Future Energy is a former accreditation scheme for green electricity in the United Kingdom, designed to support and stimulate electricity generation from renewable energy sources. The scheme was launched in 1999 [1] and was operated by the Energy Saving Trust until funding expired in 2002. [2] [3]
It is thought that funding was not renewed due to few suppliers were prepared to accept the new requirements for green tariffs proposed by the Trust following the introduction of the Renewables Obligation. [4] As of 2007 the scheme has not been replaced, although Friends of the Earth, who used to run their own scheme, have been among those calling on the government to do so. [5]
The United Kingdom's Climate Change Programme was launched in November 2000 by the British government in response to its commitment agreed at the 1992 United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED). The 2000 programme was updated in March 2006 following a review launched in September 2004.
The Renewables Obligation (RO) is designed to encourage generation of electricity from eligible renewable sources in the United Kingdom. It was introduced in England and Wales and in a different form in Scotland in April 2002 and in Northern Ireland in April 2005, replacing the Non-Fossil Fuel Obligation which operated from 1990.

Microgeneration is the small-scale production of heat or electric power from a "low carbon source," as an alternative or supplement to traditional centralized grid-connected power.

Energy in the United Kingdom came mostly from fossil fuels in 2021. Total energy consumption in the United Kingdom was 142.0 million tonnes of oil equivalent in 2019. In 2014, the UK had an energy consumption per capita of 2.78 tonnes of oil equivalent compared to a world average of 1.92 tonnes of oil equivalent. Demand for electricity in 2014 was 34.42 GW on average coming from a total electricity generation of 335.0 TWh.

Good Energy Group PLC is a British energy company based in Chippenham, Wiltshire that provides services in the electrification of transport and decentralised renewable energy generation such as domestic solar panels. The company is also an energy retailer, and built a portfolio of wind and solar generation which was sold in 2022. Founded by Juliet Davenport, its CEO is Nigel Pocklington.
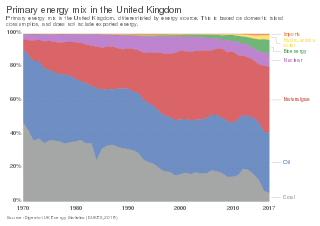
The energy policy of the United Kingdom refers to the United Kingdom's efforts towards reducing energy intensity, reducing energy poverty, and maintaining energy supply reliability. The United Kingdom has had success in this, though energy intensity remains high. There is an ambitious goal to reduce carbon dioxide emissions in future years, but it is unclear whether the programmes in place are sufficient to achieve this objective. Regarding energy self-sufficiency, UK policy does not address this issue, other than to concede historic energy security is currently ceasing to exist.
The Low Carbon Building Programme (LCBP) was a payments system in England, Scotland and Wales. The UK Government programme was administered by BERR and ran from 1 April 2006 until its closure to new applications on 24 May 2010. The scheme was replaced by the Renewable Heat Incentive in November 2011.
Energy Saving Trust (EST) is a British organization devoted to promoting energy efficiency, energy conservation, and the sustainable use of energy, thereby reducing carbon dioxide emissions and helping to prevent man-made climate change. It was founded in the United Kingdom as a government-sponsored initiative in 1992, following the global Earth Summit.
The CRC Energy Efficiency Scheme was a mandatory carbon emissions reduction scheme in the United Kingdom which applied to large energy-intensive organisations in the public and private sectors. It was estimated that the scheme would reduce carbon emissions by 1.2 million tonnes of carbon per year by 2020. In an effort to avoid dangerous climate change, the British Government first committed to cutting UK carbon emissions by 60% by 2050, and in October 2008 increased this commitment to 80%. The scheme has also been credited with driving up demand for energy-efficient goods and services.
Financial incentives for photovoltaics are incentives offered to electricity consumers to install and operate solar-electric generating systems, also known as photovoltaics (PV).

Solar power represented a very small part of electricity production in the United Kingdom until the 2010s when it increased rapidly, thanks to feed-in tariff (FIT) subsidies and the falling cost of photovoltaic (PV) panels.

The Eugene Green Energy Standard was an international standard to which national or international green electricity labelling schemes could be accredited to confirm that they provide genuine environmental benefits. It was designed to encourage the generation and use of additional renewable energy sources for electricity generation, although the limited use of additional natural gas-fired cogeneration plant was also supported. Initially funded in part through the EU's clean-e programme, but also including some participants from outside Europe, the Eugene standard was formally discontinued after February 2009.

The availability and uptake of green electricity in the United Kingdom has increased in the 21st century. There are a number of suppliers offering green electricity in the United Kingdom. In theory these types of tariffs help to lower carbon dioxide emissions by increasing consumer demand for green electricity and encouraging more renewable energy plant to be built. Since Ofgem's 2014 regulations there are now set criteria defining what can be classified as a green source product. As well as holding sufficient guarantee of origin certificates to cover the electricity sold to consumers, suppliers are also required to show additionality by contributing to wider environmental and low carbon funds.

Renewable energy in the United Kingdom contributes to production for electricity, heat, and transport.
A feed-in tariff is a policy mechanism designed to accelerate investment in renewable energy technologies by offering long-term contracts to renewable energy producers. This means promising renewable energy producers an above-market price and providing price certainty and long-term contracts that help finance renewable energy investments. Typically, FITs award different prices to different sources of renewable energy in order to encourage development of one technology over another. For example, technologies such as wind power and solar PV are awarded a higher price per kWh than tidal power. FITs often include a "degression": a gradual decrease of the price or tariff in order to follow and encourage technological cost reductions.
The electricity sector in Argentina constitutes the third largest power market in Latin America. It relies mostly on thermal generation and hydropower generation (36%). The prevailing natural gas-fired thermal generation is at risk due to the uncertainty about future gas supply.

Feed-in tariffs in Australia are the feed-in tariffs (FITs) paid under various State schemes to non-commercial producers of electricity generated by solar photovoltaic (PV) systems using solar panels. They are a way of subsidising and encouraging uptake of renewable energy and in Australia have been enacted at the State level, in conjunction with a federal mandatory renewable energy target.
A feed-in tariff is when payments are given by energy suppliers if a property or organisation generates their own electricity using technology such as solar panels or wind turbines and feeds any surplus back to the grid. In the United Kingdom, they were entered into law by the Energy Act 2008 and took effect from April 2010. The scheme closed to new applicants on 31 March 2019.

A consumer green energy program is a program that enables households to buy energy from renewable sources. By allowing consumers to purchase renewable energy, it simultaneously diverts the utilization of fossil fuels and promotes the use of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind.