molecular motion and production with a synthetic transcriptional clock", PNAS , 108 (40): E784-93, doi: 10.1073/pnas.1100060108 , PMC 3189071 , PMID 21921236 .
- ↑ Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Friedrich Simmel, Technische Universität München, archived from the original on 2014-11-13, retrieved 2014-11-13.