
Fucus vesiculosus, known by the common names bladderwrack, black tang, rockweed, sea grapes, bladder fucus, sea oak, cut weed, dyers fucus, red fucus and rock wrack, is a seaweed found on the coasts of the North Sea, the western Baltic Sea and the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. It was the original source of iodine, discovered in 1811, and was used extensively to treat goitre, a swelling of the thyroid gland related to iodine deficiency.

Ascophyllum nodosum is a large, common cold water seaweed or brown alga (Phaeophyceae) in the family Fucaceae. A. nodosum is also known in localities as feamainn bhuí, rockweed, Norwegian kelp, knotted kelp, knotted wrack or egg wrack. It is a seaweed that dominates the intertidal zone and grows only in the northern Atlantic Ocean, along the north-western coast of Europe including east Greenland and the north-eastern coast of North America, its range further south of these latitudes being limited by warmer ocean waters. Ascophyllum nodosum has been used numerous times in scientific research and has even been found to benefit humans through consumption.
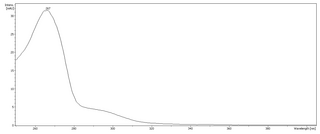
Phloroglucinol is an organic compound with the formula C6H3(OH)3. It is a colorless solid. It is used in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and explosives. Phloroglucinol is one of three isomeric benzenetriols. The other two isomers are hydroxyquinol (1,2,4-benzenetriol) and pyrogallol (1,2,3-benzenetriol). Phloroglucinol, and its benzenetriol isomers, are still defined as "phenols" according to the IUPAC official nomenclature rules of chemical compounds. Many such monophenolics are often termed polyphenols.

Arame, sea oak is a species of kelp, of the brown algae, best known for its use in Japanese cuisine.

Fucus spiralis is a species of seaweed, a brown alga, living on the littoral shore of the Atlantic coasts of Europe and North America. It has the common names of spiral wrack and flat wrack.
Eisenia arborea, or the southern sea palm, is a dominant species of kelp that is found on the western Pacific coast of North America, from Vancouver Island, Canada south to Mexico's Isla Magdalena and Baja California, as well as in Japan. They are commonly found from the midtidal areas stretching to the subtidal areas. It is an edible seaweed, a source of nutrients for grazing marine invertebrates and a source of alginic acid, a food thickener. Some of the algas have a hollow stipe above its holdfast with two branches terminating in multiple blades. Eisenia arborea is studied in order to predict environmental stress in oceans intertidal zones. Hollow stipes where present when the Eisenia arborea did not receive essential nutrients for its thalli development. Eisenia arborea with hollow stripes are believed to be evolved algae in order to increase their survival in harsh living conditions. They play a huge role in determining environmental stress.

Ecklonia is a genus of kelp belonging to the family Lessoniaceae.

Phlorotannins are a type of tannins found in brown algae such as kelps and rockweeds or sargassacean species, and in a lower amount also in some red algae. Contrary to hydrolysable or condensed tannins, these compounds are oligomers of phloroglucinol (polyphloroglucinols). As they are called tannins, they have the ability to precipitate proteins. It has been noticed that some phlorotannins have the ability to oxidize and form covalent bonds with some proteins. In contrast, under similar experimental conditions three types of terrestrial tannins apparently did not form covalent complexes with proteins.
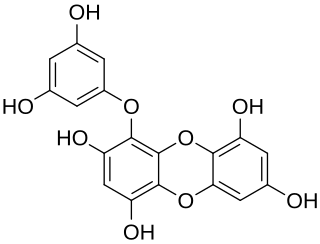
Eckol is a phlorotannin isolated from brown algae in the family Lessoniaceae such as species in the genus Ecklonia such as E. cava or E. kurome or in the genus Eisenia such as Eisenia bicyclis.
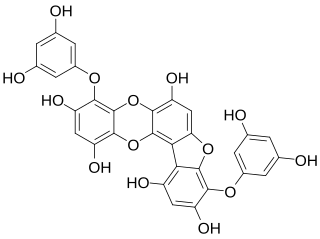
Phlorofucofuroeckol A is a phlorotannin isolated from brown algae species such as Eisenia bicyclis, Ecklonia cava, Ecklonia kurome or Ecklonia stolonifera.
Ecklonia stolonifera is a brown alga species in the genus Ecklonia found in the Sea of Japan. It is an edible species traditionally eaten in Japan.
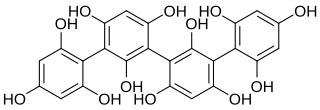
Tetrafucol A is a fucol-type phlorotannin found in the brown algae Ascophyllum nodosum, Analipus japonicus and Scytothamnus australis.
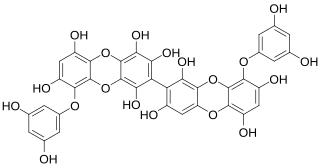
8,8'-Bieckol is an eckol-type phlorotannin found in the brown algae Ecklonia cava and Ecklonia kurome.

Eckstolonol is a phlorotannin found in the edible brown algae arame and turuarame.
Sargassum ringgoldianum is a brown alga species in the genus of Sargassum. The ethanol extract of S. ringgoldianum contains phlorotannins of the bifuhalol type, which shows an antioxidative activity.

Analipus japonicus, or sea fir, is a brown alga species in the genus Analipus.

Cystophora retroflexa is a brown alga species in the genus Cystophora. It found is found off the coasts of New Zealand and Australia. It is the type species of the genus. Prefers more sheltered environments compared to other Cystophora species, often found in sheltered reefs from 0 to 12 m in depth.
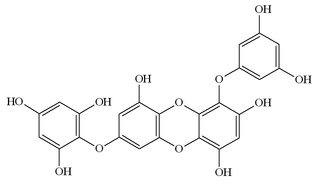
7-Phloroeckol is a phlorotannin found in the edible brown algae arame and turuarame.
The molecular formula C18H14O9 (molar mass: 374.29 g/mol, exact mass: 374.063782 u) may refer to:

Trifucol is a phlorotannin found in the brown algae Scytothamnus australis and Analipus japonicus.















