
Hanoi is the capital and second-most populous city of Vietnam. As evident by the literal translation of its name – 'inside the river' – portions of Hanoi's border are delineated by the Red and Black Rivers. As a municipality, Hanoi consists of 12 urban districts, 17 rural districts, and one district-level town. It has an area of 3,359.84 km2 (1,297.24 sq mi) and a population of 8,435,700 in 2022. In 2022, Hanoi has the second-highest gross regional domestic product of all Vietnam provinces and municipalities at 51.4 billion USD, behind Ho Chi Minh City. Hanoi Capital is also ASEAN 8th largest economy after Surabaya.
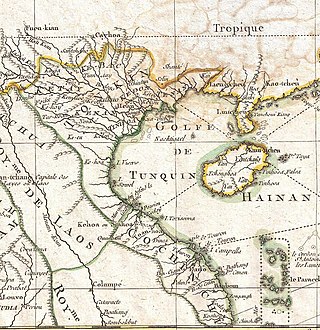
Tonkin, also spelled Tongkin, Tonquin or Tongking, is an exonym referring to the northern region of Vietnam. During the 17th and 18th centuries, this term referred to the domain Đàng Ngoài under Trịnh lords' control, including both the Northern and Thanh-Nghệ regions, north of the Gianh River. From 1884 to early 1945, this term was used for the French protectorate of Tonkin, composed of only the Northern region.

Nông Đức Mạnh is a Vietnamese politician who served as General Secretary of the Communist Party of Vietnam, the most powerful position in the Socialist Republic of Vietnam, from 22 April 2001 to 19 January 2011. His parents were Tày peasants. Nông Đức Mạnh was born in Cường Lợi, Na Rì District, Bắc Kạn Province. His own son is Nông Quốc Tuấn, party secretary for Bắc Giang Province.

Mỹ Sơn is a cluster of abandoned and partially ruined Shaiva Hindu temples in central Vietnam, constructed between the 4th and the 14th century by the Kings of Champa, an Indianized kingdom of the Cham people. The temples are dedicated to the veneration of God in accordance with Shaivism, wherein God is named Shiva, or The Auspicious One. In this particular complex, he is venerated under various local names, the most important of which is Bhadreshvara.

The culture of Vietnam are the customs and traditions of the Kinh people and the other ethnic groups of Vietnam. Vietnam is part of Southeast Asia and the Sinosphere due to the influence of Chinese culture on Vietnamese culture.

Văn Miếu, literally translated as Temple of Literature, is a temple dedicated to Confucius in Hanoi, northern Vietnam. The temple was built in 1070 at the time of Emperor Lý Thánh Tông, and it hosted the Imperial Academy, Vietnam's first national university, from 1076 to 1779.

The majority of Vietnamese do not follow any organized religion, instead participating in one or more practices of folk religions, such as venerating ancestors, or praying to deities, especially during Tết and other festivals. Folk religions were founded on endemic cultural beliefs that were historically affected by Confucianism and Taoism from ancient China, as well as by various strands of Buddhism. These three teachings or tam giáo were later joined by Christianity which has become a significant presence. Vietnam is also home of two indigenous religions: syncretic Caodaism and quasi-Buddhist Hoahaoism.

Vietnamese ceramics refers to ceramic art and pottery as a form of Vietnamese art and industry. Vietnamese pottery and ceramics has a long history spanning back to thousands of years ago, including long before Chinese domination, as archeological evidence supports.

Nguyễn Phú Trọng is a Vietnamese politician who has served as general secretary of the Communist Party of Vietnam since 2011. As the head of the party's Secretariat, Politburo and Central Military Commission, Trọng is Vietnam's paramount leader. He also previously served as president of Vietnam from 2018 to 2021.
Foreign Languages Press is a publishing house located in China.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Vietnam face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. From 2000, both male and female forms of same-sex sexual activity are legal and are believed to never have been criminalized in Vietnamese history. However, same-sex couples and households headed by same-sex couples are ineligible for the legal protections available to heterosexual couples. Vietnam provides limited anti-discrimination protections for transgender people. The right to change gender was officially legalized in Vietnam after the National Assembly passed an amendment to the Civil Code in 2015.

Venezuela and Vietnam established diplomatic links on December 8, 1989. Vietnam has an embassy in Caracas and Venezuela has an embassy in Hanoi. Though bilateral trade was US$11.7 million in 2007, relations show "great potential". Since 2008, the two countries have witnessed new developments in various fields, including politics, economics, culture and society, particularly in the oil and gas industry.

Stone stele records of imperial examinations of the Lê and Mạc dynasties is a collection of 82 stone stelae that contain the names and related information of doctoral laureates who passed the imperial examinations during the reign of the Lê and Mạc dynasties from 1442 to 1779. Preserved in good condition in the Temple of Literature of Hanoi, Vietnam, the collection became an inscription of the UNESCO's Memory of the World Programme on March 9, 2010.

The Katuic people are an ethnic group of about 102,551 who live in eastern Laos and central Vietnam. Numbered among the Katuic peoples, they speak a Mon-Khmer language. Katuic languages have been developed by Paul Sidwell, but Sidwell's work is not commonly used in Katuic communities due to language barriers.

Bún chả is a Vietnamese dish of grilled pork and noodles, which is thought to have originated from Hanoi, Vietnam. Bún chả is served with grilled fatty pork (chả) over a plate of white rice noodles (bún) and herbs with a side dish of dipping sauce. The dish was described in 1959 by Vietnamese food writer Vu Bang (1913–1984), who described Hanoi as a town "transfixed by bún chả." Hanoi's first bún chả restaurant was on Gia Ngư, Hoàn Kiếm District, in Hanoi's Old Quarter.
Kháng, also known as Mang U’, is an Austroasiatic language of Vietnam. It is closely related to the Bumang language of southern Yunnan, China.
Thế Giới Publishers is Vietnam's official foreign language publishing house.

Vũ Dân Tân was a Vietnamese artist who produced works in various media but was better known for his art objects and installation art. Most of his life he lived in Hanoi, where in 1990, together with his Russian wife Natalia Kraevskaia he co-founded Salon Natasha, the first private space for contemporary art and independent forum for creative people. He is considered one of the first protagonists of contemporary art in Vietnam.

Nguyen Van Quy was a Vietnamese composer and musician. He started as composer under the artist name Đỗ Quyên, and was later given the nicknames "Quỳ Sonate" and "Vietnamese Beethoven". He is known for having written nine sonatas for violin and piano, but also for several songs. He was a member of the French music copyright association.















