Related Research Articles

In nuclear physics, a nuclear chain reaction occurs when one single nuclear reaction causes an average of one or more subsequent nuclear reactions, thus leading to the possibility of a self-propagating series or "positive feedback loop" of these reactions. The specific nuclear reaction may be the fission of heavy isotopes. A nuclear chain reaction releases several million times more energy per reaction than any chemical reaction.

A pressurized water reactor (PWR) is a type of light-water nuclear reactor. PWRs constitute the large majority of the world's nuclear power plants. In a PWR, the primary coolant (water) is pumped under high pressure to the reactor core where it is heated by the energy released by the fission of atoms. The heated, high pressure water then flows to a steam generator, where it transfers its thermal energy to lower pressure water of a secondary system where steam is generated. The steam then drives turbines, which spin an electric generator. In contrast to a boiling water reactor (BWR), pressure in the primary coolant loop prevents the water from boiling within the reactor. All light-water reactors use ordinary water as both coolant and neutron moderator. Most use anywhere from two to four vertically mounted steam generators; VVER reactors use horizontal steam generators.

The pebble-bed reactor (PBR) is a design for a graphite-moderated, gas-cooled nuclear reactor. It is a type of very-high-temperature reactor (VHTR), one of the six classes of nuclear reactors in the Generation IV initiative.

In nuclear engineering, a critical mass is the smallest amount of fissile material needed for a sustained nuclear chain reaction. The critical mass of a fissionable material depends upon its nuclear properties, density, shape, enrichment, purity, temperature, and surroundings. The concept is important in nuclear weapon design.

In nuclear engineering, a neutron moderator is a medium that reduces the speed of fast neutrons, ideally without capturing any, leaving them as thermal neutrons with only minimal (thermal) kinetic energy. These thermal neutrons are immensely more susceptible than fast neutrons to propagate a nuclear chain reaction of uranium-235 or other fissile isotope by colliding with their atomic nucleus.

A fast-neutron reactor (FNR) or fast-spectrum reactor or simply a fast reactor is a category of nuclear reactor in which the fission chain reaction is sustained by fast neutrons, as opposed to slow thermal neutrons used in thermal-neutron reactors. Such a fast reactor needs no neutron moderator, but requires fuel that is relatively rich in fissile material when compared to that required for a thermal-neutron reactor. Around 20 land based fast reactors have been built, accumulating over 400 reactor years of operation globally. The largest was the Superphénix sodium cooled fast reactor in France that was designed to deliver 1,242 MWe. Fast reactors have been studied since the 1950s, as they provide certain advantages over the existing fleet of water-cooled and water-moderated reactors. These are:
A temperature coefficient describes the relative change of a physical property that is associated with a given change in temperature. For a property R that changes when the temperature changes by dT, the temperature coefficient α is defined by the following equation:
In nuclear engineering, the void coefficient is a number that can be used to estimate how much the reactivity of a nuclear reactor changes as voids form in the reactor moderator or coolant. Net reactivity in a reactor depends on several factors, one of which is the void coefficient. Reactors in which either the moderator or the coolant is a liquid will typically have a void coefficient which is either negative or positive. Reactors in which neither the moderator nor the coolant is a liquid will have a zero void coefficient. It is unclear how the definition of "void" coefficient applies to reactors in which the moderator/coolant is neither liquid nor gas.

The light-water reactor (LWR) is a type of thermal-neutron reactor that uses normal water, as opposed to heavy water, as both its coolant and neutron moderator; furthermore a solid form of fissile elements is used as fuel. Thermal-neutron reactors are the most common type of nuclear reactor, and light-water reactors are the most common type of thermal-neutron reactor.
Passive nuclear safety is a design approach for safety features, implemented in a nuclear reactor, that does not require any active intervention on the part of the operator or electrical/electronic feedback in order to bring the reactor to a safe shutdown state, in the event of a particular type of emergency. Such design features tend to rely on the engineering of components such that their predicted behaviour would slow down, rather than accelerate the deterioration of the reactor state; they typically take advantage of natural forces or phenomena such as gravity, buoyancy, pressure differences, conduction or natural heat convection to accomplish safety functions without requiring an active power source. Many older common reactor designs use passive safety systems to a limited extent, rather, relying on active safety systems such as diesel-powered motors. Some newer reactor designs feature more passive systems; the motivation being that they are highly reliable and reduce the cost associated with the installation and maintenance of systems that would otherwise require multiple trains of equipment and redundant safety class power supplies in order to achieve the same level of reliability. However, weak driving forces that power many passive safety features can pose significant challenges to effectiveness of a passive system, particularly in the short term following an accident.
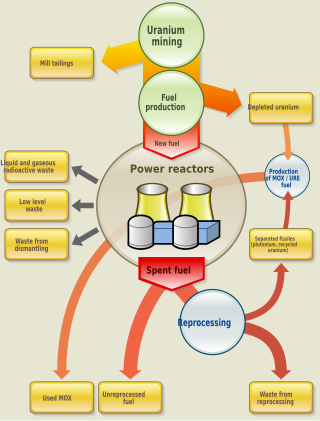
Nuclear fuel is material used in nuclear power stations to produce heat to power turbines. Heat is created when nuclear fuel undergoes nuclear fission. Nuclear fuel has the highest energy density of all practical fuel sources. The processes involved in mining, refining, purifying, using, and disposing of nuclear fuel are collectively known as the nuclear fuel cycle.

In nuclear physics, the concept of a neutron cross section is used to express the likelihood of interaction between an incident neutron and a target nucleus. The neutron cross section σ can be defined as the area in cm2 for which the number of neutron-nuclei reactions taking place is equal to the product of the number of incident neutrons that would pass through the area and the number of target nuclei. In conjunction with the neutron flux, it enables the calculation of the reaction rate, for example to derive the thermal power of a nuclear power plant. The standard unit for measuring the cross section is the barn, which is equal to 10−28 m2 or 10−24 cm2. The larger the neutron cross section, the more likely a neutron will react with the nucleus.

In atomic physics, Doppler broadening is broadening of spectral lines due to the Doppler effect caused by a distribution of velocities of atoms or molecules. Different velocities of the emitting particles result in different Doppler shifts, the cumulative effect of which is the emission (absorption) line broadening. This resulting line profile is known as a Doppler profile.
Nuclear reactor physics is the field of physics that studies and deals with the applied study and engineering applications of chain reaction to induce a controlled rate of fission in a nuclear reactor for the production of energy. Most nuclear reactors use a chain reaction to induce a controlled rate of nuclear fission in fissile material, releasing both energy and free neutrons. A reactor consists of an assembly of nuclear fuel, usually surrounded by a neutron moderator such as regular water, heavy water, graphite, or zirconium hydride, and fitted with mechanisms such as control rods which control the rate of the reaction.
In applications such as nuclear reactors, a neutron poison is a substance with a large neutron absorption cross-section. In such applications, absorbing neutrons is normally an undesirable effect. However, neutron-absorbing materials, also called poisons, are intentionally inserted into some types of reactors in order to lower the high reactivity of their initial fresh fuel load. Some of these poisons deplete as they absorb neutrons during reactor operation, while others remain relatively constant.

The neutron detection temperature, also called the neutron energy, indicates a free neutron's kinetic energy, usually given in electron volts. The term temperature is used, since hot, thermal and cold neutrons are moderated in a medium with a certain temperature. The neutron energy distribution is then adapted to the Maxwell distribution known for thermal motion. Qualitatively, the higher the temperature, the higher the kinetic energy of the free neutrons. The momentum and wavelength of the neutron are related through the de Broglie relation. The long wavelength of slow neutrons allows for the large cross section.
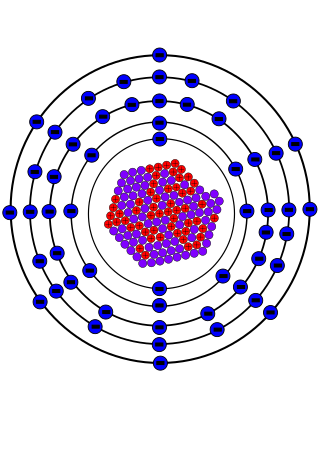
Xenon-135 (135Xe) is an unstable isotope of xenon with a half-life of about 9.2 hours. 135Xe is a fission product of uranium and it is the most powerful known neutron-absorbing nuclear poison, with a significant effect on nuclear reactor operation. The ultimate yield of xenon-135 from fission is 6.3%, though most of this is from fission-produced tellurium-135 and iodine-135.
The iodine pit, also called the iodine hole or xenon pit, is a temporary disabling of a nuclear reactor due to buildup of short-lived nuclear poisons in the reactor core. The main isotope responsible is 135Xe, mainly produced by natural decay of 135I. 135I is a weak neutron absorber, while 135Xe is the strongest known neutron absorber. When 135Xe builds up in the fuel rods of a reactor, it significantly lowers their reactivity, by absorbing a significant amount of the neutrons that provide the nuclear reaction.
A pressurized heavy-water reactor (PHWR) is a nuclear reactor that uses heavy water (deuterium oxide D2O) as its coolant and neutron moderator. PHWRs frequently use natural uranium as fuel, but sometimes also use very low enriched uranium. The heavy water coolant is kept under pressure to avoid boiling, allowing it to reach higher temperature (mostly) without forming steam bubbles, exactly as for a pressurized water reactor (PWR). While heavy water is very expensive to isolate from ordinary water (often referred to as light water in contrast to heavy water), its low absorption of neutrons greatly increases the neutron economy of the reactor, avoiding the need for enriched fuel. The high cost of the heavy water is offset by the lowered cost of using natural uranium and/or alternative fuel cycles. As of the beginning of 2001, 31 PHWRs were in operation, having a total capacity of 16.5 GW(e), representing roughly 7.76% by number and 4.7% by generating capacity of all current operating reactors.
A dollar is a unit of reactivity for a nuclear reactor, calibrated to the interval between the conditions of criticality and prompt criticality. Prompt criticality will result in an extremely rapid power rise, with the resultant destruction of the reactor, unless it is specifically designed to tolerate the condition. A cent is 1⁄100 of a dollar.