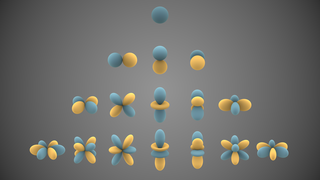In mathematics, specifically in functional analysis, a C∗-algebra is a Banach algebra together with an involution satisfying the properties of the adjoint. A particular case is that of a complex algebra A of continuous linear operators on a complex Hilbert space with two additional properties:
In mathematics, the determinant is a scalar value that is a function of the entries of a square matrix. The determinant of a matrix A is commonly denoted det(A), det A, or |A|. Its value characterizes some properties of the matrix and the linear map represented by the matrix. In particular, the determinant is nonzero if and only if the matrix is invertible and the linear map represented by the matrix is an isomorphism. The determinant of a product of matrices is the product of their determinants (which follows directly from the above properties).

In mathematical physics and mathematics, the Pauli matrices are a set of three 2 × 2 complex matrices which are Hermitian, involutory and unitary. Usually indicated by the Greek letter sigma, they are occasionally denoted by tau when used in connection with isospin symmetries.
In algebra, the dual numbers are a hypercomplex number system first introduced in the 19th century. They are expressions of the form a + bε, where a and b are real numbers, and ε is a symbol taken to satisfy with .
In category theory, a branch of mathematics, a natural transformation provides a way of transforming one functor into another while respecting the internal structure of the categories involved. Hence, a natural transformation can be considered to be a "morphism of functors". Informally, the notion of a natural transformation states that a particular map between functors can be done consistently over an entire category.

In mathematics, the orthogonal group in dimension , denoted , is the group of distance-preserving transformations of a Euclidean space of dimension that preserve a fixed point, where the group operation is given by composing transformations. The orthogonal group is sometimes called the general orthogonal group, by analogy with the general linear group. Equivalently, it is the group of orthogonal matrices, where the group operation is given by matrix multiplication. The orthogonal group is an algebraic group and a Lie group. It is compact.
In mechanics and geometry, the 3D rotation group, often denoted SO(3), is the group of all rotations about the origin of three-dimensional Euclidean space under the operation of composition.

In mathematics, the unitary group of degree n, denoted U(n), is the group of n × n unitary matrices, with the group operation of matrix multiplication. The unitary group is a subgroup of the general linear group GL(n, C). Hyperorthogonal group is an archaic name for the unitary group, especially over finite fields. For the group of unitary matrices with determinant 1, see Special unitary group.

In mathematics, the special unitary group of degree n, denoted SU(n), is the Lie group of n × n unitary matrices with determinant 1.
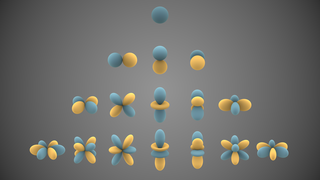
In mathematics and physical science, spherical harmonics are special functions defined on the surface of a sphere. They are often employed in solving partial differential equations in many scientific fields.

In mathematics and theoretical physics, a representation of a Lie group is a linear action of a Lie group on a vector space. Equivalently, a representation is a smooth homomorphism of the group into the group of invertible operators on the vector space. Representations play an important role in the study of continuous symmetry. A great deal is known about such representations, a basic tool in their study being the use of the corresponding 'infinitesimal' representations of Lie algebras.

In nuclear physics, the chiral model, introduced by Feza Gürsey in 1960, is a phenomenological model describing effective interactions of mesons in the chiral limit (where the masses of the quarks go to zero), but without necessarily mentioning quarks at all. It is a nonlinear sigma model with the principal homogeneous space of a Lie group as its target manifold. When the model was originally introduced, this Lie group was the SU(N), where N is the number of quark flavors. The Riemannian metric of the target manifold is given by a positive constant multiplied by the Killing form acting upon the Maurer–Cartan form of SU(N).
In theoretical physics, dimensional regularization is a method introduced by Giambiagi and Bollini as well as – independently and more comprehensively – by 't Hooft and Veltman for regularizing integrals in the evaluation of Feynman diagrams; in other words, assigning values to them that are meromorphic functions of a complex parameter d, the analytic continuation of the number of spacetime dimensions.

The Lorentz group is a Lie group of symmetries of the spacetime of special relativity. This group can be realized as a collection of matrices, linear transformations, or unitary operators on some Hilbert space; it has a variety of representations. This group is significant because special relativity together with quantum mechanics are the two physical theories that are most thoroughly established, and the conjunction of these two theories is the study of the infinite-dimensional unitary representations of the Lorentz group. These have both historical importance in mainstream physics, as well as connections to more speculative present-day theories.
In mathematics and theoretical physics, a supermatrix is a Z2-graded analog of an ordinary matrix. Specifically, a supermatrix is a 2×2 block matrix with entries in a superalgebra. The most important examples are those with entries in a commutative superalgebra or an ordinary field.
In quantum field theory and statistical mechanics, loop integrals are the integrals which appear when evaluating the Feynman diagrams with one or more loops by integrating over the internal momenta. These integrals are used to determine counterterms, which in turn allow evaluation of the beta function, which encodes the dependence of coupling for an interaction on an energy scale .
In mathematics, a logarithm of a matrix is another matrix such that the matrix exponential of the latter matrix equals the original matrix. It is thus a generalization of the scalar logarithm and in some sense an inverse function of the matrix exponential. Not all matrices have a logarithm and those matrices that do have a logarithm may have more than one logarithm. The study of logarithms of matrices leads to Lie theory since when a matrix has a logarithm then it is in an element of a Lie group and the logarithm is the corresponding element of the vector space of the Lie algebra.

In geometry, a three-dimensional space is a mathematical space in which three values (coordinates) are required to determine the position of a point. Most commonly, it is the three-dimensional Euclidean space, the Euclidean n-space of dimension n=3 that models physical space. More general three-dimensional spaces are called 3-manifolds. The term may also refer colloquially to a subset of space, a three-dimensional region, a solid figure.
In mathematics, a zonal spherical function or often just spherical function is a function on a locally compact group G with compact subgroup K (often a maximal compact subgroup) that arises as the matrix coefficient of a K-invariant vector in an irreducible representation of G. The key examples are the matrix coefficients of the spherical principal series, the irreducible representations appearing in the decomposition of the unitary representation of G on L2(G/K). In this case the commutant of G is generated by the algebra of biinvariant functions on G with respect to K acting by right convolution. It is commutative if in addition G/K is a symmetric space, for example when G is a connected semisimple Lie group with finite centre and K is a maximal compact subgroup. The matrix coefficients of the spherical principal series describe precisely the spectrum of the corresponding C* algebra generated by the biinvariant functions of compact support, often called a Hecke algebra. The spectrum of the commutative Banach *-algebra of biinvariant L1 functions is larger; when G is a semisimple Lie group with maximal compact subgroup K, additional characters come from matrix coefficients of the complementary series, obtained by analytic continuation of the spherical principal series.
In this article, we discuss certain applications of the dual quaternion algebra to 2D geometry. At this present time, the article is focused on a 4-dimensional subalgebra of the dual quaternions which we will call the planar quaternions.
J. Hoppe, Quantum Theory of a Massless Relativistic Surface and a Two dimensional Bound State Problem. PhD thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1982.