The Domain Name System (DNS) is the hierarchical and decentralized naming system used to identify computers reachable through the Internet or other Internet Protocol (IP) networks. The resource records contained in the DNS associate domain names with other forms of information. These are most commonly used to map human-friendly domain names to the numerical IP addresses computers need to locate services and devices using the underlying network protocols, but have been extended over time to perform many other functions as well. The Domain Name System has been an essential component of the functionality of the Internet since 1985.

Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is an extension of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). It is used for secure communication over a computer network, and is widely used on the Internet. In HTTPS, the communication protocol is encrypted using Transport Layer Security (TLS) or, formerly, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). The protocol is therefore also referred to as HTTP over TLS, or HTTP over SSL.

A web server is computer software and underlying hardware that accepts requests via HTTP or its secure variant HTTPS. A user agent, commonly a web browser or web crawler, initiates communication by making a request for a web page or other resource using HTTP, and the server responds with the content of that resource or an error message. A web server can also accept and store resources sent from the user agent if configured to do so.
An email client, email reader or, more formally, message user agent (MUA) or mail user agent is a computer program used to access and manage a user's email.
The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard communication protocol used for the transfer of computer files from a server to a client on a computer network. FTP is built on a client–server model architecture using separate control and data connections between the client and the server. FTP users may authenticate themselves with a clear-text sign-in protocol, normally in the form of a username and password, but can connect anonymously if the server is configured to allow it. For secure transmission that protects the username and password, and encrypts the content, FTP is often secured with SSL/TLS (FTPS) or replaced with SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP).

In computer networking, a proxy server is a server application that acts as an intermediary between a client requesting a resource and the server providing that resource.

Squid is a caching and forwarding HTTP web proxy. It has a wide variety of uses, including speeding up a web server by caching repeated requests, caching web, DNS and other computer network lookups for a group of people sharing network resources, and aiding security by filtering traffic. Although primarily used for HTTP and FTP, Squid includes limited support for several other protocols including Internet Gopher, SSL, TLS and HTTPS. Squid does not support the SOCKS protocol, unlike Privoxy, with which Squid can be used in order to provide SOCKS support.
BitTorrent is a communication protocol for peer-to-peer file sharing (P2P), which enables users to distribute data and electronic files over the Internet in a decentralized manner.
SOCKS is an Internet protocol that exchanges network packets between a client and server through a proxy server. SOCKS5 optionally provides authentication so only authorized users may access a server. Practically, a SOCKS server proxies TCP connections to an arbitrary IP address, and provides a means for UDP packets to be forwarded.
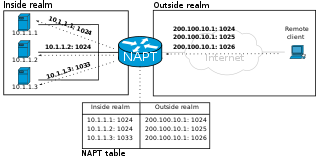
In computer networking, port forwarding or port mapping is an application of network address translation (NAT) that redirects a communication request from one address and port number combination to another while the packets are traversing a network gateway, such as a router or firewall. This technique is most commonly used to make services on a host residing on a protected or masqueraded (internal) network available to hosts on the opposite side of the gateway, by remapping the destination IP address and port number of the communication to an internal host.

A content delivery network, or content distribution network (CDN), is a geographically distributed network of proxy servers and their data centers. The goal is to provide high availability and performance by distributing the service spatially relative to end users. CDNs came into existence in the late 1990s as a means for alleviating the performance bottlenecks of the Internet as the Internet was starting to become a mission-critical medium for people and enterprises. Since then, CDNs have grown to serve a large portion of the Internet content today, including web objects, downloadable objects, applications, live streaming media, on-demand streaming media, and social media sites.
In computer networks, a tunneling protocol is a communication protocol which allows for the movement of data from one network to another, by exploiting encapsulation. It involves allowing private network communications to be sent across a public network through a process called encapsulation.
There are a number of security and safety features new to Windows Vista, most of which are not available in any prior Microsoft Windows operating system release.
Peer-to-peer file sharing (P2P) systems like Gnutella, KaZaA, and eDonkey/eMule, have become extremely popular in recent years, with the estimated user population in the millions. An academic research paper analyzed Gnutella and eMule protocols and found weaknesses in the protocol; many of the issues found in these networks are fundamental and probably common on other P2P networks. Users of file sharing networks, such as eMule and Gnutella, are subject to monitoring of their activity. Clients may be tracked by IP address, DNS name, software version they use, files they share, queries they initiate, and queries they answer to. Clients may also share their private files to the network without notice due to inappropriate settings.
Garden Networks is a not-for-profit organization registered in Canada, that specializes in providing Internet anti-censorship/Internet privacy products for free. The full name of Garden Networks is Garden Networks for Freedom of Information.

UltraSurf is a freeware Internet censorship circumvention product created by UltraReach Internet Corporation. The software bypasses Internet censorship and firewalls using an HTTP proxy server, and employs encryption protocols for privacy.
Internet censorship circumvention is the use of various methods and tools to bypass internet censorship.
Browser security is the application of Internet security to web browsers in order to protect networked data and computer systems from breaches of privacy or malware. Security exploits of browsers often use JavaScript, sometimes with cross-site scripting (XSS) with a secondary payload using Adobe Flash. Security exploits can also take advantage of vulnerabilities that are commonly exploited in all browsers.
Hotspot Shield is a public VPN service operated by AnchorFree, Inc. By establishing an encrypted connection with the Hotspot Shield servers, the service protects its users' Internet traffic from eavesdropping. Hotspot Shield was used to bypass government censorship during the Arab Spring protests in Egypt, Tunisia, and Libya.
Outline VPN is a free and open-source tool that deploys Shadowsocks servers on multiple cloud service providers. The software suite also includes client software for multiple platforms. Outline was developed by Jigsaw, a technology incubator created by Google.[3]








