Related Research Articles
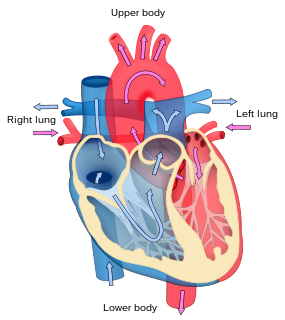
Cardiology is a branch of medicine that deals with the disorders of the heart as well as some parts of the circulatory system. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease and electrophysiology. Physicians who specialize in this field of medicine are called cardiologists, a specialty of internal medicine. Pediatric cardiologists are pediatricians who specialize in cardiology. Physicians who specialize in cardiac surgery are called cardiothoracic surgeons or cardiac surgeons, a specialty of general surgery.
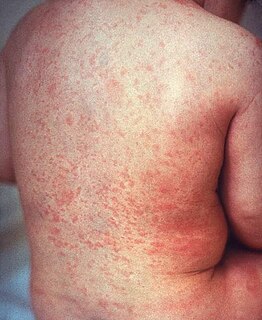
Rubella, also known as German measles or three-day measles, is an infection caused by the rubella virus. This disease is often mild with half of people not realizing that they are infected. A rash may start around two weeks after exposure and last for three days. It usually starts on the face and spreads to the rest of the body. The rash is sometimes itchy and is not as bright as that of measles. Swollen lymph nodes are common and may last a few weeks. A fever, sore throat, and fatigue may also occur. Joint pain is common in adults. Complications may include bleeding problems, testicular swelling, encephalitis, and inflammation of nerves. Infection during early pregnancy may result in a miscarriage or a child born with congenital rubella syndrome (CRS). Symptoms of CRS manifest as problems with the eyes such as cataracts, deafness, as well as affecting the heart and brain. Problems are rare after the 20th week of pregnancy.

Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is a congenital heart defect. Symptoms at birth may vary from none to severe. Later, there are typically episodes of bluish color to the skin known as cyanosis. When affected babies cry or have a bowel movement, they may develop a "tet spell" where they turn very blue, have difficulty breathing, become limp, and occasionally lose consciousness. Other symptoms may include a heart murmur, finger clubbing, and easy tiring upon breastfeeding.

An echocardiography, echocardiogram, cardiac echo or simply an echo, is an ultrasound of the heart. It is a type of medical imaging of the heart, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound.

Cardiothoracic surgery is the field of medicine involved in surgical treatment of organs inside the thoracic cavity — generally treatment of conditions of the heart, lungs, and other pleural or mediastinal structures.
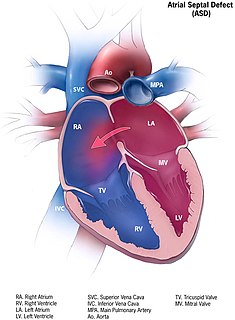
Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a congenital heart defect in which blood flows between the atria of the heart. Some flow is a normal condition both pre-birth and immediately post-birth via the foramen ovale; however, when this does not naturally close after birth it is referred to as a patent (open) foramen ovale (PFO). It is common in patients with a congenital atrial septal aneurysm (ASA).

A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. Signs and symptoms depend on the specific type of defect. Symptoms can vary from none to life-threatening. When present, symptoms may include rapid breathing, bluish skin (cyanosis), poor weight gain, and feeling tired. CHD does not cause chest pain. Most congenital heart defects are not associated with other diseases. A complication of CHD is heart failure.

Coarctation of the aorta, also called aortic narrowing, is a congenital condition whereby the aorta is narrow, usually in the area where the ductus arteriosus inserts. The word coarctation means "pressing or drawing together; narrowing". Coarctations are most common in the aortic arch. The arch may be small in babies with coarctations. Other heart defects may also occur when coarctation is present, typically occurring on the left side of the heart. When a patient has a coarctation, the left ventricle has to work harder. Since the aorta is narrowed, the left ventricle must generate a much higher pressure than normal in order to force enough blood through the aorta to deliver blood to the lower part of the body. If the narrowing is severe enough, the left ventricle may not be strong enough to push blood through the coarctation, thus resulting in a lack of blood to the lower half of the body. Physiologically its complete form is manifested as interrupted aortic arch.
Boston Children's Hospital formerly known as Children's HospitalBoston until 2012 is a nationally ranked, freestanding acute care children's hospital located in Boston, Massachusetts, adjacent both to its teaching affiliate, Harvard Medical School, and to Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. Dana-Farber and Children's jointly operate the Dana-Farber/Boston Children's Cancer and Blood Disorders Center to deliver comprehensive care for all types of childhood cancers. The hospital is home to the largest hospital based pediatric research program in the world. The hospital features 404 pediatric beds and provides comprehensive pediatric specialties and subspecialties to infants, children, teens, and young adults aged 0–21 throughout Massachusetts, the United States, and the world. The hospital also sometimes treats adults that require pediatric care. The hospital uses the Brigham and Women's Hospital's rooftop helipad and is an ACS verified level I pediatric trauma center, 1 of 3 in Boston. The hospital features a regional pediatric intensive-care unit and an American Academy of Pediatrics verified level IV neonatal intensive care unit. Boston Children's Hospital has been ranked as best pediatric medical center by U.S. News & World Report more times than any other hospital.

Pediatric surgery is a subspecialty of surgery involving the surgery of fetuses, infants, children, adolescents, and young adults.
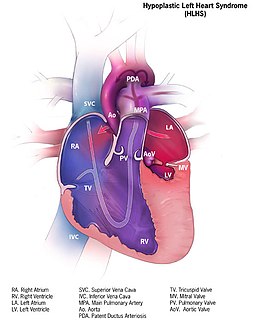
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) is a rare congenital heart defect in which the left side of the heart is severely underdeveloped. It may affect the left ventricle, aorta, aortic valve, or mitral valve.

The chordae tendineae , colloquially known as the heart strings, are tendon-resembling fibrous cords of connective tissue that connect the papillary muscles to the tricuspid valve and the mitral valve in the heart.

Valvular heart disease is any cardiovascular disease process involving one or more of the four valves of the heart. These conditions occur largely as a consequence of aging, but may also be the result of congenital (inborn) abnormalities or specific disease or physiologic processes including rheumatic heart disease and pregnancy.

Pulmonary valve stenosis (PVS) is a heart valve disorder. Blood going from the heart to the lungs goes through the pulmonary valve, whose purpose is to prevent blood from flowing back to the heart. In pulmonary valve stenosis this opening is too narrow, leading to a reduction of flow of blood to the lungs.
The Mustard procedure was developed in 1963 by Dr. William Mustard at the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto, Ontario, Canada.

Coronary artery aneurysm is an abnormal dilatation of part of the coronary artery.

Anomalous pulmonary venous connection is a congenital defect of the pulmonary veins.
John Eric Deanfield is a British professor of cardiology and past Olympic fencer.

Jane Somerville is a British emeritus professor of cardiology, Imperial College, who is best known for defining the concept and subspecialty of grown ups with congenital heart disease (GUCH) and being chosen as the physician involved with Britain's first heart transplantation in 1968.
References
- ↑ "Adult Congenital Heart Disease (ACHD) Also known as GUCH (Grown-Up Congenital Heart disease". Uhbristol.nhs.uk. Archived from the original on 2012-11-15. Retrieved 2012-06-05.
- ↑ Gatzoulis, Michael A.; Swan, Lorna; Therrien, Judith; Pantely, George A. (2008). Adult Congenital Heart Disease: A Practical Guide. Blackwell Publishing. p. 14. ISBN 978-0-7279-1668-6.
- ↑ Warnes, Carole A. (April 2008). "Jane Somerville". Clinical Cardiology. 31 (4): 183–184. doi:10.1002/clc.20279. PMC 6652976 . PMID 18404729.