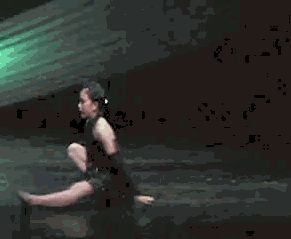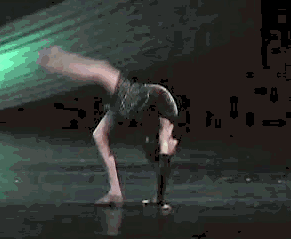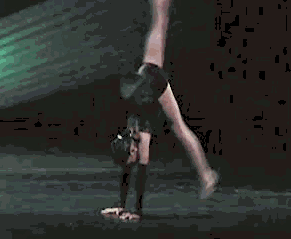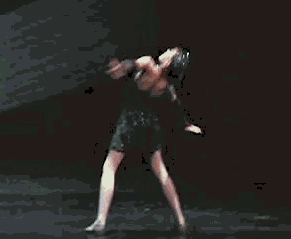Calisthenics or callisthenics is a form of strength training that utilizes an individual's body weight as resistance to perform multi-joint, compound movements with little or no equipment.

Contortion is a performance art in which performers called contortionists showcase their skills of extreme physical flexibility. Contortion acts often accompany acrobatics, circus acts, street performers and other live performing arts. Contortion acts are typically performed in front of a live audience. An act will showcase one or more artists performing a choreographed set of moves or poses, often to music, which require extreme flexibility. The physical flexibility required to perform such acts greatly exceeds that of the general population. It is the dramatic feats of seemingly inhuman flexibility that captivate audiences.
Because ballet became formalized in France, a significant part of ballet terminology is in the French language.
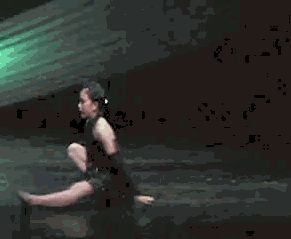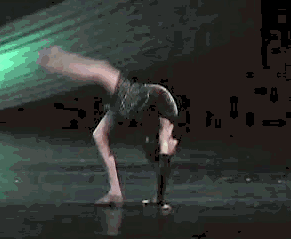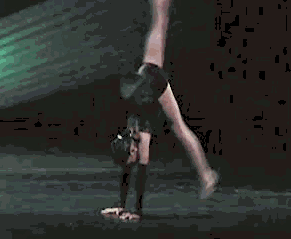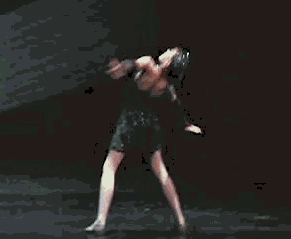
A back walkover is an acrobatic maneuver in which a person transitions from a standing position to a back bridge and then back to a standing position again, undergoing a complete revolution of the body in the process. Back walkovers are commonly performed in a variety of athletic activities, including acro dance, cheerleading, and rhythmic gymnastics. In artistic gymnastics, back walkovers are performed in floor exercises and on the balance beam.
Dance position is the position of a dancer or the mutual position of a dance couple assumed during a dance. Describing and mastering proper dance positions is an important part of dance technique.
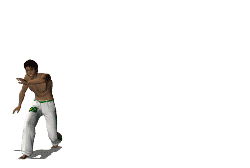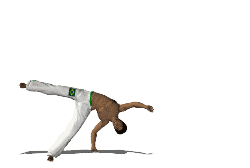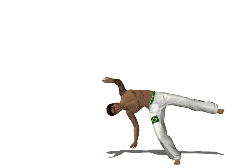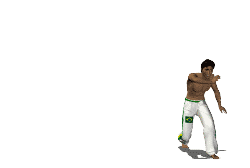
A cartwheel is a sideways rotary movement of the body. It is performed by bringing the hands to the floor one at a time while the body inverts. The legs travel over the body trunk while one or both hands are on the floor, and then the feet return to the floor one at a time, ending with the athlete standing upright. It is called a cartwheel because the performer's arms and legs move in a fashion similar to the spokes of a turning (cart) wheel.

A handspring is an acrobatic move in which a person executes a complete revolution of the body by lunging headfirst from an upright position into an inverted vertical position and then pushing off from the floor with the hands so as to leap back to an upright position. The direction of body rotation in a handspring may be either forward or backward, and either kind may be performed from a stationary standing position or while in motion.

The flare is an acrobatic move in which the performer alternates balancing the torso between either arm while swinging the legs beneath in continuous circles. It is a fundamental b-boying/bgirl power move, and in gymnastics it may be performed on a pommel horse or during the floor exercise. The move is commonly spelled flair in gymnastics and further may be called a "Thomas flair" after its originator, Kurt Thomas.

Static trapeze, also known as fixed trapeze, is a type of circus apparatus. In contrast to the other forms of trapeze, static trapeze the bars and ropes mainly stay in place.
A front limber is a gymnastics skill where the gymnast performs a handstand, carries the momentum forward, landing in a bridge, and then pulls their upper body upwards, ending in a standing position. It is related to a front walkover, but it is a variant as both legs are carried forward at once whereas each leg is taken over separately in a walkover.

Arabesque in dance, particularly ballet, is a body position in which a dancer stands on one leg–the supporting leg–with the other leg–the working leg–turned out and extended behind the body, with both legs held straight.

A front aerial is an acrobatic move in which a person executes a complete forward revolution of the body without touching the floor. Front aerials are performed in various physical activities, including acro dance and gymnastics. The front aerial is known by other names, including aerial walkover, front aerial walkover, front flip and front somersault.
This is a general glossary of the terms used in the sport of gymnastics.

The leg raise is a strength training exercise which targets the iliopsoas. Because the abdominal muscles are used isometrically to stabilize the body during the motion, leg raises are also often used to strengthen the rectus abdominis muscle and the internal and external oblique muscles.

An acrobatic flip is a sequence of body movements in which a person leaps into the air and rotates one or more times while airborne. Acrobatic flips are commonly performed in acro dance, free running, gymnastics, cheerleading, high jumping, tricking, goal celebrations, and various other activities. This contrasts with freestyle BMX flips, where a person rotates in the air along with a bicycle.

In dance and gymnastics, a turn is a rotation of the body about the vertical axis. It is usually a complete rotation of the body, although quarter (90°) and half (180°) turns are possible for some types of turns. Multiple, consecutive turns are typically named according to the number of 360° rotations.

Virabhadrasana or Warrior Pose is a group of related lunging standing asanas in modern yoga as exercise commemorating the exploits of a mythical warrior, Virabhadra. The name of the pose derives from the Hindu myth, but the pose is not recorded in the hatha yoga tradition until the 20th century. Virabhadrasana has some similarity with poses in the gymnastics of Niels Bukh the early 20th century; it has been suggested that it was adopted into yoga from the tradition of physical culture in India at that time, which was influenced by European gymnastics.

Añjaneyāsana, Crescent Moon Pose, or Ashva Sanchalanasana is a lunging back bending asana in modern yoga as exercise.