GADEROS (Galileo Demonstrator for Railway Operation System) is a study sponsored by the European Commission with the purpose to make use of the Galileo Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) when it becomes functional in 2008.
Current terrestrial railroad tracking systems require huge distances as safety margins. This leads to lower freight and passenger throughput.

Galileo is a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) that went live in 2016, created by the European Union through the European Space Agency (ESA), operated by the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA), headquartered in Prague, Czech Republic, with two ground operations centres in Fucino, Italy, and Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany. The €10 billion project is named after the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei. One of the aims of Galileo is to provide an independent high-precision positioning system so European political and military authorities do not have to rely on the US GPS, or the Russian GLONASS systems, which could be disabled or degraded by their operators at any time. The use of basic (lower-precision) Galileo services is free and open to everyone. A fully encrypted higher-precision service is available for free to government-authorized users. Galileo is intended to provide horizontal and vertical position measurements within 1 m precision. Galileo is also to provide a new global search and rescue (SAR) function as part of the MEOSAR system.
Computer reservation systems, or central reservation systems (CRS), are computerized systems used to store and retrieve information and conduct transactions related to air travel, hotels, car rental, or other activities. Originally designed and operated by airlines, CRSs were later extended for use by travel agencies, and global distribution systems (GDSs) to book and sell tickets for multiple airlines. Most airlines have outsourced their CRSs to GDS companies, which also enable consumer access through Internet gateways. Modern GDSs typically also allow users to book hotel rooms, rental cars, airline tickets as well as other activities and tours. They also provide access to railway reservations and bus reservations in some markets, although these are not always integrated with the main system. These are also used to relay computerized information for users in the hotel industry, making reservation and ensuring that the hotel is not overbooked.

A satellite navigation or satnav system is a system that uses satellites to provide autonomous geo-spatial positioning. It allows satellite navigation devices to determine their location to high precision using time signals transmitted along a line of sight by radio from satellites. The system can be used for providing position, navigation or for tracking the position of something fitted with a receiver. The signals also allow the electronic receiver to calculate the current local time to a high precision, which allows time synchronisation. These uses are collectively known as Positioning, Navigation and Timing (PNT). Satnav systems operate independently of any telephonic or internet reception, though these technologies can enhance the usefulness of the positioning information generated.

Galileo Ferraris was an Italian university professor, physicist and electrical engineer, one of the pioneers of AC power system and inventor of the induction motor although he never patented his work. Many newspapers touted that his work on the induction motor and power transmission systems were some of the greatest inventions of all ages. He published an extensive and complete monograph on the experimental results obtained with open-circuit transformers of the type designed by the power engineers Lucien Gaulard and John Dixon Gibbs.
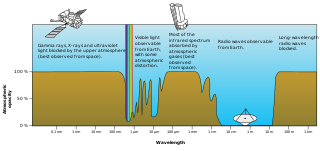
Visible-light astronomy encompasses a wide variety of observations via telescopes that are sensitive in the range of visible light. Visible-light astronomy is part of optical astronomy, and differs from astronomies based on invisible types of light in the electromagnetic radiation spectrum, such as radio waves, infrared waves, ultraviolet waves, X-ray waves and gamma-ray waves. Visible light ranges from 380 to 750 nanometers in wavelength.

The Galileo affair began around 1610 and culminated with the trial and condemnation of Galileo Galilei by the Roman Catholic Inquisition in 1633. Galileo was prosecuted for his support of heliocentrism, the astronomical model in which the Earth and planets revolve around the Sun at the centre of the universe.

Pisa International Airport, also named Galileo Galilei Airport is an airport located in Pisa, Italy. It is the main airport in Tuscany and the 10th in Italy in terms of passengers. It is named after Galileo Galilei, the famous scientist and native of Pisa. The airport was first developed for the military in the 1930s and 1940s. The airport was used by 5,233,118 passengers in 2017. It serves as a focus city of Ryanair.

The New Georgia Encyclopedia (NGE) is a web-based encyclopedia containing over 2,000 articles about the state of Georgia. It is a program of Georgia Humanities (GH), in partnership with the University of Georgia Press, the University System of Georgia/Georgia Library Learning Online (GALILEO), and the Office of the Governor.
The Digital Library of Georgia (DLG) is an online, public collection of documents and media about the history and culture of the state of Georgia, United States. The collection includes more than a million digitized objects from more than 200 Georgia-related collections. The DLG connects users to content from 65 libraries, archives, museums, historical societies, and other institutions, as well as 100 agencies of state government. It can be searched or browsed through the Digital Library of Georgia website.
Galileo is a computer reservations system (CRS) owned by Travelport. As of 2000, it had a 26.4% share of worldwide CRS airline bookings.
In geodesy and astrometry, earth orientation parameters (EOP) describe irregularities in the rotation of planet Earth. EOP provide the rotational transform from the International Terrestrial Reference System (ITRS) to the International Celestial Reference System (ICRS), or vice versa, as a function of time.
LOCOPROL has been a project to research the integration of satellite navigation into railway networks targeting low-density track lines. It is supposed to extend the ERTMS train protection systems. The partner project LOCOLOC was looking into cab signaling and speed control measures.

Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. Commonly referred to as Galileo, his name is pronounced. He was born in the city of Pisa, then part of the Duchy of Florence. Galileo has been called the "father" of observational astronomy, modern-era classical physics, the scientific method, and modern science.
"Discourse on the Tides" is an essay written by Galileo Galilei in 1616 as a letter to Alessandro Orsini that attempted to explain the motion of Earth's tides as a consequence of Earth's rotation and revolution around the Sun. The same ideas form an important part of Galileo's Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems. Galileo's theory was in fact erroneous, as proven by future scientific research and contemporary observations.

Soyuz at the Guiana Space Centre was a European Space Agency (ESA) programme for operating Soyuz-ST launch vehicles from Centre Spatial Guyanais (CSG), providing medium-size launch capability for Arianespace to complement the light Vega and heavy-lift Ariane 5. The Soyuz vehicle was supplied by the Roscosmos with TsSKB-Progress and NPO Lavochkin, while additional components were supplied by Airbus, Thales Group and RUAG. Autor LV (ICBM) = NPO "Energia", Kaliningrad.

The European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA) is a space agency, managing the European Union Space Programme as one of the agencies of the European Union (EU). It was initially created as the European Global Navigation Satellite Systems Supervisory Authority (GSA) in 2004, reorganised into the European Global Navigation Satellite Systems Agency in 2010, and established in its current form on May 12, 2021. EUSPA is a separate entity from the European Space Agency (ESA), although the two entities work together closely.
The United Kingdom Global Navigation Satellite System was a United Kingdom Space Agency (UKSA) research programme which, between May 2018 and September 2020, developed outline proposals for a United Kingdom (UK) owned and operated conventional satellite navigation system, as a British alternative to the European Union (EU) owned and operated Galileo Global Navigation Satellite System. The main reason was to provide a national and independent system, to ensure UK security following its withdrawal from the EU as a result of Brexit. It was fully supported by the Ministry of Defence.

Galileo was an American robotic space probe that studied the planet Jupiter and its moons, as well as the asteroids Gaspra and Ida. Named after the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei, it consisted of an orbiter and an entry probe. It was delivered into Earth orbit on October 18, 1989, by Space ShuttleAtlantis, during STS-34. Galileo arrived at Jupiter on December 7, 1995, after gravitational assist flybys of Venus and Earth, and became the first spacecraft to orbit an outer planet.

The 1990 Georgia lieutenant gubernatorial election was held on November 6, 1990, to elect the lieutenant governor of Georgia, concurrently with the 1990 gubernatorial election, as well as elections to the United States Senate and elections to the United States House of Representatives and various state and local elections. Georgia is one of 21 states that elects its lieutenant governor separately from its governor.